Abstract
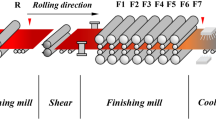
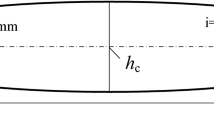
Precise selective cooling control of work roll can significantly improve the cold rolled strip flatness in steel manufacturing industry. To improve the control accuracy of the coolant output of selective work roll cooling control system, a machine learning (ML) algorithm with differential evolution-gray wolf algorithm optimization support vector machine regression (DE-GWO-SVR) model has been proposed for the first time in this study. This model combines the differential evolution (DE) with grey wolf optimization algorithm (GWO) to improve the optimization performance of the algorithm. Then, the SVR model parameters are optimized with differential evolutionary gray wolf hybrid algorithm (DE-GWO) to improve the regression accuracy. Finally, the influences of data normalization methods and the selection of SVR kernel functions were systematically investigated. Compared with the test results of other regression models, the evaluation index R2 based on the DE-GWO-SVR model is greater and the RMSE, MAE, and MAPE are smaller. The DE-GWO-SVR model performs the best, with a higher regression accuracy than the other regression models. Besides, it has been successfully applied to a 1450 mm five-stand industrial cold rolling mill. The model has higher control accuracy for the thermal crown of the work roll and better control effect for the flatness deviation of the strip steel. This study provides a novel strategy with a help of ML algorithm to effectively improve the flatness quality of cold rolled strips by optimizing the selective cooling control of work roll, which exhibits a great practical application potential in steel manufacturing.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Abbaspour, M., & Saboonchi, A. (2008). Work roll thermal expansion control in hot strip mill. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 32, 2652–2669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2007.09.011
Abidi, M. H., Alkhalefah, H., & Umer, U. (2021). Fuzzy harmony search based optimal control strategy for wireless cyber physical system with industry 4.0. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 33, 1795–1812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01757-4
Agarwal, K., & Shivpuri, R. (2015). On line prediction of surface defects in hot bar rolling based on Bayesian hierarchical modeling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26, 785–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0834-y
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. LMaching Learning, 20, 273. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Cui, C., Cao, G., Li, X., Gao, Z., Liu, J., & Liu, Z. (2023). A strategy combining machine learning and physical metallurgical principles to predict mechanical properties for hot rolled Ti micro-alloyed steels. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 311, 117810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117810
Deng, G. Y., Tieu, A. K., Si, L. Y., Su, L. H., Lu, C., Wang, H., Liu, M., Zhu, H. T., & Liu, X. H. (2014). Influence of cold rolling reduction on the deformation behavior and crystallographic orientation development. Computational Materials Science, 81, 2–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.06.054
Deng, G., Tieu, A. K., Su, L. H., Zhu, H. T., Reid, M., Zhu, Q., & Kong, C. (2019a). Microstructural study and residual stress measurement of a hot rolling work roll material during isothermal oxidation. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 102, 2107–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03305-0
Deng, G., Tieu, A. K., Su, L. H., Zhu, H. T., Zhu, Q., Zamri, W. F. H., & Kong, C. (2019b). Characterizing deformation behavior of an oxidized high speed steel: Effects of nanoindentation depth, friction and oxide scale porosity. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 155, 267–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.02.043
Deng, G. Y., Zhu, H. T., Tieu, A. K., Su, L. H., Reid, M., Zhang, L., Wei, P. T., Zhao, X., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Li, J. T., Ta, T. D., Zhu, Q., Kong, C., & Wu, Q. (2017a). Theoretical and experimental investigation of thermal and oxidation behaviours of a high speed steel work roll during hot rolling. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 131–132, 811–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.08.024
Deng, G., Zhu, Q., Tieu, K., Zhu, H. T., Reid, M., Saleh, A. A., Su, L. H., Ta, T. D., Zhang, J., Lu, C., Wu, Q., & Sun, D. L. (2017b). Evolution of microstructure, temperature and stress in a high speed steel work roll during hot rolling: Experiment and modelling. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 240, 200–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.09.025
Ding, Y., Cheng, L., Pedrycz, W., & Hao, K. (2017). Global nonlinear kernel prediction for large data set with a particle swarm-optimized interval support vector regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 26, 2521–2534. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2426182
Feng, F. Z., Zhu, D. D., Jiang, P. C., & Jiang, H. (2009). Ga-SVR based bearing condition degradation prediction. Key Engineering Materials, 413–414, 431–437. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.413-414.431
