Abstract
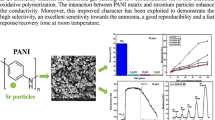
The flexible polyaniline (PAni) films were deposited on the polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrates by a spin-coating method under different magnetic field (MF) strength from 0.0 to 0.7 T. By increasing the magnetic field strength, we observed that crystalline quality, surface area as well as protonation of the PAni films were increased. Room temperature (RT) ammonia gas sensing application of these films was also investigated and it was observed the gas sensing performance of the PAni films was improved by the increase of the magnetic field strength up to 0.5 T. It was seen, the important gas sensing device parameters such as sensitivity, selectivity, stability, and response time of the PAni film, which was deposited under 0.5 T of magnetic field condition, 7.5, 1.49, 1.21, and 7.5 times, respectively, were higher than the PAni film gas sensor that was deposited under 0.0 T of magnetic field condition.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Soleimanpour, A.H. Jayatissa, G. Sumanasekera, Surface and gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline nickel oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 276, 291–297 (2013)
L.G. Close, F.I. Catlin, A.M. Cohn, Acute and chronic effects of ammonia burns of the respiratory tract. Arch. Otolaryngol. 106(3), 151–158 (1980)
S. Sharma, A. Kumar, N. Singh, D. Kaur, Excellent room temperature ammonia gas sensing properties of n-MoS2/p-CuO heterojunction nanoworms. Sens. Actuators B 275, 499–507 (2018)
S.M. Kanan, O.M. El-Kadri, I.A. Abu-Yousef, M.C. Kanan, Semiconducting metal oxide based sensors for selective gas pollutant detection. Sensors 9, 8158–8196 (2009)
A. Sáaedi, R. Yousefi, Improvement of gas-sensing performance of ZnO nanorods by group-I elements doping. J. Appl. Phys. 122, 224505 (2017)
D. Zhang, Z. Wu, X. Zong, Flexible and highly sensitive H2S gas sensor based on in situ polymerized SnO2/rGO/PANI ternary nanocomposite with application in halitosis diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B 289, 32–41 (2019)
C.-T. Lee, Y.-S. Wang, High-performance room temperature NH3 gas sensors based on polyaniline-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite sensitive membrane. J. Alloys Compd. 789, 693–696 (2019)
J. Gong, Y. Li, Z. Hu, Z. Zhou, Y. Deng, Ultrasensitive NH3 gas sensor from polyaniline nanograin enchased TiO2 fibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(21), 9970–9974 (2010)
Yang Li, Mingfei Jiao, Huijie Zhao, Mujie Yang, High performance gas sensors based on in situ fabricated ZnO/polyaniline nanocomposite: the effect of morphology on the sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 264(1), 285–295 (2018)
A.A. Syed, M.K. Dinesan, Review: polyaniline—a novel polymeric material. Talanta 38, 815–837 (1991)
G.D. Khuspe, S.T. Navale, D.K. Bandgar, R.D. Sakhare, M.A. Chougule, V.B. Patil, SnO2 nanoparticles-modified polyaniline films as highly selective, sensitive, reproducible and stable ammonia sensors. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 191–197 (2014)
D.K. Bandgar, S.T. Navale, Y.H. Navale, S.M. Ingole, F.J. Stadler, N. Ramgir, D.K. Aswal, S.K. Gupta, R.S. Mane, V.B. Patil, Flexible camphor sulfonic acid-doped PAni/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite films and their room temperature ammonia sensing activity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 189, 191–197 (2017)
P. Shabani, A. Qarehbaqi, F.A. Boroumand, Selective enhancement of intra-chain charge transport to improve ammonia sensing performance in polyaniline layers. Electron. Mater. Lett. 12(1), 107–112 (2016)
