Abstract
Purpose
Can small RNA derived from embryos in conditioned embryo culture medium (ECM) influence embryo implantation?
Methods
We employed small RNA sequencing to investigate the expression profiles of transfer RNA-derived small RNA (tsRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) in ECM from high-quality and low-quality embryos. Quantitative real-time PCR was employed to validate the findings of small RNA sequencing. Additionally, we conducted bioinformatics analysis to predict the potential functions of these small RNAs in embryo implantation. To establish the role of tiRNA-1:35-Leu-TAG-2 in embryonic trophoblast cell adhesion, we utilized co-culture systems involving JAR and Ishikawa cells.
Results
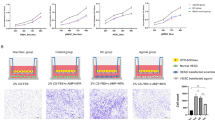
Our analysis revealed upregulation of nine tsRNAs and four miRNAs in ECM derived from high-quality embryos, whereas 37 tsRNAs and 12 miRNAs exhibited upregulation in ECM from low-quality embryos. The bioinformatics analysis of tsRNA, miRNA, and mRNA pathways indicated that their respective target genes may play pivotal roles in both embryo development and endometrial receptivity. Utilizing tiRNA mimics, we demonstrated that the prominently expressed tiRNA-1:35-Leu-TAG-2 in the low-quality ECM group can be internalized by Ishikawa cells. Notably, transfection of tiRNA-1:35-Leu-TAG-2 into Ishikawa cells reduced the attachment rate of JAR spheroids.
Conclusion
Our investigation uncovers significant variation in the expression profiles of tsRNAs and miRNAs between ECM derived from high- and low-quality embryos. Intriguingly, the release of tiRNA-1:35-Leu-TAG-2 by low-quality embryos detrimentally affects embryo implantation and endometrial receptivity. These findings provide fresh insights into understanding the molecular foundations of embryo-endometrial communication.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Additional data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Brosens JJ, Salker MS, Teklenburg G, Nautiyal J, Salter S, Lucas ES, Steel JH, Christian M, Chan YW, Boomsma CM, et al. Uterine selection of human embryos at implantation. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3894.
Cimadomo D, Capalbo A, Ubaldi FM, Scarica C, Palagiano A, Canipari R, Rienzi L. The impact of biopsy on human embryo developmental potential during preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:7193075.
Leaver M, Wells D. Non-invasive preimplantation genetic testing (niPGT): the next revolution in reproductive genetics? Hum Reprod Update. 2020;26:16–42.
Rubio C, Rodrigo L, Garcia-Pascual C, Peinado V, Campos-Galindo I, Garcia-Herrero S, Simon C. Clinical application of embryo aneuploidy testing by next-generation sequencing. Biol Reprod. 2019;101:1083–90.
Zhou W, Dimitriadis E. Secreted MicroRNA to predict embryo implantation outcome: from research to clinical diagnostic application. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:586510.
Fang F, Li Z, Yu J, Long Y, Zhao Q, Ding X, Wu L, Shao S, Zhang L, Xiang W. MicroRNAs secreted by human embryos could be potential biomarkers for clinical outcomes of assisted reproductive technology. J Adv Res. 2021;31:25–34.
Abu-Halima M, Khaizaran ZA, Ayesh BM, Fischer U, Khaizaran SA, Al-Battah F, Hammadeh M, Keller A, Meese E. MicroRNAs in combined spent culture media and sperm are associated with embryo quality and pregnancy outcome. Fertil Steril. 2020;113(970–980):e972.
Berkhout RP, Keijser R, Repping S, Lambalk CB, Afink GB, Mastenbroek S, Hamer G. High-quality human preimplantation embryos stimulate endometrial stromal cell migration via secretion of microRNA hsa-miR-320a. Hum Reprod. 2020;35:1797–807.
Russell SJ, Menezes K, Balakier H, Librach C. Comprehensive profiling of small RNAs in human embryo-conditioned culture media by improved sequencing and quantitative PCR methods. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2020;66:129–39.
Kirkegaard K, Yan Y, Sørensen BS, Hardarson T, Hanson C, Ingerslev HJ, Knudsen UB, Kjems J, Lundin K, Ahlström A. Comprehensive analysis of soluble RNAs in human embryo culture media and blastocoel fluid. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020;37:2199–209.
