Abstract
Purpose
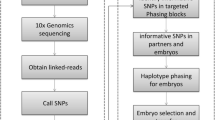
This study aimed to evaluate the value of long-read sequencing for preimplantation haplotype linkage analysis.
Methods
The genetic material of the three β-thalassemia mutation carrier couples was sequenced using single-molecule real-time sequencing in the 7.7-kb region of the HBB gene and a 7.4-kb region that partially overlapped with it to detect the presence of 17 common HBB gene mutations in the Chinese population and the haplotypes formed by the continuous array of single-nucleotide polymorphisms linked to these mutations. By using the same method to analyze multiple displacement amplification products of embryos from three families and comparing the results with those of the parents, it could be revealed whether the embryos carry disease-causing mutations without the need for a proband.
Results
The HBB gene mutations of the three couples were accurately detected, and the haplotype linked to the pathogenic site was successfully obtained without the need for a proband. A total of 68.75% (22/32) of embryos from the three families successfully underwent haplotype linkage analysis, and the results were consistent with the results of NGS-based mutation site detection.
Conclusion
This study supports long-read sequencing as a potential tool for preimplantation haplotype linkage analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lai K, Huang G, Su L, He Y. The prevalence of thalassemia in mainland China: evidence from epidemiological surveys. Sci Rep. 2017;7:920.
Mettananda S, Higgs DR. Molecular basis and genetic modifiers of thalassemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018;32:177–91.
Origa R. β-Thalassemia. Genet Med. 2017;19:609–19.
Natesan SA, Bladon AJ, Coskun S, Qubbaj W, Prates R, Munne S, et al. Genome-wide karyomapping accurately identifies the inheritance of single-gene defects in human preimplantation embryos in vitro. Genet Med. 2014;16:838–45.
Sachidanandam R, Weissman D, Schmidt SC, Kakol JM, Stein LD, Marth G, et al. A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature. 2001;409:928–33.
Logsdon GA, Vollger MR, Eichler EE. Long-read human genome sequencing and its applications. Nat Rev Genet. 2020;21:597–614.
Fu Y, Shen X, Chen D, Wang Z, Zhou C. Multiple displacement amplification as the first step can increase the diagnostic efficiency of preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disease for beta-thalassemia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45:1515–21.
Shen X, Xu Y, Zhong Y, Zhou C, Zeng Y, Zhuang G, et al. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for α-and β-double thalassemia. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2011;28:957–64.
Shen XT, Xu YW, Zhong YP, Zeng YH, Wang J, Ding CH, et al. Combination of multiple displacement amplification with short tandem repeat polymorphismin preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013;45:852–8.
Gueye NA, Jalas C, Tao X, Taylor D, Scott RT Jr, Treff NR. Improved sensitivity to detect recombination using qPCR for Dyskeratosis Congenita PGD. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31:1227–30.
Chen D, Shen X, Wu C, Xu Y, Ding C, Zhang G, et al. Eleven healthy live births: a result of simultaneous preimplantation genetic testing of alpha- and beta-double thalassemia and aneuploidy screening. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020;37:549–57.
Chen D, Shen X, Xu Y, Ding C, Ye Q, Zhong Y, et al. Successful four-factor preimplantation genetic testing: alpha- and beta-thalassemia, human leukocyte antigen typing, and aneuploidy screening. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2021:1–9.
Ardui S, Ameur A, Vermeesch JR, Hestand MS. Single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing comes of age: applications and utilities for medical diagnostics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:2159–68.
Wenger AM, Peluso P, Rowell WJ, Chang PC, Hall RJ, Concepcion GT, et al. Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37:1155–62.
Wilbe M, Gudmundsson S, Johansson J, Ameur A, Stattin EL, Anneren G, et al. A novel approach using long-read sequencing and ddPCR to investigate gonadal mosaicism and estimate recurrence risk in two families with developmental disorders. Prenat Diagn. 2017;37:1146–54.
Pinard R, de Winter A, Sarkis GJ, Gerstein MB, Tartaro KR, Plant RN, et al. Assessment of whole genome amplification-induced bias through high-throughput, massively parallel whole genome sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:216.
Amarasinghe SL, Su S, Dong X, Zappia L, Ritchie ME, Gouil Q. Opportunities and challenges in long-read sequencing data analysis. Genome Biol. 2020;21:30.
Sedlazeck FJ, Lee H, Darby CA, Schatz MC. Piercing the dark matter: bioinformatics of long-range sequencing and mapping. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19:329–46.
Funding
This study received funding from sources as follows: the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2018A030310050); National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC1000205); Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine (2012A061400003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.W., X.S., and C.Z. designed and performed the experiments, collected and analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. D.C., H.W., Y.L., P.L., and Q.Z. conducted the experiment. D.C. contributed to the interpretation of the results. P.C.C. and C.Z. supervised the experiments, and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Jiangmen Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University. We obtained informed consent from all the couples before this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Chen, D., Zhao, Q. et al. Long-read sequencing on the SMRT platform enables efficient haplotype linkage analysis in preimplantation genetic testing for β-thalassemia. J Assist Reprod Genet 39, 739–746 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-022-02415-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-022-02415-1