Abstract
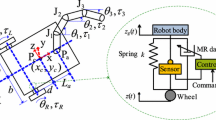
In this paper, I suggest active suspension technique for a rapid mobile robot, KDMR-1. The major purpose of KDMR-1 is object delivery. The KDMR-1 is designed to have a maximum speed of 12.8 km/hr. At this high speed, ground disturbances caused the mobile robot to vibrate. To reduce vibration, we controlled the compliance of the active suspension. The active suspension, consisting of 3-DOF highly geared electric motors was controlled by the Cartesian computed torque (CCT) control. The CCT control method has been studied widely in the literature; however, there have been few experimental realizations in joint position controlled robots. The CCT control was used to improve joint compliance while maintaining position control accuracy. We reduced the Cartesian disturbances at high speeds successfully using joint compliance. We focused on the experimental evaluation of the ability of the CCT control to improve joint compliance in the position-controlled system equipped with highly geared electric motors. A rapid object delivery experiment demonstrated the effectiveness of the active suspension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubowsky, S., Vance, E.E.: Planning mobile manipulator motions considering vehicle dynamic stability constraints Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp 1271–1276, Scottsdale, AZ, USA (1989)
Fukuda, T., Fujisawa, Y.: Manipulator/Vehicle system for man-robot cooperation Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp 74–79, Nice, France (1992)
Huang, Q., Tanie, K., Sugano, S.: Coordinated motion planning for a mobile manipulator considering stability and manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res 19, 732–742 (2000)
Vukobratovic, M., Borovac, B.: Zero-Moment Point—Thirty-five years of its life. Int. J. Humanoid Robotics 1, 157–173 (2004)
Papadopoulos, E., Rey, D.A.: The force-angle measure of tipover stability margin for mobile manipulators. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 33, 29–48 (2000)
Kim, J., Chung, W.K., Youm, Y., Lee, B.H.: Real-time ZMP compensation method using null motion for mobile manipulators Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp 1967–1972, Washington, DC, USA (2002)
Moosavian, S.A.A., Alipour, K.: Tip-over stability of suspended wheeled mobile robots Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Mechatronics and Automation, pp 1356–1361, Harbin, China (2007)
Lin, C.Y., Cheng, L.C., Huang, C.C., Chuang, L.W., Teng, W.C., Kuo, C.H., Gu, H.Y., Chung, K.L., Fahn, C.S.: Versatile humanoid robots for theatrical performances (2013)
Cha, E., Dragan, A.D., Srinivasa, S.S.: Effects of robot capability on user acceptance Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), 2013 8th ACM/IEEE International Conference on, pp. 97-98 (2013)
Dragan, A.D., Lee, K.C., Srinivasa, S.S.: Legibility and predictability of robot motion Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), 2013 8th ACM/IEEE International Conference on, pp. 301-308 (2013)
Bauml, B., Schmidt, F., Wimbock, T., Birbach, O., Dietrich, A., Fuchs, M., Friedl, W., Frese, U., Borst, C., Grebenstein, M.: Catching flying balls and preparing coffee: Humanoid Rollin’ Justin performs dynamic and sensitive tasks Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2011 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 3443-3444 (2011)
Borst, C., Wimbock, T., Schmidt, F., Fuchs, M., Brunner, B., Zacharias, F., Giordano, P.R., Konietschke, R., Sepp, W., Fuchs, S.: Rollin’ Justin–Mobile platform with variable base Robotics and Automation, 2009. ICRA’09. IEEE International Conference on, pp. 1597-1598 (2009)
Ellenberg, R.W., Vallett, R., Gross, R., Nutt, B., Oh, P.Y.: Development of the skewed rotation plane (SRP) waist joint for humanoid robots Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA), 2013 IEEE International Conference on, pp 1–6, Woburn, MA (2013)
Asfour, T., Vahrenkamp, N., Schiebener, D., Do, M., Przybylski, M., Welke, K., Schill, J., Dillmann, R., Welke, K., Vahrenkamp, N.: ARMAR-III: Advances in humanoid grasping and manipulation. J. Robotics Soc. Jpn 19, 43–57 (2013)
Przybylski, M., Vahrenkamp, N., Asfour, T., Dillmann, R.: Grasp and motion planning for humanoid robots, in Grasping in Robotics. ed: Springer, 329–359 (2013)
Asfour, T., Regenstein, K., Azad, P., Schroder, J., Bierbaum, A., Vahrenkamp, N., Dillmann, R.: ARMAR-III: An integrated humanoid platform for sensory-motor control Humanoid Robots, 2006 6th IEEE-RAS International Conference on, pp. 169-175 (2006)
Kehoe, B., Matsukawa, A., Candido, S., Kuffner, J., Goldberg, K.: Cloud-based robot grasping with the google object recognition engine IEEE Int’l Conf. on Robotics and Automation (2013)
Alunni, N., Phillips-Grafflin, C., Suay, H.B., Lofaro, D., Berenson, D., Chernova, S., Lindeman, R.W., Oh, P.: Toward a user-guided manipulation framework for high-DOF robots with limited communication Technologies for Practical Robot Applications (TePRA), 2013 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 1-6 (2013)
Kim, M., Choi, D., Oh, J.H.: Stabilization of a rapid four-wheeled mobile platform using the ZMP stabilization method In: Proc. IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, pp 317–322, Montreal, Canada (2010)
Choi, D., Kim, M., Oh, J.H.: Development of a rapid mobile robot with a Multi-Degree-of-Freedom inverted pendulum using the model-based Zero-Moment Point stabilization method. Adv. Robot 26, 515–535 (2012)
Plumet, F., Morel, G., Bidaud, P.: Shall we use a dynamic model to control the motions of industrial manipulators? In: Proceedings of the Ninth World Congress on Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, pp 235–240, Milano, Italy (1995)
Bevly, D., Dubowsky, S., Mavroidis, C.: A simplified Cartesian-computed torque controller for highly geared systems and its application to an experimental climbing robot. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control-Trans. Asme 122, 27–32 (2000)
Arteaga, M.A., Castillo-Sánchez, A., Parra-Vega, V.: Cartesian control of robots without dynamic model and observer design. Automatica 42, 473–480 (2006)
Lin, J., Lin, C., Lo, H.-S.: Pseudo-inverse Jacobian control with grey relational analysis for robot manipulators mounted on oscillatory bases. J. Sound Vib. 326, 421–437 (2009)
Park, J.H., Kim, K.D.: Biped robot walking using gravity-compensated inverted pendulum mode and computed torque control Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp 3528–3533, Leuven, Belgium (1998)
Park, I.W., Kim, J.Y., Park, S.W., Oh, J.H.: Development of humanoid robot platform KHR-2 (KAIST Humanoid Robot-2) IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, pp 292–310, Los Angeles (2004)
Liegeois, A.: Automatic supervisory control of the configuration and behavior of multibody mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Syst, Man, Cybern. SMC-7, 868–871 (1977)
Nakamura, Y., Hanafusa, H., Yoshikawa, T.: Task-priority based redundancy control of robot manipulators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 6, 3–15 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, D., Oh, JH. Active Suspension for a Rapid Mobile Robot Using Cartesian Computed Torque Control. J Intell Robot Syst 79, 221–235 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-014-0064-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-014-0064-3