Abstract
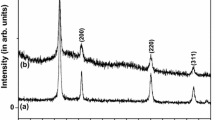
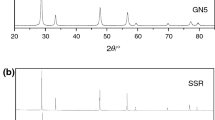
Nanosized powders of cerium dioxide with controlled physical properties were prepared by the precipitation technique using ammonium hydroxide or oxalic acid as precipitating agent. The calcined precursors were studied by nitrogen adsorption to determine the specific surface area, X-ray diffraction for phase characterization and crystallite size determination, and by laser scattering for particle size distribution. The morphology of powder particles was observed by scanning electron microscopy. It is shown that both precipitating materials may be used for the preparation of nanocrystalline powders (< 10 nm) with high values of specific surface area (> 90 m2 ⋅ g− 1). The observed differences between powders prepared from hydroxides or oxalates rely on the distribution of particle sizes and in the morphology of the agglomerated particles. Impedance spectroscopy experiments were carried out in the 5 Hz–13 MHz frequency range under controlled partial pressure of oxygen from 10 ppm to 1 atm. The analysis of these results allowed for the determination of the charge carriers responsible for the electrical transport in the ceria sintered pellets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Trovarelli, Catal. Rev.-Sci. Eng. 38, 439 (1996).
H. Inaba and H. Tagawa, Solid State Ionics 83, 1 (1996).
T. Tsuzuki and P.G. McCormick, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 1453 (2001).
N.B. Kirk and J.V. Wood, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 2171 (1995).
P.-L. Chen and I.-W. Chen, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 1577 (1993).
Y.C. Zhou, and M.N. Rahaman, J. Mater. Res. 8, 1680 (1993).
R.D. Purohit, B.P. Sharma, K.T. Pillai, and A.K. Tyagi, Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2711 (2001).
B. Xia, I.W. Lenggoro, and K. Okuyama, J. Mater. Chem. 11, 2925 (2001).
Y.-M. Chiang, E.B. Lavik, I. Kosacki, H.L. Tuller, and J.Y. Ying, J. Electroceram. 1, 7 (1997).
S.K. Tadokoro and E.N.S. Muccillo, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 22, 1723 (2002).
S.K. Tadokoro and E.N.S. Muccillo, J. Alloys Compounds 344, 186 (2002).
R.N. Blumenthal, F.S. Brugner, and J.E. Garnier, J. Electrochem. Soc. 120, 1230 (1973).
H.L. Tuller and A.S. Nowick, J. Electrochem. Soc. 122, 255 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muccillo, E.N.S., Rocha, R.A., Tadokoro, S.K. et al. Electrical Conductivity of CeO2 Prepared from Nanosized Powders. J Electroceram 13, 609–612 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5166-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-004-5166-z