Abstract
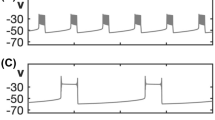
Using two-cell and 50-cell networks of square-wave bursters, we studied how excitatory coupling of individual neurons affects the bursting output of the network. Our results show that the effects of synaptic excitation vs. electrical coupling are distinct. Increasing excitatory synaptic coupling generally increases burst duration. Electrical coupling also increases burst duration for low to moderate values, but at sufficiently strong values promotes a switch to highly synchronous bursts where further increases in electrical or synaptic coupling have a minimal effect on burst duration. These effects are largely mediated by spike synchrony, which is determined by the stability of the in-phase spiking solution during the burst. Even when both coupling mechanisms are strong, one form (in-phase or anti-phase) of spike synchrony will determine the burst dynamics, resulting in a sharp boundary in the space of the coupling parameters. This boundary exists in both two cell and network simulations. We use these results to interpret the effects of gap-junction blockers on the neuronal circuitry that underlies respiration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertram, R., Butte, M. J., Kiemel, T., & Sherman, A. (1995). Topological and phenomenological classification of bursting oscillations. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 57, 413–439.
Best, J., Borisyuk, A., Rubin, J., Terman, D., & Wechselberger, M. (2005). The dynamic range of bursting in a model respiratory pacemaker network. SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, 4, 1107–1139.
Bou-Flores, C., & Berger, A. J. (2001). Gap junctions and inhibitory synapses modulate inspiratory motoneuron synchronization. Journal of Neurophysiology, 85, 1543–1551.
Butera, R. J., Jr., Rinzel, J., & Smith, J. C. (1999). Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Botzinger complex. I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 82, 382–397.
De Vries, G., Sherman, A., & Zhu, H. R. (1998). Diffusively coupled bursters: effects of cell heterogeneity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 60, 1167–1200.
Ermentrout, B. (2002). Simulating, analyzing, and animating dynamical systems: a guide to XPPAUT for researchers and students. Philadelphia: SIAM.
Hines, M. L., & Carnevale, N. T. (1997). The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Computation, 9, 1179–1209.
Izhikevich, E. M. (2000). Neural excitability, spiking, and bursting. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 10, 1171–1266.
Komendantov, A. O., & Canavier, C. C. (2002). Electrical coupling between model midbrain dopamine neurons: effects on firing pattern and synchrony. Journal of Neurophysiology, 87, 1526–1541.
Purvis, L. K., Smith, J. C., Koizumi, H., & Butera, R. J. (2007). Intrinsic bursters increase the robustness of rhythm generation in an excitatory network. Journal of Neurophysiology, 97, 1515–1526.
Rinzel, J. (1985). Bursting oscillations in an excitable membrane model. In B. D. Sleeman & R. J. Jarvis (Eds.), Lecture notes in mathematics, vol. 1151 (pp. 304–316). Berlin: Springer.
Sherman, A. (1994). Anti-phase, asymmetric and aperiodic oscillations in excitable cells–I. Coupled bursters. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 56, 811–835.
Sherman, A., & Rinzel, J. (1991). Model for synchronization of pancreatic beta-cells by gap junction coupling. Biophysical Journal, 59, 547–559.
Sherman, A., & Rinzel, J. (1992). Rhythmogenic effects of weak electrotonic coupling in neuronal models. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 89, 2471–2474.
Solomon, I. C., Chon, K. H., & Rodriguez, M. N. (2003). Blockade of brain stem gap junctions increases phrenic burst frequency and reduces phrenic burst synchronization in adult rat. Journal of Neurophysiology, 89, 135–149.
Wright, T. M., & Butera, R. J. (2006a). Effects of electrical coupling on excitatory coupled pacemaker neurons in the pre-Botzinger complex. Proceedings of 15th Annual Computational Neuroscience Meeting (CNS 2006), July 16–20, 2006. Scotland: Edinburgh.
Wright, T. M., & Butera, R. J. (2006b) Modeling study of the dynamical effects of electrical coupling on pre-Botzinger complex neurons. Program No 63522006, Society for Neuroscience
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01-HL088886) and the National Science Foundation IGERT Program (DGE-0333411). M. Wright acknowledges A. Olypher for help with Matlab analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: Frances K. Skinner
Natalia Toporikova and Tzu-Hsin Tsao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toporikova, N., Tsao, TH., Wright, T.M. et al. Conflicting effects of excitatory synaptic and electric coupling on the dynamics of square-wave bursters. J Comput Neurosci 31, 701–711 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-011-0340-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-011-0340-1