Abstract
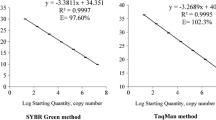
Cylindrospermopsin (CYN) is of great concern to human and animal health due to its potential toxicity. The cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii is considered the most common cyanobacterial species that produces CYN. The discovery of the cyr gene cluster responsible for CYN biosynthesis allows us to develop molecular methods that detect and quantify potentially CYN-producing C. raciborskii. This paper describes the development of real-time PCR (qPCR) assays capable of quantifying the total and CYN-producing C. raciborskii in subtropical reservoirs of southern China. We designed primers and probes specifically targeting the rpoC1 and cyrJ genes of C. raciborskii, and enabling quantification of its total cell numbers and potentially toxic genotypes, respectively. The qPCR showed strong linearity between 102 and 106 copies per reaction for both genes. This molecular method was validated against microscopic counting and a high correlation was found between them for quantifying C. raciborskii cell numbers in cyanobacterial cultures and water samples. Using qPCR, we detected potentially CYN-producing C. raciborskii in 34 of the 46 subtropical reservoirs of southern China, with the cyrJ/rpoC1 proportion ranging from 0.3 to 34.7%. CYN concentrations significantly correlated with both the copy numbers of cyrJ gene and the proportion of toxic C. raciborskii. Thus, the present real-time PCR method provides a reliable and faster method for estimating the potential toxicity of C. raciborskii blooms in this region. The wide distribution of potential CYN-producing C. raciborskii in the investigated subtropical reservoirs highlights the need for further monitoring.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Gómez EB, Kaštovský J, Echenique RO, Salerno GL (2018) The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, cyanobacteria). Phycologia 57:130–146
Al-Tebrineh J, Merrick C, Ryan D, Humpage A, Bowling L, Neilan BA (2012) Community composition, toxigenicity, and environmental conditions during a cyanobacterial bloom occurring along 1,100 kilometers of the Murray River. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:263–272
Antunes JT, Leão PN, Vasconcelos VM (2015) Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front Microbiol 6:473–485
Ballot A, Ramm J, Rundberget T, Kaplan-Levy RN, Hadas O, Sukenik A, Wiedner C (2011) Occurrence of non-cylindrospermopsin-producing Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Anabaena bergii in Lake Kinneret (Israel). J Plankton Res 33:1736–1746
Bar-Yosef Y, Sukenik A, Hadas O, Viner-Mozzini Y, Kaplan A (2010) Enslavement in the water body by toxic Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, inducing alkaline phosphatase in phytoplankton. Curr Biol 20:1557–1561
Burford MA, Davis TW, Orr PT, Sinha R, Willis A, Neilan BA (2014) Nutrient-related changes in the toxicity of field blooms of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:135–148
Burford M, Beardall J, Willis A, Orr P, Magalhaes VF, Rangel LM, Azevedo SMFOE, Neilan BA (2016) Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 54:44–53
Campo E, Lezcano M-Á, Agha R, Cirés S, Quesada A, El-Shehawy R (2013) First TaqMan assay to identify and quantify the cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon ovalisporum in water. Adv Microbiol 3:430–437
Davis TW, Orr PT, Boyer GL, Burford MA (2014) Investigating the production and release of cylindrospermopsin and deoxy-cylindrospermopsin by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii over a natural growth cycle. Harmful Algae 31:18–25
Dyble J, Tester PA, Litaker RW (2006) Effects of light intensity on cylindrospermopsin production in the cyanobacterial HAB species Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Afr J Mar Sci 28:309–312
Fergusson KM, Saint CP (2003) Multiplex PCR assay for Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacteria. Environ Toxicol 18:120–125
Ha JH, Hidaka T, Tsuno H (2009) Quantification of toxic-Microcystis and evaluation of its dominance ratio in blooms using real-time PCR. Environ Sci Technol 43:812–818
Humpage AR, Falconer IR (2003) Oral toxicity of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in male Swiss albino mice, determination of no observed adverse effect level for deriving a drinking water guideline value. Environ Toxicol 18:94–103