Fu, L., Xiao, H., Yu, C., Lv, Q., Zhang, S., & Xie, H. (2022). Bonding enhancement of cold rolling Al/steel composite plates via self-nano film modification. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 300, 117427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117427
Galdos, F., Mendiguren, J., & de Argando, S. (2014). Testing and modeling of roll leveling process. Key Engineering Materials, 611–612, 1753–1762. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.611-612.1753
Gao, S. F., Liu, H. F., Xi, A. M., & Yang, X. (2016). Closed-loop control strategy of segmented cooling in hot rolling of aluminum alloys. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 52, 207–212. https://doi.org/10.3901/JME.2016.08.207
Guo, R. (1996). Optimal profile and shape control of flat sheet metal using multiple control devices. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 32, 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1109/28.491496
Jiang, M., Li, X., Wu, J., & Wang, G. (2014). A precision on-line model for the prediction of thermal crown in hot rolling processes. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 78, 967–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.07.061
Lei, X., & Ouyang, H. (2021). Kernel-based intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation based on grey wolf optimizer with differential mutation. IEEE Access, 2021(9), 85455–85463. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070044
Li, D. C., Fang, Y. H., Liu, C. W., & Juang, C. J. (2012). Using past manufacturing experience to assist building the yield forecast model for new manufacturing processes. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23, 857–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-010-0442-z
Li, J., Cao, L., Hu, J., Sheng, M., Zhou, Q., & Jin, P. (2020). A prediction approach of SLM based on the ensemble of metamodels considering material efficiency, energy consumption, and tensile strength. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 33, 687–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01665-z
Mathieu, N., Potier-Ferry, M., & Zahrouni, H. (2017). Reduction of flatness defects in thin metal sheets by a pure tension leveler. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 122, 267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.01.036
Mohamed, M. A. M., Hasanien, H. M., & Alkuhayli, A. (2020). A novel hybrid GWO-PSO optimization technique for optimal reactive power dispatch problem solution. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 12, 621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.07.011
Najm, S. M., & Paniti, I. (2021a). Artificial neural network for modeling and investigating the effects of forming tool characteristics on the accuracy and formability of thin aluminum alloy blanks when using SPIF. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 114, 2591–2615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-021-06712-4
Najm, S. M., & Paniti, I. (2021b). Predict the effects of forming tool characteristics on surface roughness of aluminum foil components formed by SPIF using ANN and SVR. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 22, 13–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-020-00434-5
Najm, S. M., & Paniti, I. (2023). Investigation and machine learning-based prediction of parametric effects of single point incremental forming on pillow effect and wall profile of AlMn1Mg1 aluminum alloy sheet. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 34, 331–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-022-02026-8
Najm, S. M., Paniti, I., Trzepiecinski, T., Nama, S. A., Viharos, Z. J., & Jacso, A. (2021). Parametric effects of single point incremental forming on hardness of AA1100 aluminium alloy sheets. Materials, 14, 7263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237263
Najm, S. M., Trzepiecinski, T., & Kowalik, M. (2023). Modelling and parameter identifcation of coefcient of friction for deep-drawing quality steel sheets using the CatBoost machine learning algorithm and neural networks. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 124, 2229–2259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10544-1
Nie, N., Su, L., Deng, G., Li, H., Yu, H., & Tieu, A. K. (2021). A review on plastic deformation induced surface/interface roughening of sheet metallic materials. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 15, 6574–6607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.11.087
Park, C. M., Choi, J. T., Moon, H. K., & Park, G. J. (2009). Thermal crown analysis of the roll in the strip casting process. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209, 3714–3723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.08.029
Pin, G., Francesconi, V., Cuzzola, F. A., & Parisini, T. (2013). Adaptive task-space metal strip-flatness control in cold multi-roll mill stands. Journal of Process Control, 23, 108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2012.08.008
Shao, J., Yao, C., & He, W. (2015). Setup system of selective roll cooling based on profile prediction in aluminum hot strip mill. Manufacturing Technology, 15, 204–209.
