Abstract
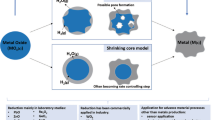
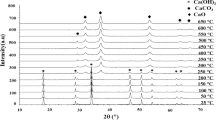
In this paper, the hydrogen storage capacity of some synthetic and natural iron oxides is presented. The results of the activity tests and characterization techniques of natural and synthetic iron oxides (N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, temperature-programmed reduction, X-ray diffraction, and plasma atomic emission spectroscopy) suggest that the use of chromium on iron oxide systems improved their hydrogen storage capacity. This is related to the capacity of chromium to modify the iron oxide reduction profile when Cr was incorporated. A direct reduction from Fe3O4 to Fe was observed as the mechanism for H2 storage. In addition, natural oxides as commercial Superfine and Densinox-L oxides are proved to be suitable materials to store and purify H2 due to their high stability during different cycles of reduction and oxidation. The best results among the natural ones were Densinox-L and among the synthetic ones Fe–10Cr.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Otsuka K, Kaburagi T, Yamada C, Takenaka S (2003) J Power Sources 122:111
Lebon A, Garcia-Fuente A, Vega A, Aguilera-Granja F (2012) J Phys Chem 116:126
Lebon A, Garcia-Fuente A, Vega A, Aguilera-Granja F (2011) Phys Rev B 83:125427
Kobayashi H, Yamauchi M, Kitagawa H (2012) J Am Chem Soc 134:6893
Kobayashi H, Yamauchi M, Kitagawa H (2011) J Am Chem Soc 133:11034
Kusada K, Yamauchi M, Kobayashi H, Kubota Y (2010) J Am Chem Soc 132:15896
Huang ZG, Guo ZP, Calka A, Wexler D, Lukey C, Liu HK (2006) J Alloy Compd 422:299
Hacker V, Faleschini G, Fuchs H, Fankhauser R, Simader G, Ghaemi M (1998) J Power Sources 71:226
Hacker V, Faleschini G, Fuchs H, Fankhauser R, Simader G, Ghaemi M (2000) J Power Sources 86:531
Hacker V (2003) J Power Sources 118:311
Mignard D, Pritchard C (2007) Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:5039
David E (2005) J Mater Process Technol 169:162–163
Kock AJHM, Fortuin HM, Geus JW (1985) J Catal 96:261
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Pure Appl Chem 57:603
Lowell S, Shields JE, Thomas MA, Thommes M (2006) Characterization of porous solids and powers: surface area, pore size and density. Springer, Netherlands
De Boer JH (1958) The structure and properties of porous materials. Butterworths, London
Jozwiak WK, Kaczmarek E, Maniecki TP, Ignaczak W, Maniukiewicz W (2007) Appl Catal A 326:17
Liu X, Shen K, Wang Y, Wang Y, Guo Y, Guo Y et al (2008) Catal Commun 9:2316
Jimenez-Lopez A, Rodriguez-Castellon E, Maireles-Torres P, Díaz L, Mérida-Robles J (2001) Appl Catal A Gen 218:295
Batista MS, Assaf EM, Assaf JM, Ticianelli EA (2006) Int J Hydrogen Energy 31:1204
Popa T, Guoqing X, Barton TF, Argylea MD (2010) Appl Catal A 379:15
Lorente E, Peña JA, Herguido J (2011) Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:7043
Lorente E, Peña JA, Herguido J (2009) J Power Sources 192:224
Sharma T (1994) ISIJ Int 34(12):960
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of the Universidad del País Vasco and Basque Regional Government for this work (Saiotek program) and to Tecnalia for its kind collaboration to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Requies, J., Güemez, M.B., Perez Gil, S. et al. Natural and synthetic iron oxides for hydrogen storage and purification. J Mater Sci 48, 4813–4822 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7377-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7377-7