Jiang Y, Xiao P, Yu G, Sano T, Pan Q, Li R (2012) Molecular basis and phylogenetic implications of deoxycylindrospermopsin biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis curvata. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:2256–2263
Jiang Y, Xiao P, Yu G, Shao J, Liu D, Azevedo SM, Li R (2014) Sporadic distribution and distinctive variations of cylindrospermopsin genes in cyanobacterial strains and environmental samples from Chinese freshwater bodies. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:5219–5230
Jungblut AD, Hawes I, Mountfort D, Hitzfeld B, Dietrich DR, Burns BP, Neilan BA (2005) Diversity within cyanobacterial mat communities in variable salinity meltwater ponds of McMurdo ice shelf, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 7:519–529
Kardinaal WEA, Janse I, Agterveld MPK, Meima M, Snoek J, Mur LR, Huisman J, Zwart G, Visser PM (2007) Microcystis genotype succession in relation to microcystin concentrations in freshwater lakes. Aquat Microb Ecol 48:1–12
Kellmann R, Mills T, Neilan BA (2006) Functional modeling and phylogenetic distribution of putative cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis enzymes. J Mol Evol 62:267–280
Komárek J, Komárková J (2003) Phenotype diversity of the cyanoprokaryotic genus Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales); review 2002. Czech Phycol 3:1–30
Lei L, Peng L, Huang X, Han BP (2014) Occurrence and dominance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and dissolved cylindrospermopsin in urban reservoirs used for drinking water supply, South China. Environ Monit Assess 186:3079–3090
Lei L, Peng L, Yang Y, Han BP (2018a) Development of time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for detection of cylindrospermopsin using its novel monoclonal antibodies. Toxins (Basel) 10:255
Lei M, Peng L, Han BP, Lei L (2018b) Distribution and affecting factors of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Guangdong reservoirs. Environ Sci 39:5523–5531
Li R, Carmichael WW, Brittain S, Eaglesham GK, Shaw GR, Liu Y, Watanabe MM (2001) First report of the cyanotoxins cylindrospermopsin and deoxycylindrospermopsin from Raphidiopsis curvata (cyanobacteria). J Phycol 37:1121–1126
Manali KM, Arunraj R, Kumar T, Ramya M (2017) Detection of microcystin producing cyanobacteria in Spirulina dietary supplements using multiplex HRM quantitative PCR. J Appl Phycol 29:1279–1286
Mankiewicz-Boczek J, Kokociński M, Gagała I, Pawełczyk J, Jurczak T, Dziadek J (2012) Preliminary molecular identification of cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacteria in two polish lakes (Central Europe). FEMS Microbiol Lett 326:173–179
Mazmouz R, Chapuis-Hugon F, Mann S, Pichon V, Méjean A, Ploux O (2010) Biosynthesis of cylindrospermopsin and 7-epicylindrospermopsin in Oscillatoria sp. strain PCC 6506: identification of the cyr gene cluster and toxin analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4943–4949
Mihali TK, Kellmann R, Muenchhoff J, Barrow KD, Neilan BA (2008) Characterization of the gene cluster responsible for cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:716–722
Moreira C, Martins A, Azevedo J, Freitas M, Regueiras A, Vale M, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V (2011) Application of real-time PCR in the assessment of the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii abundance and toxicological potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:189–197
Moreira C, Azevedo J, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V (2013) Cylindrospermopsin: occurrence, methods of detection and toxicology. Appl Microbiol 114:605–620
Moreira C, Ramos V, Azevedo J, Vasconcelos V (2014) Methods to detect cyanobacteria and their toxins in the environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8073–8082
Moustaka-Gouni M, Kormas KA, Vardaka E, Katsiapi M, Gkelis S (2009) Raphidiopsis mediterranea Skuja represents non-heterocytous life-cycle stages of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju in Lake Kastoria (Greece), its type locality: evidence by morphological and phylogenetic analysis. Harmful Algae 8:864–872
Neilan BA, Jacobs D, Therese DD, Blackall LL, Hawkins PR, Cox PT, Goodman AE (1997) rRNA sequences and evolutionary relationships among toxic and nontoxic cyanobacteria of the genus Microcystis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:693–697
Orr PT, Rasmussen JP, Burford MA, Eaglesham GK, Lennox SM (2010) Evaluation of quantitative real-time PCR to characterise spatial and temporal variations in cyanobacteria, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya et Subba Raju and cylindrospermopsin concentrations in three subtropical Australian reservoirs. Harmful Algae 9:243–254
