Abstract
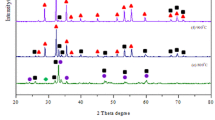
The high electrical resistivity and excellent magnetic properties make ferrites a preferred choice in electronics and telecommunications in higher frequency region (upper MHz and GHz). We chose to investigate experimentally the effect of temperature on a sample’s properties which are important to microwave scientists and engineers, after undergoing heat treatments. In this study, yttrium iron garnet (YIG) was prepared via mechanical alloying involving a 24 h milling time of a mixture of yttrium oxide (Y2O3) and iron oxide (Fe2O3). The samples were then sintered at different temperatures at 900, 1100, 1200 and 1350 °C with 10 h holding time and optimized for microstructure. The microstructure, magnetic and physical properties were studied in order to understand the resulting materials. Starting powders were successfully prepared using high energy ball milling technique for 24 h. The XRD patterns confirmed the formation of the single-phase cubic garnet structure with no extra lines corresponding to any other crystallographic phase or unreacted ingredient. A complete phase of YIG was observed to form at 900 °C sintering temperature due to the high reactivity of the nanosized starting powder. SEM micrographs showed larger grain size as the sintering temperature increased, consequently increasing the number of multi-domain grains. The permeability values were influenced by several factors which are degree of crystallinity, dominant magnetization process (ease of domain walls movement in multi-domain grains or spin rotation in single-domain grains) and large enough grain size which exceed the critical grain size for transition from single-domain to multi-domain grains. As for magnetic properties, the Hc values were found to increase as the sintering temperature increased from 900 to 1200 °C and subsequently reduced at 1350 °C sintering temperature. The increased value of coercivity for lower sintering was due to shape and magnetocrystalline anisotropy for small enough grains. An integrated analysis of phase, microstructural and hysteresis data pointed to existence of three distinct shape-differentiated groups of B–H hysteresis loops which belong to samples with moderate and strong magnetism.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Garskaite, K. Gibson, A. Leleckaite, J. Glaser, D. Niznansky, A. Kareiva, H.J. Mayer, On the synthesis and characterizations of iron-containing garnets (Y3Fe5O12, YIG, and Fe3Al5O12, IAG). Chem. Phys. 323, 204–210 (2006)
R.J. Joseyphus, A. Narayanasamy, A.K. Nigam, R. Krishnan, Effect of mechanical milling on the magnetic properties of garnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 296, 57–64 (2006)
M.B. Park, N.H. Cho, Structural and magnetic characteristics of yttrium iron garnet (YIG, Ce:YIG) films prepared by RF magnetron sputter techniques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 231, 253–264 (2001)
H. Xu, H. Yang, W. Xu, S. Feng, Magnetic properties of Ce, Gd-substituted yttrium iron garnet ferrite powders fabricated using a sol–gel method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 197, 296–300 (2008)
T. Sekijima, H. Itoh, T. Fujii, K. Wakino, M. Okada, J. Cryst. Growth 229, 409–414 (2011)
A.C. Rastogi, V.N. Moorthy, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 95, 131–136 (2002)
H. Yu, L. Zeng, C. Lu, W. Zhang, G. Xu, Mater. Charact. 62, 378–381 (2011)
M. Ristic, I. Nowik, S. Popovic, I. Felner, S. Music, Mater. Lett. 57, 2584–2590 (2003)
M. Pal, D. Chakravorty, Phys. E 5, 200–203 (2000)
P. Vaqueiro, M.P.C. Lopez, M.A.L. Quintela, J. Solid State Chem. 126, 161–168 (1996)
M.N. Akhtar, M.U. Islam, S.B. Niazi, M.U. Rana, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 25, 1149–1160 (2011)
A. Dias, R.L. Moreira, N.D.S. Mohallem, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 58, 543–547 (1997)
S. Deka, P.A. Joy, Mater. Chem. Phys. 100, 98–101 (2006)
S. Woltz, R. Hiergeist, P. Gornert, C. Russel, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 298, 7–13 (2006)
J. Ding, H. Yang, W.F. Miao, P.G. Mccormick, R. Street, J. Alloys Compd. 221, 70–73 (1995)
N. Yahya, M.N. Akhtar, A.F. Masuri, M. Kashif, J. Appl. Sci. 11, 1303–1308 (2011)
M.N. Akhtar, N. Yahya, K. Koziol, N. Nasir, Ceram. Int. 37, 3237–3245 (2011)
P. Concalves, F.M. Figueiredo, Mechanosynthesis of La1–xSrxGa1–yMgyO3–δ materials. Solid State Ionics 179, 991–994 (2008)
B.G. Ravi, X.Z. Guo, Q.Y. Yan, R.J. Gambino, S. Sampath, J.B. Parise, Surf. Coat. Technol. 201, 7597–7605 (2007)
T. Kimura, H. Takizawa, K. Uheda, T. Endo, M. Shimada, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 2961–2964 (1998)
R. Nazlan, M. Hashim, I.R. Ibrahim, I. Ismail, Dependence of magnetic hysteresis on evolving single-sample sintering in fine-grained yttrium iron garnet. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. doi:10.1007/s10948-013-2328-8
N. Rodziah et al., Dependence of developing magnetic hysteresis characteristics on stages of evolving microstructure in polycrystalline yttrium iron garnet. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 2679–2685 (2012)
R. Nazlan, I. Ismail, M. Hashim, K. Samikannu, N. MohdSaidin, Complex permeability, Curie temperature and activation energy as a function of microstructure evolution in a mechanically alloyed Y3Fe5O12 single-sample. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 8(3), 474–482 (2014)
R.L. Coble, Sintering crystalline solids. I. intermediate and final state diffusion models. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 787–792 (1961)
T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, DC resistivity of Ni-Zn ferrites prepared by oxalate precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys 111, 87–91 (2008)
M. Jarcho, C.H. Bolen, M.B. Thomas, J. Bobick, J.K. Kay, R.H. Doremus, Hydroxylapatite synthesis and characterization in dense polycrystalline form. J. Mater. Sci. 11, 2027–2035 (1976)
M. Syazwan Mustaffa, M. Hashim, R.S. Azis, I. Ismail, S. Kanagesan, M. Misbah Zulkimi, Magnetic phase-transition dependence on nano-to-micron grain-size microstructural changes of mechanically alloyed and sintered Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 1451–1462 (2014)
R.S. Tebble, D.J. Craik, in Magnetic Materials (Wiley, London, 1969)
I. Ismail, M. Hashim, Sintering temperature dependence of evolving morphologies and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 synthesized via mechanical alloying. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 1551–1561 (2012)
I.R. Idza et al., Influence of evolving microstructure on magnetic hysteresis characteristics in polycrystalline nickel–zinc ferrite, Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1345–1352 (2012)
S.B. Waje, M. Hashim, W.D. WanYusoff, Z. Abbas, Sintering temperature dependence of room temperature magnetic and dielectric properties of Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared using mechanically alloyed nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 322, 686–691 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) for providing Research University Grant Scheme (RUGS) with the vot number 91553 and also to Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) for providing the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) with the vot number 5523649.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hapishah, A.N., Hashim, M., Syazwan, M.M. et al. Phase, microstructure and magnetic evaluation in yttrium iron garnet (YIG) synthesized via mechanical alloying. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 15270–15278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7407-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7407-3