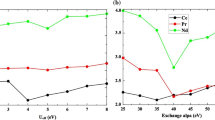
Abstract
The structure, elastic properties, thermal expansion, and thermal conductivity of the orthorhombic-structured A3+B3+O3 perovskites are determined using atomistic simulations with classical potentials. When considered as pseudo-cubic monoclinic systems, they show relatively small deviations in structure and properties from their cubic perovskite parent phase. The variations in properties are shown to be related to the magnitude of the tilting of the BO6 octahedra, which in turn is related to the relative sizes of the A and B ions, as encapsulated in the tolerance factor.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier SM, Gupta DK (1994) J Eng Gas Turbines Power 116:250
Clarke DR, Levi CG (2003) Ann Rev Mater Res 33:383
Winter MR, Clarke DR (2007) J Am Ceram Soc 90:533
Mitchell RH (2002) Perovskites: modern and ancient. Almaz Press, Thunder Bay
Levy MR, Grimes RW, Sickafus KE (2004) Philos Mag 84:533
Jiang S, Chan S (2004) J Mater Sci 39:4405. doi:https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000034135.52164.6b
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Crystallogr A32:751
Glazer AM (1972) Acta Crystallogr B28:3384
International Tables for Crystallography Online (2006) Springer, New York
Nye JF (1985) Physical properties of crystals: their representation by tensors and matrices. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Gale JD, Rohl A (2003) Mol Simul 29:291
Gale JD (1997) J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 93:629
Turney JE, McGaughey AJH, Amon CH (2009) Phys Rev B 79:224305
Sławiński W, Przeniosło R, Sosnowska I, Brunelli M, Bieringer M (2007) Nucl Instrum Methods B 254:149
Schelling PK, Phillpot SR, Grimes RW (2004) Philos Mag Lett 84:127
Williford R, Stevenson J, Chou S, Pederson L (2001) J Solid State Chem 156:394
Schelling PK, Phillpot SR (2001) J Am Ceram Soc 84:2997
Stevens RJ, Zhigilei LV, Norris PM (2007) Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:3977
Yates B, Cooper RF, Pojur AF (1972) J Phys C Solid State Phys 5:1046
Hummer DR, Heaney PJ, Post JE (2008) Powder Diffr 23:267
Usvyat DE, Evarestov RA, Smirnov VP (2004) Int J Quantum Chem 100:352
Acknowledgements
We are happy to acknowledge valuable conversations with Prof. David Clarke (Harvard) and Prof. Susan Sinnott (UF). This work was supported by a Materials World Network Project, NSF DMR-0710523 and EPSRC EP/F026463/1. The work of AC was supported by DARPA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steele, B., Burns, A.D., Chernatynskiy, A. et al. Anisotropic thermal properties in orthorhombic perovskites. J Mater Sci 45, 168–176 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3912-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3912-y