Abstract
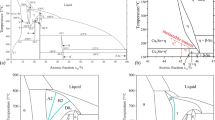
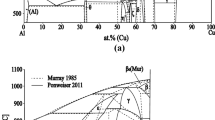
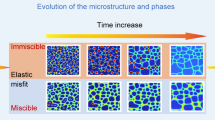
The influence of both bulk supercooling and cooling rate on the microstructure and phase selection during solidification of Cu–Co, Cu–Co–Fe, and Cu–Nb alloys exhibiting metastable liquid miscibility gaps were investigated using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy. Containerless electromagnetic levitation was used to achieve large bulk supercoolings in the specimens. Supercooling of these alloys below a certain temperature resulted in metastable separation of the melt into two liquids, a Cu-lean (Co, Co + Fe, or Nb enriched) melt (L1) and a Cu-rich melt (L2). Usually, the microstructure of the phase-separated alloys consisted of spherulites corresponding to one of the phase-separated liquids embedded in a matrix corresponding to the other. The microstructure and phase selection are found to depend on factors such as: alloy composition, supercooling level, whether the material was dropped before or after recalescence, and the cooling rate during solidification. The following results were observed: (1) solidification of metastable ε-Cu with enhanced Co (or Co + Fe, or Nb) solubility; (2) partitionless solidification of the L1 and L2 liquids; (3) spinodal decomposition of the supercooled liquid, and (4) secondary melt separation. The results are discussed and related to current solidification theories regarding solidification paths for the different conditions examined. The miscibility gap boundaries for the different alloys were determined and compared with those reported in the literature.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Froes FH (1995) In: Advanced synthesis of light metals, Korean journal of metals and materials conference. Hongik University, Seoul, p 28
Jones H (1981) In: Herman H (ed) Treatise on materials science and technology, vol 20. Academic Press, New York, p 1
Bardes BP, Flemings MC (1966) Trans AFS 74:406
Mehrabian R (1982) Int Metals Rev 27:185
Munitz A, Elder SP, Abbaschian R (1992) Metall Trans A 23A:1817
Clyne TW (1983) Metall Trans B 15B:369
Miroshnichenko GP, Brekharya IS (1970) Fiz Metal Metalloved 664
Munitz A (1987) Metall Trans B 18B:565
Berkowitz BJ, Scattergood RO (1987) In: Kelly TF, Vander Sande JB (eds) Chemistry and physics of rapidly solidified materials. TMS-AIME, Warrendale, p 35
Boettinger WJ, Oriel SR, Sekerka RF (1982) In: Kelly TF, Vander Sande JB (eds) Chemistry and physics of rapidly solidified materials. TMS-AIME, Warrendale, p 45
Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1987) In: Collings EW, Koch CC (eds) Undercooled alloy phases. TMS-AIME, Warrenadle, p 23
Das SK, Kear BH, Adam CM (1985) In: Flemings M, Cohen MC (eds) Rapidly solidified crystalline alloys. TMS-AIME, Warrendale, p 3
Elder SP, Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1989) Mater Sci Forum 50:137
Nakagawa Y (1958) Acta Metall 6:704
Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1996) Met Mater Trans A 27:4049
Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1998) J Mater Sci 33:3639. doi:10.1023/A:1004663530929
Elder SP (1990) Ph.D. Dissertation University of Florida, Gainesville
Kim DI, Abbaschian R (2000) J Phase Equilibria 21:1
Bamberger M, Munitz A, Kaufman L (2002) CALPAD 26:375
Munitz A, Bamberger M, Wannaparhun S, Abbaschian R (2006) J Mater Sci 41:2749. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-5598-8
Munitz A, Bamberger M, Venkert A, Landau P, Abbaschian R (2009) J Mater Sci 44:64. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3115-y
PerepezkoJH, ShiaharaY, Paik JS, Flemings MC (1982) In: Mehrabian R (ed) Rapid solidification processing: principles and technologies III. NBS, Gaithersburg, p 28
Walker JH (1961) In: St. Pierre GR (ed) Physical chemistry of process metallurgy. Interscience Publication, New York, p 845
Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1986) In: Collings EW, Koch CC (eds) Undercooled alloy phases new orleans Louisiana. The Metallurgical Society of AIME, Louisiana, p 23
Abbaschian GJ, Flemings MC (1983) Metall Trans A 14A:1147
Munitz A, Abbaschian R (1991) J Mater Sci 26:6458. doi:10.1007/BF02387830
Robinson MB, Li D, Rathz TJ, Williams G (1999) J Mater Sci 34:3747. doi:10.1023/A:1004688313591
Reed SJB (1977) In: Electron microprobe analysis. Cambridge University Pressto, Cambridge, p 175
Klug HP, Alexander LE (1974) In: X-ray diffraction procedures for polycrystalline and amorphous materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Wiles D, Young R (1981) J Appl Cryst 14:149
Cullity BD (1977) In: Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Boston, p 506
Nishizawa T, Ishida K (1984) Bull Alloy Phase Diagr 5:161
Porter DA, Easterling KE (1984) Phase transformation in metals and alloys. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, p 308
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Dr G. Kimmel for his technical assistance with the X-ray diffraction measurements and Mr. C. Cotler for the microstructural characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munitz, A., Venkert, A., Landau, P. et al. Microstructure and phase selection in supercooled copper alloys exhibiting metastable liquid miscibility gaps. J Mater Sci 47, 7955–7970 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6354-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6354-x