A.G. Revelli, T. Kusne, J.L. Kowalewski, L.E. Snyder, G.K. Weiss, R.D. Fedder, D.N.Lambeth McCullough, Volatile organic compound detection using nanostructured copolymers. Nano Lett. 6, 1598–1602 (2006)
S. Matindoust, A. Farzi, M. Baghaei-Nejad, M.H. Shahrokh-Abadi, Z. Zou, L.R. Zheng, Ammonia gas sensor based on flexible polyaniline films for rapid detection of spoilage in protein-rich foods. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(11), 7760–7768 (2017)
J. Torbet, Y.F. Nicolau, D. Djurado, Orientation of CSA-protonated polyaniline chains in solution in m-cresol and in films induced by a high magnetic field. Synth. Met. 101, 825–826 (1999)
O.P. Dimitriev, Formation of organic films via a magnetomechanical effect. J. Phys. D 40, 850–855 (2007)
L. Ma, W. Lu, K.L. Huang, M.Y. Gan, C. Chen, J. Yan, Analysis and characterization of microscopic morphology and orientation structure of polyaniline polymerized in a constant magnetic field. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 27, 487–492 (2009)
I. Rintoul, C. Wandrey, Magnetic field effects on the free radical solution polymerization of acrylamide. Polymer 48, 1903–1914 (2007)
D.K. Bandgar, S.T. Navale, S.R. Nalage, R.S. Mane, F.J. Stadler, D.K. Aswal, S.K. Gupta, V.B. Patil, Simple and low-temperature polyaniline-based flexible ammonia sensor: a step towards laboratory synthesis to economical device design. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 9461–9468 (2015)
J.H. Lee, M.S. Cho, H.J. Choi, M.S. Jhon, Effect of polymerization temperature on polyaniline based electrorheological suspensions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 227, 73–76 (1999)
L. Ma, L. Luo, H. Ma, X. Li, W. Su, S. Hao, Characterization and analysis of the electrochemical properties of the polyaniline synthesized by emulsion polymerization in constant magnetic field (0.4 T). Chin. J. Chem. 28, 1871–1875 (2010)
S.S. Pandule, M.R. Patil, R.S. Keri, Properties and ammonia gas sensing applications of different inorganic acid-doped poly (2-chloroanilines). Polym. Bull. 75(10), 4469–4483 (2018)
L. Ma, W. Lu, M. Gan, Influences of constant magnetic field (0.4 T) on PANI micro-orientation structure. J. Chem. 66, 1259–1264 (2008)
A.Z. Sadek, C.O. Baker, D.A. Powell, W. Wlodarski, R.B. Kaner, K. Kalantarzadeh, Polyaniline nanofiber based surface acoustic wave gas sensors—effect of nanofiber diameter on H2 response. IEEE Sens. J. 7, 213–218 (2007)
J.E. Albuquerque, L.H.C. Mattoso, R.M. Faria, J.G. Masters, A.G. MacDiarmid, Study of the interconversion of polyaniline oxidation states by optical absorption spectroscopy. Synth. Met. 146, 1 (2004)
R.P. McCall, J.M. Ginder, M.G. Roe, G.E. Asturias, E.M. Scherr, A.G. MacDiarmid, A.J. Epstein, Massive polarons in large-energy-gap polymers”. J. Phys. Rev. B 39, 10174–10179 (1989)
M. Trchovaa, J. Stejskal, Polyaniline: the infrared spectroscopy of conducting polymer nanotubes. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 83, 1801 (2011)
J. Dominic, T. David, A. Vanaja, K.K.S. Kumar, Effect of LiCl on conductivity of polyaniline synthesized via in-situ chemical oxidative method. Eur. Polym. J. 85, 236–243 (2016)
H.R. Tantawy, B.-A.F. Kengne, D.N. McIlroy, T. Nguyen, D. Heo, Y. Qiang, D. Eric Aston, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis for the chemical impact of solvent addition rate on electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of HCl-doped polyaniline nanopowders. J. Appl. Phys. 118, 175501 (2015)
G. Ren, H. Qiu, Q. Wu, H. Li, H. Fan, C. Fang, Thermal stability of composites containing HCl-doped polyaniline and Fe nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 127–133 (2010)