Pacheco AB, Guedes IA, Azevedo SM (2016) Is qPCR a reliable indicator of cyanotoxin risk in freshwater? Toxins (Basel) 8:172
Pichardo S, Cameán AM, Jos A (2017) In vitro toxicological assessment of cylindrospermopsin: a review. Toxins (Basel) 9:402
Pierangelini M, Sinha R, Willis A, Burford MA, Orr PT, Beardall J, Neilan BA (2015) Constitutive cylindrospermopsin pool size in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii under different light and CO2 partial pressure conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3069–3076
Poniedziałek B, Rzymski P, Kokociński M (2012) Cylindrospermopsin: water-linked potential threat to human health in Europe. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34:651–660
Rasmussen JP, Giglio S, Monis PT, Campbell RJ, Saint CP (2008) Development and field testing of a real-time PCR assay for cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacteria. Appl Microbiol 104:1503–1515
Rzymski P, Poniedziałek B (2014) In search of environmental role of cylindrospermopsin: a review on global distribution and ecology of its producers. Water Res 66:320–337
Saker ML, Neilan BA (2001) Varied diazotrophies, morphologies, and toxicities of genetically similar isolates of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanophyceae) from northern Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1839–1845
Schembri MA, Neilan BA, Saint CP (2001) Identification of genes implicated in toxin production in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Environ Toxicol 16:413–421
Scherer PI, Millard AD, Miller A, Schoen R, Raeder U, Geist J, Zwirglmaier K (2017) Temporal dynamics of the microbial community composition with a focus on toxic cyanobacteria and toxin presence during harmful algal blooms in two South German lakes. Front Microbiol 8:2387
Sinha R, Pearson LA, Davis TW, Muenchhoff J, Pratama R, Jex A, Burford MA, Neilan BA (2014) Comparative genomics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains with differential toxicities. BMC Genomics 15:83–96
Stucken K, John U, Cembella A, Murillo AA, Soto-Liebe K, Fuentes-Valdés JJ, Friedel M, Plominsky AM, Vásquez M, Glöckner G (2010) The smallest known genomes of multicellular and toxic cyanobacteria: comparison, minimal gene sets for linked traits and the evolutionary implications. PLoS One 5:9235
Te SH, Chen EY, Gin KY (2015) Comparison of quantitative PCR and droplet digital PCR multiplex assays for two genera of bloom-forming cyanobacteria, Cylindrospermopsis and Microcystis. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:5203–5211
Willis A, Adams MP, Chuang AW, Orr PT, O’Brien KR, Burford MA (2015) Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii ((Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju). Harmful Algae 47:27–34
Willis A, Chuang AW, Woodhouse JN, Neilan BA, Burford MA (2016) Intraspecific variation in growth, morphology and toxin quotas for the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Toxicon 119:307–310
Yang Y, Jiang Y, Li X, Li H, Chen Y, Xie J, Cai F, Li R (2016) Variations of growth and toxin yield in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii under different phosphorus concentrations. Toxins (Basel) 9:13
Yang Y, Chen Y, Cai F, Liu X, Wang Y, Li R (2018) Toxicity-associated changes in the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in response to nitrogen fluctuations. Environ Pollut 237:1041–1049
Žegura B, Straser A, Filipič M (2011) Genotoxicity and potential carcinogenicity of cyanobacterial toxins-a review. Mutat Res 727:16–41
Zhang W, Lou I, Ung WK, Kong Y, Mok KM (2014) Analysis of cylindrospermopsin-and microcystin-producing genotypes and cyanotoxin concentrations in the Macau storage reservoir. Hydrobiologia 741:51–68
Funding
This work was funded by a National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (No. 31770507) and the Water Resource Science and Technology Innovation Program of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2016-29).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, L., Lei, M., Lu, Y. et al. Development of real-time PCR for quantification of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii cells and potential cylindrospermopsin-producing genotypes in subtropicalreservoirs of southern China. J Appl Phycol 31, 3749–3758 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01898-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01898-3