Abstract
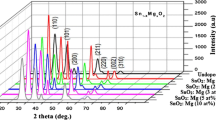
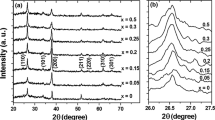
In this work, tin oxide thin films alloyed with manganese up to 60 at.% were deposited by spray pyrolysis route, and the effect of Mn on the structural, optical, electrical and thermo-electrical properties of the films was investigated. The results show that all the deposited films are polycrystalline with tetragonal rutile structure. The solubility limit of Mn in SnO2 sprayed films was found to be about 15 at.%. The lattice volume of SnO2:Mn films turned out to be minimum at the critical Mn concentration of 15% implying that two different mechanisms should work for Mn addition: For low Mn concentration (< 15%) substitutional doping is the working mechanism, while for more Mn concentration, interstitial doping is predominant in the involved films. Mn addition in SnO2 films varied their crystallite size, transparency, band-gap, resistivity and carrier concentration. The most striking effect of Mn addition was revealed as getting p-type conductivity in SnO2:Mn films with Mn concentration in the range of 15–40%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Znaidi, Sol–gel-deposited ZnO thin films: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 174, 18–30 (2010)
D. Dastan, S.L. Panahi, N.B. Chaure, Characterization of titania thin films grown by dip-coating technique. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 27, 12291–12296 (2016)
A. Fakhim Lamrani, M. Belaiche, A. Benyoussef, El Kenz, Electronic structures and ferromagnetism of SnO2 (rutile) doped with double-impurities: first-principles calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 115(6), 013910 (2015)
Y. Ziat, A. Benyoussef, A. El, Kenz, Magnetic and electronic properties of Cr- and Mn-doped SnO2: ab initio calculations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 75, 701–709 (2014)
A. Stashans, P. Puchaicela, R. Rivera, DFT study of chromium-doped SnO2 materials. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 2904–2911 (2014)
H. Kawazoe, M. Yasukawa, H. Hyodo, M. Kurita, H. Yanagi, H. Hosono, P-type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of CuAlO2. Nature 389, 939–942 (1997)
Z. Ji, Z. He, Y. Song, K. Liu, Y. Xiang, A novel transparent pn+ junction based on indium tin oxides. Thin Solid Films 460, 324–326 (2004)
S.B. Ogale, R.J. Choudhary, J.P. Buban, S.E. Lofland, S.R. Shinde, S.N. Kale, V.N. Kulkarni, J. Higgins, C. Lanci, J.R. Simpson, N.D. Browning, S. Das Sarma, H.D. Drew, R.L. Greene, T. Venkatesan, High temperature ferromagnetism with a giant magnetic moment in transparent co-doped SnO2−δ. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 077205 (2003)
Sk..F. Ahmed, S. Khan, P.K. Ghosh, M.K. Mitra, K.K. Chattopadhyay, Effect of Al doping on the conductivity type inversion and electro-optical properties of SnO2 thin films synthesized by sol–gel technique. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 39, 241–247 (2006)
T.I. Gandhi, R.R. Babu, K. Ramamurthi, Structural, morphological, electrical and optical studies of Cr doped SnO2 thin films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(2), 472–479 (2013)
C. Van Komen, A. Thurber, K.M. Reddy, J. Hays, A. Punnoose, Structure–magnetic property relationship in transition metal (M = V,Cr,Mn,Fe,Co,Ni) doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J.Appl. Phys. 103, 07D141 (2008)
C.B. Fitzgerald, M. Venkatesan, L.S. Dorneles, R. Gunning, P. Stamenov, J.M.D. Coey, P.A. Stampe, R.J. Kennedy, E.C. Moreira, U.S. Sias, Magnetism in dilute magnetic oxide thin films based on SnO2. Phys. Rev. B 74, 115307 (2006)
K. Gopinadhan, S.C. Kashyap, D.K. Pandya, S. Chaudhary, High temperature ferromagnetism in Mn-doped SnO2 nanocrystalline thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 113513 (2007)
K. Vadivel, V. Arivazhagan, S. Rajesh, Mn doped SnO2 Semiconducting magnetic thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis method. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2, 43–47 (2011)
J. Joseph, V. Mathew, K.E. Abraham, Studies on Cu, Fe, and Mn doped SnO2 semi-conducting transparent films prepared by a vapour deposition technique. Chinese. J. Phys. 45(1), 84–97 (2007)
M.M. Bagheri Mohagheghi, Sh Tabatabai Yazdi, M. Mousavi, Transport, structural and optical properties of SnO2 transparent semiconductor thin films alloyed with chromium: carrier type conversion. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 13328–13335 (2017)
D. Dastan, Effect of preparation methods on the properties of titania nanoparticles: solvothermal versus sol-gel. Appl. Phys. A 123, 699 (2017).https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1309-3
L. Hartnagel, A.L. Dawar, A.K. Jain, C.J. Jagadish, Semi-conducting transparent thin films. (IOP, Bristol, 1995)
E.G. Birgin, I. Chambouleyron, J.M. Martínez, Estimation of the optical constants and the thickness of thin films using unconstrained optimization. J. Comput. Phys. 151, 862–880 (1999)
D. Dastan, Nanostructured anatase titania thin films prepared by sol-gel dip coating technique. J. At. Mol. Condens Nano Phys. (JAMCNP) 2(2), 109–114 (2015)
Y. Xiao, S. Ge, Y. Li Xi, X. Zuo, B. Zhou, Li Zhang, C. Zhang, X. Li, Z. Han, Wen, Room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped SnO2 thin films fabricated by sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci 254, 7459–7463 (2008)
Y. Ichiyanagi, T. Yamada, Y. Kanazawa, T. Uehashi, Magnetic properties of Mn3O4 nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 850, 1155–1156 (2006)
M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi, N. Shahtahmasebi, M.R. Alinejad, A. Youssefi, M. Shokooh-Saremi, Fe-doped SnO2 transparent semi-conducting thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique: thermoelectric and p-type conductivity properties. Solid State Sci. 11, 233–239 (2009)
M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi, M. Shokooh-Saremi, The electrical, optical, structural and thermoelectrical characterization of n- and p-type cobalt-doped SnO2 transparent semiconducting films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. B 405, 4205–4210 (2010)
G. Sanon, R. Rup, A. Mansingh, Band-gap narrowing and band structure in degenerate tin oxide (SnO2) films. Phys. Rev. B 44, 5672–5680 (1991)
N.M. Hosny, A. Dahshan, Facile synthesis and optical band gap calculation of Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 137, 637–643 (2012)
L. ShunJun, M. ZiChuan, W. Lin, L. JingZe, Influence of MnO2 on the photocatalytic activity of P-25 TiO2 in the degradation of methyl orange. Sci. China Ser. B 51(2), 179–185 (2008)
W.-L. Zhu, X.-Y. Chen, Y.-J. Zhao, T.-S. Lai, Theoretical study of stability and electronic structure of the new type of ferroelectric materials XSnO3 (X = Mn, Zn, Fe, Mg). Inter. J. Mod. Phys. B 28, 1450224 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousavi, M., Tabatabai Yazdi, S. & Bagheri Mohagheghi, M.M. Effect of a wide range of Mn concentration on structural, electrical and optical properties of SnO2 transparent semiconducting films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 2860–2867 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8215-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-8215-5