Huang P, Tu B, Liao HJ, Huang FZ, Li ZZ, Zhu KY, Dai F, Liu HZ, Zhang TY, Sun CZ. Elevation of plasma tRNA fragments as a promising biomarker for liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2021;11:5886.
Tosar JP, Cayota A. Extracellular tRNAs and tRNA-derived fragments. RNA Biol. 2020;17:1149–67.
Tosar JP, Segovia M, Castellano M, Gambaro F, Akiyama Y, Fagundez P, Olivera A, Costa B, Possi T, Hill M, et al. Fragmentation of extracellular ribosomes and tRNAs shapes the extracellular RNAome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:12874–88.
Ivanov P, O’Day E, Emara MM, Wagner G, Lieberman J, Anderson P. G-quadruplex structures contribute to the neuroprotective effects of angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:18201–6.
Martinez G. tRNA-derived small RNAs: new players in genome protection against retrotransposons. RNA Biol. 2018;15:170–5.
Buck VU, Kohlen MT, Sternberg AK, Rosing B, Neulen J, Leube RE, Classen-Linke I. Steroid hormones and human choriogonadotropin influence the distribution of alpha6-integrin and desmoplakin 1 in gland-like endometrial epithelial spheroids. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021;155:581–91.
DeVeale B, Liu L, Boileau R, Swindlehurst-Chan J, Marsh B, Freimer JW, Abate A, Blelloch R. G1/S restriction point coordinates phasic gene expression and cell differentiation. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3696.
Wade SL, Langer LF, Ward JM, Archer TK. MiRNA-mediated regulation of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex controls pluripotency and endodermal differentiation in human ESCs. Stem Cells. 2015;33:2925–35.
Dong X, Sui C, Huang K, Wang L, Hu D, Xiong T, Wang R, Zhang H. MicroRNA-223-3p suppresses leukemia inhibitory factor expression and pinopodes formation during embryo implantation in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):1155–63.
Jing MY, Xie LD, Chen X, Zhou Y, Jin MM, He WH, Wang DM, Liu AX. Circ-CCNB1 modulates trophoblast proliferation and invasion in spontaneous abortion by regulating miR-223/SIAH1 axis. Endocrinology. 2022;163:8.
Nechooshtan G, Yunusov D, Chang K, Gingeras TR. Processing by RNase 1 forms tRNA halves and distinct Y RNA fragments in the extracellular environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:8035–49.
Li X, Liu X, Zhao D, Cui W, Wu Y, Zhang C, Duan C. tRNA-derived small RNAs: novel regulators of cancer hallmarks and targets of clinical application. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:249.
Yu M, Lu B, Zhang J, Ding J, Liu P, Lu Y. tRNA-derived RNA fragments in cancer: current status and future perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:121.
Ivanov P, Emara MM, Villen J, Gygi SP, Anderson P. Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol Cell. 2011;43:613–23.
Kim HK, Fuchs G, Wang S, Wei W, Zhang Y, Park H, Roy-Chaudhuri B, Li P, Xu J, Chu K, et al. A transfer-RNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 2017;552:57–62.
Koera K, Nakamura K, Nakao K, Miyoshi J, Toyoshima K, Hatta T, Otani H, Aiba A, Katsuki M. K-ras is essential for the development of the mouse embryo. Oncogene. 1997;15(10):1151–9.
Liu J, Zhou Y, Tong L, Wang X, Li Y, Wang H. Developmental potential of different embryos on day 3: a retrospective study. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;42:3322–7.
Liu S, Cui H, Li Q, Zhang L, Na Q, Liu C. RhoGDI2 is expressed in human trophoblasts and involved in their migration by inhibiting the activation of RAC1. Biol Reprod. 2014;90:88.
Tu Z, Wang Q, Cui T, Wang J, Ran H, Bao H, Lu J, Wang B, Lydon JP, DeMayo F, et al. Uterine RAC1 via Pak1-ERM signaling directs normal luminal epithelial integrity conducive to on-time embryo implantation in mice. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:169–81.
