Abstract
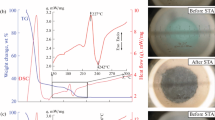
In this study, a series of α-Fe2O3–CeO2 nanocomposites containing 5, 15, 30, and 50 % Fe as well as the pure oxides, α-Fe2O3 and CeO2, were synthesized by a novel route of auto-combustion method at temperatures lower than those reported previously. The as-synthesized catalysts were characterized by several techniques such as XRD, XRF, N2 physisorption, DSC/TGA, NH3-TPD, TEM, and EDX. The catalytic activity of the synthesized nanocomposites was examined under ethanol conversion. The results revealed that the solid-solution formation was established for all the Fe-substituted CeO2 samples while maintaining the fluorite structure of ceria. Only a hardly noticeable segregation of α-Fe2O3 was appreciated for the catalyst samples with higher iron content (30 and 50 wt% Fe). The results confirmed that the adopted auto-combustion method allowed a good control of the chemical composition of the prepared composites with the proper structural and textural characteristics. The 30 % Fe–Ce sample was the most active and selective catalyst toward ethylene production compared with the other samples under study, owing to the pronounced Brönsted acid sites. The overall data collected through this work revealed that the synthesized nanocomposites are promising candidates for the production of ethylene from ethanol.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mogensen M, Sammes NM, Tompsett GA (2000) Physical chemical and electrochemical properties of pure and doped ceria. Solid State Ion 129:63
Yashima M, Sasaki S, Yamaguchi Y, Kakihana M, Yoshimura M, Mori T (1998) Internal distortion in ZrO2–CeO2 solid solutions: neutron and high-resolution synchrotron x-ray diffraction study. Appl Phys Lett 72:182
Nikolaou K (1999) Emissions reduction of high and low polluting new technology vehicles equipped with a CeO2 catalytic system. Sci Total Environ 235:71
Ozawa M (1998) Role of cerium-zirconium mixed oxides as catalysts for car pollution: a short review. J Alloys Compd 275–277:886
Feng X, Sayle DC, Wang ZL, Paras MS, Santora B, Sutorik AC, Sayle TXT, Yang Y, Ding Y, Wang XD, Her YS (2006) Converting ceria polyhedral nanoparticles into single-crystal nanospheres. Science 312:1504
Imanaka N, Masui T, Hirai H, Adachi G (2003) Amorphous cerium-titanium solid solution phosphate as a novel family of band gap tunable sunscreen materials. Chem Mater 15:2289
Kakuta N, Morishima N, Kotobuki M, Iwase T, Mizushima T, Sato Y, Matsuura S (1997) Oxygen storage capacity (OSC) of aged Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts: roles of Pt and CeO2 supported on Al2O3. Appl Surf Sci 121–122:408
Lira-Cantu M, Krebs FC (2006) Hybrid solar cells based on MEH-PPV and thin film semiconductor oxides (TiO2, Nb2O5, ZnO, CeO2 and CeO2–TiO2): performance improvement during long-time irradiation. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:2076
Zhou J, Mullins DR (2006) Adsorption and reaction of formaldehyde on thin-film cerium oxide. Surf Sci 600:1540
Tsunekawa S, Ishikawa K, Li Z-Q, Kawazoe Y, Kasuya A (2000) Origin of anomalous lattice expansion in oxide nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett 85:3440
Wang ZW, Saxena SK, Pischedda V, Liermann HP, Zha CS (2001) In situ x-ray diffraction study of the pressure-induced phase transformation in nanocrystalline CeO2. Phys Rev B 6401(1):2102
Tsunekawa S, Fukuda T, Kasuya A (2000) Blue shift in ultraviolet absorption spectra of monodisperse CeO2-x nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 87:1318
Chen H, Chang H (2005) Synthesis of nanocrystalline cerium oxide particles by the precipitation method. Ceram Int 31:795