M.G. Han, S.S. Im, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of electrically conducting polyaniline/polyimide blends. Polymer 41, 3253–3262 (2000)
H.R. Tantawy, D.E. Aston, J.R. Smith, J.L. Young, A comparison of electromagnetic shielding with polyaniline nanopowders produced in solvent-limited conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5(11), 4648–4658 (2013)
H.R. Tantawy, A.T. Weakley, D.E. Aston, Chemical effects of a solvent-limited approach to HCl-doped polyaniline nanopowder synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 1294–1305 (2014)
D. Thomas, A. Thomas, A.E. Tom, K.K. Sadasivuni, D. Ponnamma, S. Goutham, J.J. Cabibihan, K.V. Rao, Highly selective gas sensors from photo-activated ZnO/PANI thin films synthesized by mSILAR. Synth. Met. 232, 123–130 (2017)
L. Wang, H. Huang, S. Xiao, D. Cai, Y. Liu, B. Liu, D. Wang, C. Wang, H. Li, Y. Wang, Q. Li, T. Wang, Enhanced sensitivity and stability of room-temperature NH3 sensors using core-shell CeO2 nanoparticles@cross-linked PANI with p–n heterojunctions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6(16), 14131–14140 (2014)
X.L. Huang, N.T. Hu, R.G. Gao, Y. Yu, Y.Y. Wang, Z. Yang, E.S. Kong, H. Wei, Y.F. Zhang, Reduced graphene oxide − polyaniline hybrid: preparation, characterization and its applications for ammonia gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 22488–22495 (2012)
Z. Wu, X. Chen, S. Zhu, Z. Zhou, Y. Yao, W. Quan, B. Liu, Enhanced sensitivity of ammonia sensor using graphene/polyaniline nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B 178, 485–493 (2013)
H. Tai, Y. Jiang, G. Xie, J. Yu, X. Chen, Fabrication and gas sensitivity of polyaniline − titanium dioxide nanocomposite thin film. Sens. Actuators B 125, 644–650 (2007)
M. Das, D. Sarkar, One-pot synthesis of zinc oxide-polyaniline nanocomposite for fabrication of efficient room temperature ammonia gas sensor. Ceram. Int. 43, 11123–11131 (2017)
S.T. Navale, A.T. Mane, M.A. Chougule, V.B. Patil, Highly sensitive, reproducible, selective and stable CSA-polypyrrole NO2 sensor. Synth. Met. 189, 111–118 (2014)
A.G. Sonkusare, S. Tyagi, R. Kumar, S. Mishra, Room temperature ammonia gas sensing using polyaniline nanoparticles based sensor. Int. J. Mater. 12(2), 283–291 (2017)
A.L. Kukla, Y.M. Shirshov, S.A. Piletsky, Ammonia sensors based on sensitive polyaniline films. Sens. Actuators B 37(3), 135–140 (1996)
S. Bai, Y. Tian, M. Cui, J. Sun, Y. Tian, R. Luo, A. Chen, D. Li, Polyaniline@SnO2 heterojunction loading on flexible PET thin film for detection of NH3 at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B 226, 540–547 (2016)
A. Mani, K. Athinarayanasamy, P. Kamaraj, S.T. Selvan, S. Ravichandran, K.L.N. Phani, S. Pitchumani, Crystalline order in polyaniline. Mater. Sci. Lett. 14(22), 1594–1596 (1995)
S. Bai, Y. Zhao, J. Sun, Z. Tong, R. Luo, D. Li, A. Chen, Preparation of conducting films based on α-MoO3/PANI hybrids and their sensing properties to triethylamine at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B 239, 131–138 (2017)
Acknowledgements
R. Yousefi and P. Shabani gratefully acknowledge the Islamic Azad University (I.A.U), Masjed-Soleiman and Mahshahr Branches for their supports of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sáaedi, A., Shabani, P. & Yousefi, R. Study on the effects of the magneto assisted deposition on ammonia gas sensing properties of polyaniline. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 10765–10775 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01420-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01420-y