Abstract
Purpose
Cardiac sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by ventricular arrhythmias. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is used to prevent sudden cardiac death.
Methods
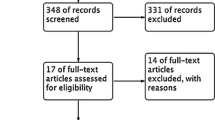
We performed literature search for studies that addressed the outcome and complications of ICD in Cardiac Sarcoidosis (CS). Multiple search sites were reviewed from January 1, 2000 until December 1, 2018. We then performed a meta-analysis using a random effects model. Two investigators independently extracted the data and assessed studies’ quality.
Results
Ten studies with 585 patients qualified for the analysis. In the pooled analysis, 57% were male with mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 38.4%. Appropriate and inappropriate ICD treatments (AT and IAT) were reported in 39% and 15% of patients respectively over mean follow-up period of 25 months and mortality rate of 8%. A sub-analysis of four studies indicated that patients with appropriate therapy did not differ from the rest of CS population in LVEF% (mean difference (MD) = − 7.37%, 95% confidence interval (CI) − 16.89 to 2.15, p = 0.12), age (MD = − 3.87 years, 95% CI − 10.19 to 2.46, p = 0.23), primary prevention (range difference (RD) = − 0.11, 95% CI − 0.31 to 0.10, p = 0.31) or secondary prevention indication (RD = 0.09, 95% CI − 0.12 to 0.3, p = 0.37). High degree AV block was more common in patients with AT (RD = 0.07, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.14 p = 0.05).
Conclusions
ICD placement in CS is associated with high incidence of both appropriate and inappropriate therapy. High degree AV block appears to be predictive of appropriate ICD therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT:
-
Appropriate treatment
- IAT:
-
Inappropriate treatment
- VT:
-
Ventricular tachycardia
- F/U:
-
Follow-up
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- AAD:
-
Anti-arrhythmia drugs
- ACCESS:
-
A Case Control Etiologic Study of Sarcoidosis
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- CHB:
-
Complete heart block
- NR:
-
Not reported
- JMHW:
-
Japanese Ministry of Health and Welfare Criteria
- VT/VFib:
-
Ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation
- RTS:
-
Retrospective study
References
Hulten E, Aslam S, Osborne M, Abbasi S, Bittencourt MS, Blankstein R. Cardiac sarcoidosis-state of the art review. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016;6(1):50–63.
Heck PM, Roberts PR. The role of implantable cardiac defibrillators in cardiac sarcoidosis: saviour or sinner? Europace. 2013;15(3):309–10.
Rosenthal DG, Bravo PE, Patton KK, Goldberger ZD. Management of Arrhythmias in cardiac Sarcoidosis. Clin Cardiol. 2015;38(10):635–40.
Banba K, Kusano KF, Nakamura K, Morita H, Ogawa A, Ohtsuka F, et al. Relationship between arrhythmogenesis and disease activity in cardiac sarcoidosis. Heart Rhythm. 2007;4(10):1292–9.
Betensky BP, Tschabrunn CM, Zado ES, Goldberg LR, Marchlinski FE, Garcia FC, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with cardiac sarcoidosis and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Heart Rhythm. 2012 Jun;9(6):884–91.
Yazaki Y, Isobe M, Hiroe M, Morimoto SI, Hiramitsu S, Nakano T, et al. Prognostic determinants of long-term survival in Japanese patients with cardiac sarcoidosis treated with prednisone. Am J Cardiol. 2001;88(9):1006–10.
Fussner LA, Karlstedt E, Hodge DO, Fine NM, Kalra S, Carmona EM, et al. Management and outcomes of cardiac sarcoidosis: a 20-year experience in two tertiary care centres. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20(12):1713–20.
Louise A, Lin Y-J, Chen Y-Y, Chung F-P, Chang S-L, Lo L-W, et al. Increased risk of ventricular tachycardia in patients with sarcoidosis during the very long term follow-up. Int J Cardiol. 2017;228:68–73.
Salama A, Abdullah A, Wahab A, Eigbire G, Hoefen R, Alweis R. Cardiac sarcoidosis and ventricular arrhythmias. A rare association of a rare disease. A retrospective cohort study from the National Inpatient Sample and current evidence for management. Cardiol J. 2018;1(1897):5593.
Al-Khatib SM, Stevenson WG, Ackerman MJ, Bryant WJ, Callans DJ, Curtis AB, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: executive summary. Circulation. 2018;138(13):e210–71.