Qi RJ, Zhu YJ, Huang YH (2005) Sonochemical synthesis of single-crystalline CeOHCO3 rods and their thermal conversion to CeO2 rods. Nanotechnology 16:2502
Shuk P, Greenblatt M (1999) Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of mixed conductors based on Ce1-x Pr x O2 solid solutions. Solid State Ion 116:217
Bumajdad A, Zaki MI, Eastoe J, Pasupulety L (2004) Microemulsion-based synthesis of CeO2 powders with high surface area and high-temperature stabilities. Langmuir 20:11223
Tsuzuki T, Robinson JS, McCormick PGJ (2002) UV-shielding ceramic nanoparticles synthesised by mechanochemcial processing. J Aust Ceram Soc 38:15
Wang Y, Mori T, Li J, Ikegami T (2002) Low-temperature synthesis of praseodymium-doped ceria nanopowders. J Am Ceram Soc 85:3105
Navarrete EL, Caballero A, Elipe ARG, Ocana M (2002) Low-temperature preparation and structural characterization of Pr-doped ceria solid solutions. J Mater Res 17:797
Hartridge A, Bhattacharya AK (2002) Preparation and analysis of zirconia doped ceria nanocrystal dispersions. J Phys Chem Solids 63:441
Hirano M, Fukuda Y, Iwata H, Hotta Y, Inagaki M (2000) Preparation and spherical agglomeration of crystalline cerium (IV) oxide nanoparticles by thermal hydrolysis. J Am Ceram Soc 83:1287
Gao Y, Bao Y, Beerman M, Yasuhara A, Shindo D, Krishman MK (2004) Superstructures of self-assembled cobalt nanocrystals. Appl Phys Lett 84:3361
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995
Jing Z, Wang Y, Wu S (2006) Preparation and gas sensing properties of pure and doped γ-Fe2O3 by an anhydrous solvent method. Sens Actuator B 113(1):177
Bora DK, Deb P (2009) Fatty acid binding domain mediated conjugation of ultrafine magnetic nanoparticles with albumin protein. Nanoscale Res Lett 4:138
Liu Q, Cui Z, Ma Z, Bian S, Song W, Wan L (2007) Morphology control of Fe2O3 nanocrystals and their application in catalysis. Nanotechnology 18:385605
Willard MA, Kurihara LK, Carpenter EE, Calvin S, Harris VG (2004) Chemically prepared magnetic nanoparticles. Int Mater Rev 49:125
Jovalekic C, Zdujic M, Radakovic A, Mitric M (1995) Mechanochemical synthesis of NiFe2O4 ferrite. Mater Lett 24:365
Lee S, Jeong J, Shin S, Kim J, Kim J (2004) Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation technique. J Magn Magn Mater 282:147
Sahooa SK, Mohapatraa M, Pandeyb B, Vermab HC, Dasa RP, Ananda S (2009) Preparation and characterization of γ-Fe2O3-CeO2 composite. Mater Charact 6:425
Zaki T (2005) Catalytic dehydration of ethanol using transition metal oxide catalysts. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:606
Wu L-P, Li X-J, Yuan Z-H, Chen Y (2009) The fabrication of TiO2-supported zeolite with core/shell heterostructure for ethanol dehydration to ethylene. Catal Commun 11:67
Xiao Y, Li X, Yuan Z, Li J, Chen Y (2009) Catalytic dehydration of ethanol to ethylene on TiO2/4A zeolite composite catalysts. Catal Lett 130:308
Zhang X, Wang R, Yang X, Zhang F (2008) Comparison of four catalysts in the catalytic dehydration of ethanol to ethylene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 116:210
Zhang D, Wang R, Yang X (2008) Effect of P content on the catalytic performance of P-modified HZSM-5 catalysts in dehydration of ethanol to ethylene. Catal Lett 124:384
Takahara I, Saito M, Inaba M, Murata K (2005) Dehydration of ethanol into ethylene over solid acid catalysts. Catal Lett 105:249
Varisli D, Dogu T, Dogu G (2007) Ethylene and diethyl-ether production by dehydration reaction of ethanol over different heteropolyacid catalysts. Chem Eng Sci 62:5349
Varisli D, Dogu T, Dogu G (2008) Silicotungstic acid impregnated MCM-41-like mesoporous solid acid catalysts for dehydration of ethanol. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:4071
