Abstract
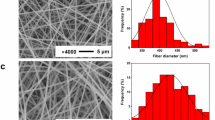
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes have been prepared with different NaY zeolite contents up to 32 wt%. Inclusion of zeolites induces an increase of average fiber size from ~200 nm in the pure polymer up to ~500 nm in the composite with 16 wt% zeolite content. For higher filler contents, a wider distribution of fibers occurs leading to a broader size distribution between the previous fiber size values. Hydrophobicity of the membranes increases from ~115º water contact angle to ~128º with the addition of the filler and is independent on filler content, indicating a wrapping of the zeolite by the polymer. The water contact angle further increases with fiber alignment up to ~137°. Electrospun membranes are formed with ~80 % of the polymer crystalline phase in the electroactive β phase, independently on the electrospinning processing conditions or filler content. Viability of MC3T3-E1 cells on the composite membranes after 72 h of cell culture indicates the suitability of the membranes for tissue engineering applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martins P, Lopes AC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2013) Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog Polym Sci. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.07.006
Mistry AS, Pham QP, Schouten C, Yeh T, Christenson EM, Mikos AG et al (2010) In vivo bone biocompatibility and degradation of porous fumarate-based polymer/alumoxane nanocomposites for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 92:451–462
Ghosh S (2004) Recent research and development in synthetic polymer-based drug delivery systems. J Chem Res 4:241–246
Prest WM, Luca DJ (1978) Formation of gamma-phase from alpha-polymorphs and beta-polymorphs of polyvinylidene fluoride. J Appl Phys 49:5042–5047
Gregorio R, Cestari M (1994) Effect of crystallization temperature on the crystalline phase content and morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Polym Sci Polym Phys 32:859–870
Sencadas V, Moreira VM, Lanceros-Mendéz S, Pouzada AS, Gregório R Jr (2006) α - To - β transformation on PVDF films obtained by uniaxial stretch. Mater Sci Forum 514:872–876
Sencadas V, Gregorio Filho R, Lanceros-Mendez S (2006) Processing and characterization of a novel nonporous poly(vinilidene fluoride) films in the β phase. J Non-Cryst Solids 352:2226–2229
Firmino Mendes S, Costa CM, Sencadas V et al (2009) Effect of the ceramic grain size and concentration on the dynamical mechanical and dielectric behavior of poly(vinilidene fluoride). Appl Phys A 96:1037
Martins P, Costa CM, Botelho G, Lanceros-Mendez S, Barandiaran JM, Gutierrez J (2012) Dielectric and magnetic properties of ferrite/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. Mater Chem Phys 131:698–705
Corma A, Martinez A (1995) Zeolites and zeotypes as catalysts. Adv Mater 7:137–144
Martínez C, Corma A (2011) Inorganic molecular sieves: preparation, modification and industrial application in catalytic processes. Coordin Chem Rev 255:1558–1580
Dong Y, Chen S, Zhang X, Yang J, Liu X, Meng G (2006) Fabrication and characterization of low cost tubular mineral-based ceramic membranes for micro-filtration from natural zeolite. J Membrane Sci 281:592–599
Bae D, Park H, Kim JS, Lee Jb, Kwon OY, Kim KY et al (2008) Hydrogen adsorption in organic ion-exchanged zeolites. J Phys Chem Solids 69:1152–1154
Townsend RP, Coker EN (2001) Ion exchange in zeolites. Stud Surf Sci Catal 137:467–524
Lopes AC, Caparros C, Ferdov S, Lanceros-Mendez S (2013) Influence of zeolite structure and chemistry on the electrical response and crystallization phase of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Mater Sci 48:2199–2206. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6995-9
Lopes AC, Caparros C, Ribelles JLG, Neves IC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2012) Electrical and thermal behavior of gamma-phase poly(vinylidene fluoride)/NaY zeolite composites. Micropor Mesopor Mater 161:98–105
Gonçalves R, Lopes AC, Botelho G, Neves IC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2013) Influence of solvent properties on the electrical response of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/NaY composites. J Polym Res 20. doi:10.1007/s10965-013-0143-3
Lopes AC, Gonçalves R, Costa CM, Fonseca AM, Botelho G, Neves IC, Lanceros-Mendez S (2012) Effect of zeolite content in the electrical, mechanical and thermal degradation response of poly/vinylidene fluoride)/NaY zeolite composites. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:6804–6810
Nunes-Pereira J, Lopes AC, Costa CM, Rodrigues LC, Silva MM, Lanceros-Mendez S (2013) Microporous membranes of NaY zeolite/poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) for Li-ion battery separators. J Electroanal Chem 689:223–232
Shi H, Liu F, Xue L (2013) Fabrication and characterization of antibacterial PVDF hollow fibre membrane by doping Ag-loaded zeolites. J Membrane Sci 437:205–215
Costa R, Ribeiro C, Lopes AC, Martins P, Sencadas V, Soares R et al (2013) Osteoblast, fibroblast and in vivo biological response to poly(vinylidene fluoride) based composite materials. J Mater Sci 24:395–403. doi:10.1007/s10856-012-4808-y
Bhardwaj N, Kundu SC (2010) Electrospinning: a fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv 28:325–347
Ribeiro C, Sencadas V, Ribelles JLG, Lanceros-Méndez S (2010) Influence of processing conditions on polymorphism and nanofiber morphology of electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes. Soft Mater 8:274–287
