Abstract
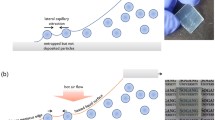
A novel pore-filling system was prepared using spray as the key-technique, for solar cells and various other applications. High performance in perovskite, dye-sensitized and eta cells is often achieved using metal oxide layers or their mesoporous analogues. One dimensional scaffold materials such as nanorods or nanotubes are also employed in order to improve charge collection. Herein, we introduce a method to more efficiently fill the pores in the most common nanostructure architecture namely mesoporous, nanorods or nanotubes. The method employs the use of spray technique with applied DC voltage (through two different voltage supplies) as the cost-effective technology for time efficient pore filling. SnS nanoparticles and N719 dye have been pore-filled onto a previously deposited ZnO nanorods and mesoporous TiO2 film, respectively, using the novel setup. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed an improved pore-filling, the complementary enhancement of ~ 24% in the DSSC efficiency and ~ 16% and 7% in terms of current density and fill factor, respectively has been found in comparison to the reference standard device. It is attributed to an increase in the concentration of dye molecules into the pores of TiO2 nanostructures due to better dye loading and hence observed an improvement in light absorption, electron transportation and charge collection. This pioneer pore filling technique exponentially reduced the dye loading time duration from overnight immersion of photo anodes in dye solution to 15–20 min.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.I. Hoffert, K. Caldeira, G. Benford, D.R. Criswell, C. Green, H. Herzog, A.K. Jain, H.S. Kheshgi, K.S. Lackner, J.S. Lewis, H.D. Lightfoot, W. Manheimer, J.C. Mankins, M.E. Mauel, L.J. Perkins, M.E. Schlesinger, T. Volk, T.M.L. Wigley, Science 298, 981 (2002)
X. Ji, K.T. Lee, L.F. Nazar, Nat. Mater. 8, 500–506 (2009)
X. Ji, L.F. Nazar, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9821–9826 (2010)
C. Weinberger, S. Ren, M. Hartmann, T. Wagner, D.Ş. Karaman, J.M. Rosenholm, M. Tiemann, A.C.S. Appl, Nano Mater. 1, 455–462 (2018)
T. Yamaguchi, H. Zhou, S. Nakazawa, N. Hara, Adv. Mater. 19, 592–596 (2007)
A. Belaidi, T. Dittrich, D. Kieven, J. Tornow, K. Schwarzburg, M. Lux-Steiner, Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2(4), 172 (2008)
M. Grӓtzel, Photochem. Photobiol. A 164, 3 (2004)
K. Kakiage, Y. Aoyama, T. Yano, K. Oya, J.I. Fujisawa, M. Hanaya, Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 51(88), 15894–15897 (2015)
P. Wang, S.M. Zakeeruddin, J.E. Moser, M.K. Nazeeruddin, T. Sekiguchi, Gr€atzel, M. Nat. Mater. 2, 402 (2003)
M. Matsumoto, H. Miyazaki, K. Matsuhiro, Y. Kumashiro, Y. Takaoka, Solid State Ionics 89, 263 (1996)
J.N. de Freitas, A.F. Nogueira, M.A. De Paoli, J. Mater. Chem. 19, 5279 (2009)
Y. Cao, Y. Saygili, A. Ummadisingu, J. Teuscher, J. Luo, N. Pellet, F. Giordano, N. Pellet, S.M. Zakeeruddin, J.E. Moser, M. Freitag, A. Hagfeldt, 11% efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with copper (II/I) hole transport materials. Nat. Commun. 8, 15390 (2017)
X.H. Lu, Y.Z. Zheng, S.Q. Bi, Y. Wang, X. Tao, L. Dai, J.F. Chen, Multidimensional ZnO architecture for dye sensitized solar cells with high efficiency up to 735%. Adv. Energy Mater 4(9), 1301802 (2014)
G.K. Mor, J. Basham, M. Paulose, S. Kim, O.K. Varghese, A. Vaish, S. Yoriya, C.A. Grimes, High-efficiency Forster resonance energy transfer in solid-state dye sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett. 10(7), 2387–2394 (2010)
Q. Miao, L. Wu, J. Cui, M. Huang, T. Ma, A New type of dye-sensitized solar cell with a multilayered photoanode prepared by a film-transfer technique. Adv. Mater. 23(24), 2764–2768 (2011)
S. Nejati, K.K. Lau, Pore filling of nanostructured electrodes in dye sensitized solar cells by initiated chemical vapor deposition. Nano Lett. 11(2), 419–423 (2010)
S.K. Swami, N. Chaturvedi, A. Kumar, V. Dutta, Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl. 24, 78 (2015)
H.J. Snaith, R. Humphry-Baker, P. Chen, I. Cesar, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Gratzel, Nanotechnology 19, 424003 (2008)
Firoz Alam, Viresh Dutta, Tin sulfide (SnS) nanostructured films deposited by continuous spray pyrolysis (CoSP) technique for dye-sensitized solar cells applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 358, 491–497 (2015)
C. Dwivedi, V. Dutta, Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 3, 015011 (2012)
C. Longo, J. Freitas, M.A. de Paoli, Performance and stability of TiO2/dye solar cells assembled with flexible electrodes and a polymer electrolyte. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 159, 33–39 (2003)
M.C. Bernard, H. Cachet, P. Falaras, A. Hugot-Le Goff, M. Kalbac, I. Lukes, N.T. Oanh, T. Stergiopoulos, I. Arabatzis, Sensitization of TiO2 by polypyridine dyes: Role of the electron donor. J Electrochem Soc. 150, E155–E164 (2003)
L.Y. Lin, M.H. Yeh, C.P. Lee, C.Y. Chou, K.C. Ho, Flexible dye-sensitized solar cells with one-dimensional ZnO nanorods as electron collection centers in photoanodes. Electrochim. Acta 88, 421–428 (2013)
P.S. Chandrashekhar, P.K. Parashar, S.K. Swami, V. Dutta, V.K. Komarala, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 9651 (2018)
Acknowledgments
Tauheed Mohammad sincerely thanks to the University Grant Commission (UGC), India for providing a scholarship under the Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) programme and Govt. of India for awarding Merit Cum Means fellowship to pursue professional & technical courses. One of the other author Charu Dwivedi is thankful to Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India for support through DST-WOS-A project. Authors want to thanks to Ms. Sapna Mudgal for her help in this work and NRF-CRF, IIT Delhi for providing the necessary characterization techniques.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammad, T., Sekhar, P.S.C., Dwivedi, C. et al. Electric-field assisted spray technique for controlled pore filling of nanostructured films: device applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 13567–13575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01724-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01724-z