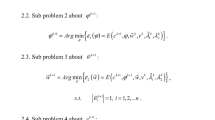Abstract
Contour tracking in complex environments is a difficult problem due to the cluttered backgrounds, illumination changes, occlusion and camera viewpoint variations etc. This paper presents a region functional based on the Earth Mover’s Distance (EMD), computation of which is mathematically modeled as the transportation problem (TP), for robust contour tracking in the challenging conditions. Formulation of EMD-based functional can be described as variational EMD (VEMD) since the contour curve function is involved for optimization. Minimizing the EMD-based functional is nontrivial and we develop a two-phase method for its optimization. In the first phase, letting the candidate contour be fixed, we seek the best solution to the TP by the Simplex algorithm. Then through the shape derivative theory, we make a perturbation analysis of the contour around the best solution to the TP. As a result we obtain a partial differential equation (PDE) that is solved by the level-set algorithm. The two-phase procedure iterates until the appropriate stopping criterions are satisfied. Alongside the EMD-based functional formulation, we introduce a dimensionality reduction method by tensor decomposition, achieving a low-dimensional Tensor-SIFT features for object representation. Applicable to both the color and gray-level images, Tensor-SIFT features are distinctive, insensitive to illumination and viewpoint changes. Finally, we develop an integrated algorithm that combines various techniques, e.g. the Simplex algorithm, narrow-band level set and fast marching algorithms. Particularly, we provide a method for the level-set initialization between two successive frames and the criterions for stopping the iterative functional optimization. Experiments in challenging image sequences show that the proposed work has promising performance.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubert, G., Barlaud, M., Faugeras, O., Jehan-Besson, S.: Image segmentation using active contours: calculus of variations or shape gradients? SIAM J. Appl. Math. 63(6), 2128–2154 (2003)
Bajramovic, F., Grabl, C., Denzler, J.: Efficient combination of histograms for real-time tracking using mean-shift and trust-region optimization. In: Proc. 27th DAGM Symposium on Pattern Recognition, pp. 254–261 (2005)
Blake, A., Isard, M.: Active Contours: The Application of Techniques from Graphics, Vision, Control Theory and Statistics to Visual Tracking of Shapes in Motion. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Brox, T., Rousson, M., Deriche, R., Weickert, J.: Colour, texture, and motion in level set based segmentation and tracking. Image Vis. Comput. 28, 376–390 (2010)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22(1), 61–79 (1997)
Chan, T.F., Vese, L.A.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Collins, R.T.: Mean-shift blob tracking through scale space. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., pp. 234–241 (2003)
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., Meer, P.: Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., pp. 142–149 (2000)
Comaniciu, D., Ramesh, V., Meer, P.: Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 25(5), 564–575 (2003)
Cremers, D., Rousson, M., Deriche, R.: A review of statistical approaches to level set segmentation: integrating color, texture, motion and shape. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 72(2), 195–215 (2007)
Csurka, G., Bray, C., Dance, C., Fan, L.: Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In: ECCV Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, pp. 1–22 (2004)
Delfour, M.C., Zolesio, J.-P.: Shapes and Geometries: Analysis, Differential Calculus, and Optimization. SIAM, Philadelphia (2001)
Faber, N.K.M., Bro, R., Hopke, P.K.: Recent developments in cande-comp/parafac algorithms: A critical review. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 65, 119–137 (2003)
Fitzgibbon, A., Pilu, M., Fisher, R.B.: Direct least square fitting of ellipses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(5), 476–480 (1999)
Fleet, D.J., Weiss, Y.: Handbook of Mathematical Models in Computer Vision. Springer, Berlin (2006). Chap. 15, Chapter Optical Flow Estimation
Freedman, D., Zhang, T.: Active contours for tracking distributions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 518–526 (2004)
Haker, S., Zhu, L., Tannenbaum, A., Angenent, S.: Optimal mass transport for registration and warping. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 225–240 (2004)
Herbulot, A., Jehan-Besson, S., Duffner, S., Barlaud, M., Aubert, G.: Segmentation of vectorial image features using shape gradients and information measures. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 25(3), 365–386 (2006)
Irani, M., Anandan, P.: A unified approach to moving object detection in 2d and 3d scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(6), 577–589 (1998)
Jehan-Besson, S., Barlaud, M., Aubert, G., Faugeras, O.: Shape gradients for histogram segmentation using active contours. In: Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, p. 408. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2003)
Kantorovich, L.V.: On the translocation of masses. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 37, 199–201 (1942)
Kass, M., Witkin, A.P., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Kolda, T.G., Bader, B.W.: Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev. 51(3), 455–500 (2009)
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., Ponce, J.: Beyond bags of features: spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., Washington, DC, USA, pp. 2169–2178. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2006)
Li, F.-F., Perona, P.: A bayesian hierarchical model for learning natural scene categories. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., Washington, DC, USA, pp. 524–531. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2005)
Ling, H., Okada, K.: An efficient earth mover’s distance algorithm for robust histogram comparison. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(5), 840–853 (2007)