Agarwal S, Wendorff JH, Greiner A (2008) Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 49:5603–5621
Naderi H, Matin MM, Bahrami AR (2011) Review paper: critical issues in tissue engineering: biomaterials, cell sources, angiogenesis, and drug delivery systems. J Biomater Appl 26:383–417
Ratner BD (2004) Biomaterials science an introduction to materials in medicine. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam; Boston
Rebollar E, Frischauf I, Olbrich M, Peterbauer T, Hering S, Preiner J et al (2008) Proliferation of aligned mammalian cells on laser-nanostructured polystyrene. Biomaterials 29:1796–1806
Ribeiro C, Moreira S, Correia V, Sencadas V, Rocha JG, Gama FM et al (2012) Enhanced proliferation of pre-osteoblastic cells by dynamic piezoelectric stimulation. RSC Adv 2:11504–11509
Areias AC, Ribeiro C, Sencadas V, Garcia-Giralt N, Diez-Perez A, Gómez Ribelles JL et al (2012) Influence of crystallinity and fiber orientation on hydrophobicity and biological response of poly(l-lactide) electrospun mats. Soft Matter 8:5818–5825
Mikulikova R, Moritz S, Gumpenberger T et al (2005) Cell microarrays on photochemically modified polytetrafluoroethylene. Biomaterials 26:5572–5580
Hu Q, Wu H, Zhang L, Fong H, Tian M (2012) Rubber composite fibers containing silver nanoparticles prepared by electrospinning and in situ chemical crosslinking. Express Polym Lett 6:258–265
Choi JM, Jang HC, Hyeon JY, Sok JH (2012) Fabrication of PCL/MWCNTs nanofiber by electrospinning. Korean J Met Mater 50:763–768
Gai GQ, Wang LY, Dong XT et al (2013) Electrospinning preparation and properties of magnetic-photoluminescent bifunctional bistrand-aligned composite nanofibers bundles. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1539
Li Q, Chen Y, Lee DJ, Li F, Kim H (2012) Preparation of Y-zeolite/CoCl2 doped PVDF composite nanofiber and its application in hydrogen production. Energy 38:144–150
Madhugiri S, Dalton A, Gutierrez J, Ferraris JP, Balkus KJ Jr (2003) Electrospun MEH-PPV/SBA-15 composite nanofibers using a dual syringe method. J Am Chem Soc 125:14531–14538
Cucchi I, Spano F, Giovanella U, Catellani M, Varesano A, Calzaferri G et al (2007) Fluorescent electrospun nanofibers embedding dye-loaded zeolite crystals. Small 3:305–309
Chiang AST, Chao KJ (2001) Membranes and films of zeolite and zeolite-like materials. J Phys Chem Solids 62:1899–1910
Keeting PE, Oursler MJ, Wiegand KE, Bonde SK, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL (1992) Zeolite-A increases proliferation, differentiation, and transforming growth-factor-beta production in normal adult human osteoblast-like cells in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 7:1281–1289
Firling CE, Evans GL, Wakley GK, Sibonga J, Turner RT (1996) Lack of an effect of sodium zeolite A on rat tibia histomorphometry. J Bone Miner Res 11:254–263
Rosales-Leal JI, Rodríguez-Valverde MA, Mazzaglia G, Ramón-Torregrosa PJ, Díaz-Rodríguez L, García-Martínez O et al (2010) Effect of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion. Colloids Surf B 365:222. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.12.017
Bellat J-P, Paulin C, Jeffroy M, Boutin A, Paillaud J-L, Patarin J et al (2009) Unusual hysteresis loop in the adsorption—desorption of water in NaY zeolite at very low pressure. J Phys Chem C 113:8287–8295
Zheng J, He A, Li J, Han CC (2007) Polymorphism control of poly(vinylidene fluoride) through electrospinning. Macromol Rapid Commun 28:2159–2162
Salimi A, Yousefi AA (2003) FTIR studies of β-phase crystal formation in stretched PVDF films. Polym Test 22:699–704
Lanceros-Méndez S, Mano JF, Costa AM, Schmidt VH (2001) FTIR and DSC studies of mechanically deformed β-PVDF films. J Macromol Sci Phys 40:517–527
Lovinger AJ (1982) In: Bassett DC (ed) Developments in crystalline polymers-1. Elsevier, London
Amorim R, Vilaça N, Martinho O, Reis RM, Sardo M, Rocha J, Fonseca AM, Baltazar F, Neves IC (2012) Zeolite structures loading with an anticancer compound as drug delivery systems. J Phys Chem C 116:25642–25650
Čík G, Bujdáková H, Šeršeň F (2001) Study of fungicidal and antibacterial effect of the Cu(II)-complexes of thiophene oligomers synthesized in ZSM-5 zeolite channels. Chemosphere 44:313–319
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by FEDER through the COMPETE Program and by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) in the framework of the Strategic Project PEST-C/FIS/UI607/2011 and the project Matepro-Optimizing Materials and Processes, “ref. NORTE-07-0124-FEDER-000037,” co-funded by the “Programa Operacional Regional do Norte” (ON.2—O Novo Norte), under the “Quadro de Referência Estratégico Nacional” (QREN), through the “Fundo Europeu de Desenvolvimento Regional” (FEDER). A.C.L., C.R., and V.S. thank the support of the FCT (Grants SFRH/BD/62507/2009, SFRH/BPD/90870/2012 and SFRH/BPD/63148/2009 respectively).We also thank the support from the COST Action MP0902, Composites of Inorganic Nanotubes and Polymers, COINAPO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, A.C., Ribeiro, C., Sencadas, V. et al. Effect of filler content on morphology and physical–chemical characteristics of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/NaY zeolite-filled membranes. J Mater Sci 49, 3361–3370 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8043-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8043-4