Haber J, Pamin K, Matachowski L, Napruszewska B, Połtowicz J (2002) Potassium and silver salts of tungstophosphoric acid as catalysts in dehydration of ethanol and hydration of ethylene. J Catal 207:296
Gayubo AG, Alonso A, Valle B, Aguayo AT, Bilbao J (2010) Selective production of olefins from bioethanol on HZSM-5 zeolite catalysts treated with NaOH. Appl Catal B 97:299
Aguayo AT, Gayubo AG, Atutxa A, Olazar M, Bilbao J (2002) Catalyst deactivation by coke in the transformation of aqueous ethanol into hydrocarbons. Kinetic modeling and acidity deterioration of the catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:4216
Aguayo AT, Gayubo AG, Atutxa A, Valle B, Bilbao J (2005) Regeneration of a HZSM-5 zeolite catalyst deactivated in the transformation of aqueous ethanol into hydrocarbons. Catal Today 107–108:410
Gayubo AG, Aguayo AT, Tarrío AM, Olazar M, Bilbao J (2001) Kinetic modelling for deactivation by coke deposition of a HZSM-5 zeolite catalyst in the transformation of aqueous ethanol into hydrocarbons. Stud Surf Sci 139:455
Bedia J, Barrionuevo R, Rodríguez-Mirasol J, Cordero T (2011) Ethanol dehydration to ethylene on acid carbon catalysts. Appl Catal B 103:302
Nakanishi M, Bolm C (2007) Iron-catalyzed benzylic oxidation with aqueous tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Adv Synth Catal 349(6):861
Martin SE, Garrone A (2003) Efficient solvent-free iron (III) catalyzed oxidation of alcohols by hydrogen peroxide. Tetrahedron Lett 44(3):549
Shi F, Kin Tse M, Pohl M, Radnik J, Brückner A, Zhang S, Beller M (2008) Nano-iron oxide-catalyzed selective oxidations of alcohols and olefins with hydrogen peroxide. J Mol Catal A 292:28
Wang S, Lu GQ (1998) Role of CeO2 in Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalysts for carbon dioxide reforming of methane. Appl Catal B 19:267
Piras A, Trovarelli A, Dolcetti G (2000) Remarkable stabilization of transition alumina operated by ceria under reducing and redox conditions. Appl Catal B 28:77
Cai W, Wang F, Zhan E, VanVeen AC, Mirodatos C, Shen W (2008) Hydrogen production from ethanol over Ir/CeO2 catalysts: a comparative study of steam reforming, partial oxidation and oxidative steam reforming. J Catal 257:96
Purohit RD, Saha S, Tyagi AK (2006) Powder characteristics and sinterability of ceria powders prepared through different routes. Ceram Int 32:143
Shinohara Y, Nakajima T, Suzuki S (1999) A theoretical study of the dehydration and the dehydrogenation processes of alcohols on metal oxides using MOPAC. J Mol Struct (Theochem) 460:231
Hassan SA, Gobara HM, Gomaa MM, Mohamed RS, Khalil FH (2015) Can microwave assisted in situ reduction of supported Pt nanoparticles challenge the chemical method in controlling the dispersion profile catalytic performance relationship? RSC Adv 5:54460
Chen P-L, Chen I-W (1993) Reactive cerium (IV) oxide powders by the homogeneous precipitation method. J Am Ceram Soc 76:1577
Purohit RD, Saha S, Tyagi AK (2000) Combustion synthesis and bulk thermal expansion studies of Ba and Sr thorates. J Nucl Mater 280:51
Purohit RD, Saha S, Tyagi AK (2006) Structure-activity relation of Fe2O3–CeO2 composite catalysts in CO oxidation. Ceram Int 32:143
Laguna OH, Centeno MA, Boutonnet M, Odriozola JA (2011) Fe-doped ceria solids synthesized by the microemulsion method for CO oxidation reactions. Appl Catal B 3–4(11):621
Neri G, Bonavita A, Rizzo G, Galvagno S, Capone S, Siciliano P (2006) Methanol gas-sensing properties of CeO2–Fe2O3 thin films. Sens Actuators B 114:687–695
Laguna OH, Centeno MA, Arzamendi G, Gandía LM, Romero-Sarria F, Odriozola JA (2010) ron-modified ceria and Au/ceria catalysts for total and preferential oxidation of CO (TOX and PROX). Catal Today 157:155
