Abstract
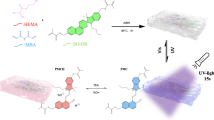
Biodegradable inverse opal (IoPPC) was synthesized from a multifunctional carboxylic acid and polyols by colloidal crystal templating. The IoPPC was prepared by infiltration of the monomer solution into interparticle voids of silica colloidal crystal template, polycondensation of the infiltrated film, and removal of the template. The synthesized IoPPC was characterized by infrared absorption, X-ray diffraction measurements, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermogravimetry/mass spectrometry analysis. In order to clarify the effect of biodegradation on the inverse opal structure and the optical reflection property, the IoPPC was implanted in subcutaneous tissue of the lower back of three mice (ICR, 10 weeks, female). After the 2 weeks implantation, fragmented samples were harvested from the implant location and investigated by scanning electron microscope observations and optical reflection measurements. It was found that the reflection peak for the harvested samples decayed from that for the sample without implantation. Such a spectral change is considered to be attributed to the deterioration of the regularity of the inverse opal structures through biodegradation. The finding of this study will serve in the development of reflection-based sensing in various biomedical applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Notes
The refractive index of silica colloids was estimated to be 1.29 from Eq. 3 with a λ max value of 597 nm (Fig. 7b). Such a small refractive index as compared with the value of crystalline silicon dioxide (1.45) is derived from the mesoporous structure of the silica colloids.
References
Karageorgiou V, Kaplan D (2005) Biomaterials 26:5474
Hua FJ, Kim GE, Lee JD, Son YK, Lee DS (2002) J Biomed Mater Res 63:161
Harris LD, Kim BS, Mooney DJ (1998) J Biomed Mater Res 42:396
Ma PX, Choi JW (2001) Tissue Eng 7:23
Marshall AJ, Ratner BD (2005) AIChE J 51:1221
Ratner BD, Marshall AJ (2006) Polym Prepr 47:69
Zhang K, Yan H, Stein A, Francis LF (2005) J Am Ceram Soc 88:587
Zhang K, Yan H, Bell DC, Stein A, Francis LF (2003) J Biomed Mater Res 66A:860
Yan H, Zhang K, Blanford CF, Francis LF, Stein A (2001) Chem Mater 13:1374
Grayson CR, Choi IS, Tyler BM, Wang PP, Brem H, Cima MJ, Langer R (2003) Nat Mater 2:767
Levenberg S, Langer R (2004) Curr Top Dev Biol 61:113
Xia Y, Gates B, Yin Y, Lu Y (2000) Adv Mater 12:693
Stein A, Schroden RC (2001) Curr Opin Solid-State Mater Sci 5:553
Diop M, Lessard RA (2003) J Nonlinear Opt Quantum Opt 30:203
Lee YJ, Braun PV (2003) Adv Mater 15:563
Takeoka Y, Watanabe M (2003) Adv Mater 15:199
Cassagneau T, Caruso F (2002) Adv Mater 14:1629
Liu J, Li G, Wu Z, An Q, Qiu Y (2007) ChemPhysChem 8:1298
Fujishima M, Sakata S, Kikoku M, Ogawa D, Uchida K (2007) Chem Lett 36:1510
Weissleder R (2001) Nat Biotechnol 19:316
Li YY, Cunin F, Link JR, Gao T, Betts RE, Reiver SH, Chin V, Bhatia SN, Sailor MJ (2003) Science 299:2045
Dupuis A, Guo N, Gao Y, Godlbout N, Lacroix S, Dubois C, Skorobogatiy M (2007) Opt Lett 32:109
Ikada Y, Tsuji H (2000) Macromol Rapid Commun 21:117
Yang J, Webb AR, Ameer GA (2004) Adv Mater 16:511
Yang J, Webb AR, Pickerill SJ, Hageman G, Ameer GA (2006) Biomaterials 27:1889
Denkov ND, Velev OD, Kralchevsky PA, Ivanov IB, Yoshimura H, Nagayama K (1993) Nature 361:26
Míguez H, Meseguer F, López C, Mifsud A, Moya JS, Vázquez L (1997) Langmuir 13:6009
Nagata M, Kono Y, Sakai W, Tsutsumi N (1999) Macromolecules 32:7762
Schroden RC, Al-Daous M, Blanford CF, Stein A (2002) Chem Mater 14:3305
Blanford CF, Schroden RC, Al-Daous M, Stein A (2001) Adv Mater 13:26
Richel A, Johnson NP, McComb DW (2000) App Phys Lett 76:1816
Míguez H, Meseguer F, López C, Lopez-Tejeira F, Sanchez-Dehesa J (2001) Adv Mater 13:393
Busch K, John S (1998) Phys Rev E 58:3896
Acknowledgements
The authors thank H. Kitagawa of Kyushu University for XRD measurements and TG/MS analyses. We also acknowledge R. Moriyama of Kinki University for technical instruction in the animal experiments. This work was partly supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (No. 18500369) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and by the Circle for the Promotion of Science and Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The in vivo degradation experiment was approved by the committee on animal experiments of School of Science and Engineering, Kinki University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujishima, M., Sakata, S., Iwasaki, T. et al. Implantable photonic crystal for reflection-based optical sensing of biodegradation. J Mater Sci 43, 1890–1896 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2419-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2419-7