Du ZQ, Liang H, Liu XM, Liu YH, Wang C, Yang CX. Single cell RNA-seq reveals genes vital to in vitro fertilized embryos and parthenotes in pigs. Sci Rep. 2021;11:14393.
Kaneko Y, Lecce L, Day ML, Murphy CR. Focal adhesion kinase localizes to sites of cell-to-cell contact in vivo and increases apically in rat uterine luminal epithelium and the blastocyst at the time of implantation. J Morphol. 2012;273:639–50.
Harden SL, Zhou J, Gharanei S, Diniz-da-Costa M, Lucas ES, Cui L, Murakami K, Fang J, Chen Q, Brosens JJ, Lee YH. Exometabolomic analysis of decidualizing human endometrial stromal and perivascular cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:626619.
Paule S, Nebl T, Webb AI, Vollenhoven B, Rombauts LJ, Nie G. Proprotein convertase 5/6 cleaves platelet-derived growth factor A in the human endometrium in preparation for embryo implantation. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015;21:262–70.
Purnell ET, Warner CM, Kort HI, Mitchell-Leef D, Elsner CW, Shapiro DB, Massey JB, Roudebush WE. Influence of the preimplantation embryo development (Ped) gene on embryonic platelet-activating factor (PAF) levels. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2006;23:269–73.
Stepanjuk A, Koel M, Pook M, Saare M, Jaager K, Peters M, Krjutskov K, Ingerpuu S, Salumets A. MUC20 expression marks the receptive phase of the human endometrium. Reprod Biomed Online. 2019;39:725–36.
Moharrami T, Ai J, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Nouri M, Ziadi M, Pashaiefar H, Yazarlou F, Ahmadvand M, Najafi S, Modarressi MH. Influence of follicular fluid and seminal plasma on the expression of endometrial receptivity genes in endometrial cells. Cell J. 2021;22:457–66.
Elnaggar A, Farag AH, Gaber ME, Hafeez MA, Ali MS, Atef AM. AlphaVBeta3 integrin expression within uterine endometrium in unexplained infertility: a prospective cohort study. BMC Womens Health. 2017;17:90.
Jiang C, Gong W, Chen R, Ke H, Qu X, Yang W, Cheng Z. RhoA/ROCK/ARHGAP26 signaling in the eutopic and ectopic endometrium is involved in clinical characteristics of adenomyosis. J Int Med Res. 2018;46:5019–29.
Pfendler KC, Yoon J, Taborn GU, Kuehn MR, Iannaccone PM. Nodal and bone morphogenetic protein 5 interact in murine mesoderm formation and implantation. Genesis. 2000;28(1):1–14.
Acknowledgements
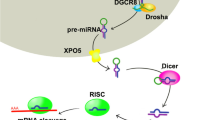
We thank Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) for expert assistance in the pattern drawing.
Funding
This work is supported by the Scientific Research Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission (No. WJ2021M162), the Innovation and Cultivation Fund of Zhongnan Hospital (No. CXPY2022010), and the Basic and Clinical Medical Research Joint Fund of Zhongnan Hospital, Wuhan University (No. ZNLH202206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed the study and edited the final text: Yao Xiong, Ling Ma. Performed the experiments: Lei Shi, Zihan Wang, Zhidan Hong, Yanhong Mao. Wrote the manuscript and prepared the figures: Ling Ma, Ming Zhang. Contributed to manuscript revision and critical discussion: Ma Ling, Chun Zhou, Yao Xiong.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yao Xiong and Lei Shi were the co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10815_2024_3034_MOESM1_ESM.tif
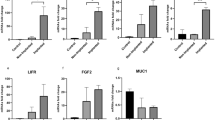
Supplementary file1 RT-qPCR validation of miRNAs. qRT-PCR validation of miR-302 and miR-223 family members’ expression in high- and low-quality embryo culture medium compared to control medium. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (TIF 5111 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, Y., Shi, L., Zhang, M. et al. Differential expression of tsRNAs and miRNAs in embryo culture medium: potential impact on embryo implantation. J Assist Reprod Genet 41, 781–793 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-024-03034-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-024-03034-8