Abstract
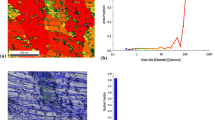
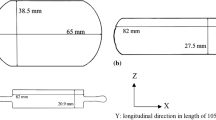
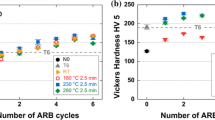
The mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of AA6082 with ultrafine-grained (UFG) microstructure were investigated. The material was processed by equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) up to eight extrusions at room temperature in a 90°-die with active backpressure. Besides the peak-aged temper, which provides maximum strengths and strongly reduced ductility, the solution heat treated condition was considered as well. Combined with post-ECAP aging, an optimum of high strength, ductility and impact toughness was achieved. The corrosion investigations and the examination of the corrosion damage of the UFG-materials show higher pitting corrosion resistance compared to the unprocessed material. The optimised condition was used for the production of screw prototypes which showed appreciable higher strength and ductility compared to the identically manufactured screws from the CG counterpart. Such materials are potential candidates to be used for several engineering applications such as high strength screws even at higher temperatures.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Segal VM, Reznikov AE, Drobyshevskiy AE, Kopylov VI (1981) Russ Metall 7 (English translation)
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2006) Prog Mater Sci 51:881. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.02.003
Horita Z, Fujinami T, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (2000) Metall Mater Trans A Phys Metall Mater Sci 31:691. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-000-0011-8
Horita Z, Ohashi K, Fujita T, Kaneko K, Langdon TG (2005) Adv Mater 17:1599. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200500069
Liu M, Roven HJ, Yu Y, Werenskiold JC (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 483–484:59. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.09.144
Roven HJ, Liu M, Werenskiold JC (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 483–484:54. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.09.142
Ferrasse S, Segal VM, Alford F, Kardokus J, Strothers S (in press) Mater Sci Eng A
Friedrich C (2004) Reliable lightweight fastening of magnesium components in automotive applications. In: SAE World Congress & Exhibition, SAE Technical Papers, Detroit, MI, March 2004
Valiev RZ, Islamgaliev RK, Alexandrov IV (2000) Prog Mater Sci 45:103. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00007-9
Vinogradov A, Mimaki T, Hashimoto S, Valiev R (1999) Scr Mater 41:319. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00170-0
Balyanov A, Kutnyakova J, Amirkhanova NA, Stolyarov VV, Valiev RZ, Liao XZ et al (2004) Scr Mater 51:225. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.04.011
Akiyama E, Zhang Z, Watanabe Y, Tsuzaki K (2007) J Solid State Electrochem 1–6
Hadzima B, Janecek M, Hellmig RJ, Kutnyakova Y, Estrin Y (2006) Mater Sci Forum 503–504:883
Vinogradov A, Miyamoto H, Mimaki T, Hashimoto S (2002) Ann Chim 27:65. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0151-9107(02)80008-3
Chung M-K, Choi Y-S, Kim J-G, Kim Y-M, Lee J-C (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 366:282. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.08.056
Son IJ, Nakano H, Oue S, Kobayashi S, Fukushima H, Horita Z (2006) Mater Trans 47:1163. doi:https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.47.1163
Wei W, Wei KX, Du QB (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 454–455:536. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.11.063
Segal VM (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 386:269
Furukawa M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2002) Mater Sci Eng A 332:97. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01716-6
Barber RE, Dudo T, Yasskin PB, Hartwig KT (2004) Scr Mater 51:373. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.05.022
Cheng S, Zhao YH, Zhu YT, Ma E (2007) Acta Mater 55:5822. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.06.043
Wang YM, Ma E, Valiev RZ, Zhu YT (2004) Adv Mater 16:328. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200305679
Zhao YH, Liao XZ, Cheng S, Ma E, Zhu YT (2006) Adv Mater 18:2280. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600310
Zhao YH, Liao XZ, Jin Z, Valiev RZ, Zhu YT (2004) Acta Mater 52:4589. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2004.06.017
Kim WJ, Kim JK, Kim HK, Park JW, Jeong YH (2008) J Alloy Compd 450:222
Kim JK, Jeong HG, Hong SI, Kim YS, Kim WJ (2001) Scr Mater 45:901. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(01)01109-5
Kim JK, Kim HK, Park JW, Kim WJ (2005) Scr Mater 53:1207. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.06.014
Kim WJ, Chung CS, Ma DS, Hong SI, Kim HK (2003) Scr Mater 49:333. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(03)00260-4
Hockauf M, Meyer LW, Zillmann B, Hietschold M, Schulze S, Krüger L. Mater Sci Eng A (accepted for publication)
Hockauf M, Meyer LW, Halle T, Kuprin C, Hietschold M, Schulze S et al (2006) Int J Mater Res 97:1392
Matsuda K, Naoi T, Fujii K, Uetani Y, Sato T, Kamio A et al (1999) Mater Sci Eng A 262:232. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(98)00962-9
Chakrabarti DJ, Laughlin DE (2004) Prog Mater Sci 49:389. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6425(03)00031-8
Kim WJ, Wang JY (2007) Mater Sci Eng A 464:23. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.03.074
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for supporting this work carried out within the framework of Sonderforschungsbereich 692 (Collaborative Research Center; A2, B2). The authors would like to thank Dr. Harry Podlesak for performing the STEM investigations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hockauf, M., Meyer, L.W., Nickel, D. et al. Mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of ultrafine-grained AA6082 produced by equal-channel angular pressing. J Mater Sci 43, 7409–7417 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2724-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2724-9