Birnie DH, Sauer WH, Bogun F, Cooper JM, Culver DA, Duvernoy CS, et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Hear Rhythm. 2014;11(7):1305–23.
Schuller JL, Zipse M, Crawford T, Bogun F, Beshai J, Patel AR, et al. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012;23(9):925–9.
Mohsen A, Jimenez A, Hood RE, Dickfeld T, Saliaris A, Shorofsky S, et al. Cardiac sarcoidosis: electrophysiological outcomes on long-term follow-up and the role of the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2014;25(2):171–6.
Takaya Y, Kusano K, Nishii N, Nakamura K, Ito H. Early and frequent defibrillator discharge in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis compared with patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2017;240:302–6.
Bandyopadhyay D, Sahoo D, Zein J, Brunken RC, Tchou PJ, Culver DA. Outcome of cardiac sarcoidosis after radiofrequency ablation and placement of AICD- a propensity matched analysis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffus Lung Dis. 2015;32(1):70–9.
Aizer A, Stern EH, Gomes JA, Teirstein AS, Eckart RE, Mehta D. Usefulness of programmed ventricular stimulation in predicting future arrhythmic events in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(2):276–82.
Kron J, Sauer W, Schuller J, Bogun F, Crawford T, Sarsam S, et al. Efficacy and safety of implantable cardiac defibrillators for treatment of ventricular arrhythmias in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis. Europace. 2013;15(3):347–54.
Mehta D, Mori N, Goldbarg SH, Lubitz S, Wisnivesky JP, Teirstein A. Primary prevention of sudden cardiac death in silent cardiac sarcoidosis role of programmed ventricular stimulation. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2011;4(1):43–8.
Watanabe H, Chinushi M, Izumi D, Sato A, Okada S, Okamura K, et al. Decrease in amplitude of intracardiac ventricular electrogram and inappropriate therapy in patients with an implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Int Heart J. 2006;47:363–70.
Nakano M, Kondo Y, Nakano M, Miyazawa K, Hayashi T KY. Prognosis of cardiac sarcoidosis in patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillator-primary versus secondary prevention. In: Sudden cardiac death and implantable defibrillator [internet]. EP Europace, volume 19, issue suppl_3, 1 June 2017, pages iii301; 2017. p. Pages iii301. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/eux158.105.
Higgins JPT GS. Cochrane handbookfor systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [Internet]. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. Available from: www.handbook.cochran.org
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ Br Med J. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa Hosp Res Inst. 2013;3:1–4.
Viechtbauer W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw [Internet]. 2010;36(3). Available from: https://www.jstatsoft.org/v036/i03
Vaseghi M, Hu TY, Tung R, Vergara P, Frankel DS, Di Biase L, et al. Outcomes of catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia based on etiology in nonischemic heart disease. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4(9):1141–50.
Køber L, Thune JJ, Nielsen JC, Haarbo J, Videbæk L, Korup E, et al. Defibrillator implantation in patients with nonischemic systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(13):1221–30.
Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB, Poole JE, Packer DL, Boineau R, et al. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter–defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(3):225–37.
Greulich S, Deluigi CC, Gloekler S, Wahl A, Zürn C, Kramer U, et al. CMR imaging predicts death and other adverse events in suspected cardiac sarcoidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6(4):501–11.
Lin G, Dispenzieri A, Brady PA. Successful termination of a ventricular arrhythmia by implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in a patient with cardiac amyloidosis: insight into mechanisms of sudden death. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(12):1538.
Yodogawa K, Seino Y, Ohara T, Takayama H, Katoh T, Mizuno K. Effect of corticosteroid therapy on ventricular arrhythmias in patients with cardiac Sarcoidosis. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2011;16(2):140–7.
Sohail MR, Uslan DZ, Khan AH, Friedman PA, Hayes DL, Wilson WR, et al. Risk factor analysis of permanent pacemaker infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(2):166–73.
Kandolin R, Lehtonen J, Airaksinen J, Vihinen T. Cardiac sarcoidosis: epidemiology, characteristics, and outcome over 25 years in a nationwide study. Circulation. 2015;17(131):624–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 214 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halawa, A., Jain, R., Turagam, M.K. et al. Outcome of implantable cardioverter defibrillator in cardiac sarcoidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 58, 233–242 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00705-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-020-00705-1