Shen, X. T., Gong, X. Y., Cai, Y. P., Guo, Y., Tu, J., Li, H., Zhang, T., Wang, J., Xue, F., & Zhu, Z. J. (2016). Normalization and integration of large-scale metabolomics data using support vector regression. Metabolomics, 12, 89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-016-1026-5
Sm, A., Smm, B., & Al, A. (2014). Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 69, 46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Song, C. N., Cao, J. G., Wang, L. L., Xiao, J., & Zhao, Q. F. (2022). The prediction model for transverse thickness difference of electric steel in 6-high cold rolling mills based on GA-PSO-SVR approach. Steel Research International, 93, 2200302. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202200302
Su, L., Lu, C., Deng, G., & Tieu, A. K. (2014). Microstructure and mechanical properties of AA5005/AA6061 laminated composite processed by accumulative roll bonding. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 45, 515–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9869-x
Su, L., Lu, C., Deng, G., Tieu, A. K., Li, J. T., Zhu, H. T., Li, H. J., & Sun, X. D. (2013a). Investigation of deformation behavior during cold rolling cladding process of four-layer composite aluminium alloys. Advanced Materials Research, 651, 424–429. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.651.424
Su, L., Lu, C., Deng, G., Tieu, A. K., & Sun, X. D. (2013b). Microstructure and mechanical properties of 1050/6061 laminated composite processed by accumulative roll bonding. Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 33, 33–37.
Su, L., Lu, C., Tieu, K., & Deng, G. (2013c). Annealing behavior of accumulative roll bonding processed aluminum composites. Steel Research International, 84, 1241–1245. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201300032
Trzepiecinski, T., & Najm, S. M. (2022). Application of artificial neural networks to the analysis of friction behaviour in a drawbead profile in sheet metal forming. Materials, 15, 9022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15249022
Vapnik, V. (1998). Statistical learning theory. Wiley, Interscience
Wang, W., Wei, P., Liu, H., Zhu, C., Deng, G., & Liu, H. (2023). A micromechanics-based machine learning model for evaluating the microstructure-dependent rolling contact fatigue performance of a martensitic steel. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 237, 107784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107784
Wang, Z. H., Liu, Y. M., Gong, D. G., & Zhang, D. H. (2018). A new predictive model for strip crown in hot rolling by using the hybrid AMPSO-SVR-based approach. Steel Research International, 89, 1800003. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201800003
Wu, Z. Q., Tang, Y. C., Xiao, X. F., & Yu, J. P. (2013). Adaptive fuzzy backstepping control for hydraulic roll-gap system of a cold rolling mill. Zhendong Yu Chongji/Journal of Vibration and Shock, 32, 146–151.
Xia, C., Pan, Z., Polden, J., Li, H., Xu, Y., & Chen, S. (2022). Modelling and prediction of surface roughness in wire arc additive manufacturing using machine learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 33, 1467–1482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01725-4
Yi, Y., Wang, L., & Chen, Z. (2021). Adaptive global kernel interval SVR-based machine learning for accelerated dielectric constant prediction of polymer-based dielectric energy storage. Renewable Energy, 176, 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.05.045
Yu, W. A., Cl, A., Lp, A., Ra, A., & Xin, J. B. (2021). Application of convolutional neural networks for prediction of strip flatness in tandem cold rolling process. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 68, 512–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.062
Zhang, H., Chen, L., Qu, Y., Zhao, G., & Guo, Z. W. (2014). Support vector regression based on grid-search method for short-term wind power forecasting. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2014, 835791. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/835791
Zhang, L., Qian, K., Huang, J., Liu, M., & Shibuta, Y. (2021). Molecular dynamics simulation and machine learning of mechanical response in non-equiatomic FeCrNiCoMn high-entropy alloy. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 13, 2043–2054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.021
Acknowledgements
This project is funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52074242 and No. U20A20187), Central Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Special Fund Project (Grant No. 216Z1602G), Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No. E2020203068), the open fund of the State Key Laboratory of Rolling and Automation (No. 2022RALKFKT001), and Liao Ning Revitalization Talents Program of Liao Ning Province (No. XLYC2007087). L.S. is very grateful for the support from the Australian Research Council (ARC) through Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DECRA) fellowship (No. DE180100124). G.D. would like to acknowledge the support from the University of Queensland (UQ) for awarding him the UQ Research Stimulus Allocation Fellowship.
Funding
This study was funded by Australian Research Council, DE180100124, Lihong Su, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 52074242, Pengfei Wang, Grant No. U20A20187, Pengfei Wang, Central Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Special Fund Project, Grant No. 216Z1602G, Pengfei Wang, Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, No. E2020203068, Pengfei Wang, E2020203068, Pengfei Wang, the open fund of the State Key Laboratory of Rolling and Automation, No. 2022RALKFKT001, Pengfei Wang, Liao Ning Revitalization Talents Program of Liao Ning Province, No. XLYC2007087, Xu Li.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing—review & editing. JD: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation. XL: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing—review & editing. CH: Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Resources. LS: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing—review & editing. GD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Deng, J., Li, X. et al. A novel strategy based on machine learning of selective cooling control of work roll for improvement of cold rolled strip flatness. J Intell Manuf (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-023-02204-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-023-02204-2