Liu, C., Yuen, J., Torralba, A., Sivic, J., Freeman, W.T.: Sift flow: dense correspondence across different scenes. In: Proc. of European Conf. on Computer Vision, pp. 28–42. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Lowe, D.G.: Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, p. 1150. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (1999)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Luenberger, D.G., Ye, Y.: Linear and Nonlinear Programming. Springer, Berlin (2007)
McKenna, S.J., Raja, Y., Gong, S.: Tracking colour objects using adaptive mixture models. Image Vis. Comput. 17(3–4), 225–231 (1999)
Mikolajczyk, K., Schmid, C.: A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(10), 1615–1630 (2005)
Monge, G.: Mémoire sur la théorie des déblais et des remblais. In: Hist. de l’Acad. des Sciences de Paris, pp. 666–704 (1781)
Mutch, J., Lowe, D.G.: Multiclass object recognition with sparse, localized features. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., New York, NY, pp. 11–18 (2006, June)
Ni, K., Bresson, X., Chan, T., Esedoglu, S.: Local histogram based segmentation using the wasserstein distance. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 84(1), 97–111 (2009)
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Osher, S., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active contours and level sets for the detection and tracking of moving objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(3), 266–280 (2000)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active regions: a new framework to deal with frame partition problems in computer vision. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 13, 249–268 (2002)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active regions and level set methods for motion estimation and tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 97(3), 259–282 (2005)
Parlett, B.N.: The Symmetric Eigenvalue Problem. Upper Saddle River. Prentice-Hall, New York (1998)
Pele, O., Werman, M.: A linear time histogram metric for improved sift matching. In: Proc. of Eur. Conf. Comp. Vis, pp. 495–508 (2008)
Pele, O., Werman, M.: Fast and robust earth mover’s distances. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Comp. Vis. (2009)
Peleg, S., Werman, M., Rom, H.: A unified approach to the change of resolution: space and gray-level. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(7), 739–742 (1989)
Precioso, F., Barlaud, M., Blu, T., Unser, M.: Robust real-time segmentation of images and videos using a smooth-spline snake-based algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(7), 910–924 (2005)
Rachev, S., Rüschendorf, L.: Mass Transportation Problems. Vol. I: Theory, Vol. II: Applications. Probability and Its Application. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Rathi, Y., Vaswani, N., Tannenbaum, A., Yezzi, A.: Tracking deforming objects using particle filtering for geometric active contours. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(8), 1470–1475 (2007)
Ronfard, R.: Region-based strategies for active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 13(2), 229–251 (1994)
Rubner, Y., Tomasi, C., Guibas, L.J.: The earth mover’s distance as a metric for image retrieval. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 40(2), 99–121 (2000)
Sethian, J.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Shirdhonkar, S., Jacobs, D.: Approximate earth mover’s distance in linear time. In: Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, Alaska, USA, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Sokolowski, J., Zolesio, J.-P.: Introduction to Shape Optimization: Shape Sensitivity Analysis. Springer, Berlin (1992)
Turk, M., Pentland, A.: A unified approach to the change of resolution: space and gray-level. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 3(1), 71–862 (1991)
Vasilescu, M., Terzopoulos, D.: Multilinear analysis of image ensembles: tensorfaces. In: Proc. of European Conf. on Computer Vision, p. 447–460. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Vasilescu, M., Terzopoulos, D.: Multilinear subspace analysis for image ensembles. In: Proc. of IEEE Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 93–99. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2003)
Wang, H., Ahuja, N.: A tensor approximation approach to dimensionality reduction. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 76(3), 217–229 (2008)
Wu, C.: SiftGPU: A GPU Implementation of Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) (2007). http://cs.unc.edu/~ccwu/siftgpu
Yan, K., Sukthankar, R.: PCA-SIFT: a more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comp. Vis. Patt. Recog., pp. 506–513. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos (2004)
Zhang, T., Freedman, D.: Improving performance of distribution tracking through background mismatch. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(2), 282–287 (2005)
Zhao, Q., Yang, Z., Tao, H.: Differential earth mover’s distance with its applications to visual tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(2), 274–287 (2010)
Zhong, Y., Jain, A.K., Dubuisson-Jolly, M.-P.: Object tracking using deformable templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(5), 544–549 (2000)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the reviewers for their helpful comments which improved both the quality and presentation of this paper. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (60973080,61170149), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University from Chinese Ministry of Education (NCET-10-0151), Key Project by Chinese Ministry of Education (210063). It was also supported by High-level professionals (innovative teams) of Heilongjiang University (Hdtd2010-07). We thank Nannan Zhao for writing the code to implement EMD computation via the simplex algorithm, and Qilong Wang for assistance in conducting experiments in Sect. 6.2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P. Tensor-SIFT Based Earth Mover’s Distance for Contour Tracking. J Math Imaging Vis 46, 44–65 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-012-0369-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-012-0369-4