Laguna OH, Romero Sarria F, Centeno MA, Odriozola JA (2010) Gold supported on metal-doped ceria catalysts (M=Zr, Zn and Fe) for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). J Catal 276:360
Bao H, Chen X, Fang J, Jiang Z, Huang W (2008) Structure-activity relation of Fe2O3–CeO2 composite catalysts in CO oxidation. Catal Lett 125:160
Hernández WY, Romero-Sarria F, Centeno MA, Odriozola JA (2010) In situ characterization of the dynamic gold-support interaction over ceria modified Eu3+. Influence of the oxygen vacancies on the CO oxidation reaction. J Phys Chem C 114:10857
Romero-Sarria F, Vargas JC, Roger A-C, Kiennemann A (2008) Hydrogen production by steam reforming of ethanol: study of mixed oxide catalysts Ce2Zr1.5Me0.5O8: comparison of Ni/Co and effect of Rh. Catal Today 133–135:149
Rossignol S, Micheaud-Especel C, Duprez D, Avelino Corma FVMSM, José Luis GF (2000) Structural and catalytic properties of Zr–Ce–O mixed oxides. Role of the anionic vacancies. Stud Surf Sci Catal 130:3327
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations). Pure Appl Chem 57:603
Leofanti G, Padovan M, Tozzola G, Venturelli B (1998) Surface area and pore texture of catalysts. Catal Today 41:207
Yu X, Li F, Ye X, Xin X, Xue Z (2000) Synthesis of cerium (IV) oxide ultrafine particles by solid-state reactions. J Am Ceram Soc 83:964
Xie G, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Liu Q, Ge J, Huang Z (2004) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gas using a CuO/Al2O3 catalyst sorbent: II. Promotion of SCR activity by SO2 at high temperatures. J Catal 224:42
Long RQ, Yang RT (2000) Characterization of Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia. J Catal 194:80
Ramis G, Yi L, Busca G, Turco M, Kotur E, Willey RJ (1995) Adsorption, activation, and oxidation of ammonia over SCR catalysts. J Catal 157:523
Si Z, Weng D, Wu X, Yang J, Wang B (2010) Modifications of CeO2-ZrO2 solid solutions by nickel and sulfate as catalysts for NO reduction with ammonia in excess O2. Catal Commun 11:1045
Ilieva L, Pantaleo G, Ivanov I, Zanella R, Venezia AM, Andreeva D (2009) A comparative study of differently prepared rare earths-modified ceria-supported gold catalysts for preferential oxidation of CO. Int J Hydrog Energy 34:6505
Damyanova S, Pawelec B, Arishtirova K, Huerta MVM, Fierro JLG (2008) The effect of CeO2 on the surface and catalytic properties of Pt/CeO2–ZrO2 catalysts for methane dry reforming. Appl Catal A 337:86
Brown R, Cooper ME, Whan DA (1982) Temperature programmed reduction of alumina-supported iron, cobalt and nickel bimetallic catalysts. Appl Catal 3:177
Li S, Krishnamoorthy S, Li A, Meitzner GD, Iglesia E (2002) Promoted iron-based catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: design, synthesis, site densities, and catalytic properties. J Catal 206:202
Li S, Li A, Krishnamoorthy S, Iglesia E (2001) Effects of Zn, Cu, and K promoters on the structure and on the reduction, carburization, and catalytic behavior of iron-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Catal Lett 77:197
Zhong Z, Highfield J, Lin M, Teo J, Han Y-F (2008) Insights into the oxidation and decomposition of CO on Au/alpha-Fe2O3 and on alpha-Fe2O3 by coupled TG-FTIR. Langmuir 24:8576
Grunewald GC, Drago RS (1991) Carbon. Molecular sieves as catalysts and catalyst supports. J Am Chem Soc 113(5):1636
Riad M, Sobhi Z, Mikhail S (2002) Catalytic dehydration reaction of ethanol over transition metal catalysts. J Eng Appl Sci 49(1):195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gobara, H.M., Aboutaleb, W.A., Hashem, K.M. et al. A novel route for synthesis of α-Fe2O3–CeO2 nanocomposites for ethanol conversion. J Mater Sci 52, 550–568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0353-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0353-2