Abstract
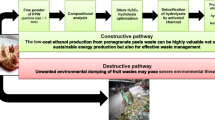
Massive alginate production in China, the major producer of cultivated brown seaweeds in the world, produces a substantial amount of organic kelp waste which is often dumped as landfill. Reutilization of the dealginated kelp waste is a timely point of research in the alginate industry. Kelp waste extracts (KWE) produced via enzymatic hydrolysis of the dealginated residue of the kelp Saccharina japonica were found to render a biostimulant effect that improved the growth of vegetables such as the pak choi and color pepper and microalgae such as Chlorella sorokiniana. Thus, owing to the far-reaching importance of KWE in agriculture and biofuel production, the objective of this study is to optimize the enzymatic degradation of the dealginated kelp waste. The optimization process was carried out by integrating single-factor method, orthogonal experimental design, and response surface method (RSM) based on central composite design (CCD) experiments. The optimization parameters were enzyme ratio, enzymolysis time, temperature, and phosphate buffer solution (PBS) pH. An orthogonal experimental design (L16 (34)) was followed to achieve the optimum combination ratio for cellulase, pectinase, and papain enzymes. Results of the experiment that asserted highest results could be attained at 4, 2, and 1.5% (w/v) ration of cellulase, pectinase, and papain, respectively. Furthermore, optimized conditions of the enzymolysis time (3.8 days), reaction temperature (50 °C), and initial phosphate buffer solution pH (5.8) were predicted through RSM based on CCD experiments. The prediction was confirmed through a triplicate experiment giving a mean total soluble sugar yield of 12.20% ± 0.04. The optimization process was successful in reducing the enzymolysis time by more than 50% from 8 days to 3.8 days. Moreover, the extract was found to contain 18 types of amino acids, alanine being the major one.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Q, Xu H, Mai K, Xu W, Wang J, Zhang W (2011) Effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis and fructooligosaccharide on growth performance, survival, non-specific immune response and disease resistance of juvenile large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 317:155–161
Battacharyya D, Babgohari MZ, Rathor P, Prithiviraj B (2015) Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci Hortic 196:39–48
Behera SK, Meena H, Chakraborty S, Meikap BC (2018) Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of leaching parameters for ash reduction from low-grade coal. Int J Min Sci Technol 28:621–629
Bird MI, Wurster CM, de Paula Silva PH, Bass AM, de Nys R (2011) Algal biochar--production and properties. Bioresour Technol 102:1886–1891
Buschmann AH, Prescott S, Potin P, Faugeron S, Vásquez JA, Camus C, Infante J, Hernández-González MC, Gutíerrez A, Varela DA (2014) The status of kelp exploitation and marine agronomy, with emphasis on Macrocystis pyrifera, in Chile. Adv Bot Res 71:161–188
Cho S, Lee D, Luong TT, Park S, Oh YK, Lee T (2011) Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on fatty acid contents and composition in the green microalga, Chlorella sp. 227. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1073–1080
Çinar İ (2005) Effects of cellulase and pectinase concentrations on the colour yield of enzyme extracted plant carotenoids. Process Biochem 40:945–949
Demirel M, Kayan B (2012) Application of response surface methodology and central composite design for the optimization of textile dye degradation by wet air oxidation. Int J Ind Chem 3:24
DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Fan T, Hu J, Fu L, Zhang L (2015) Optimization of enzymolysis-ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Momordica charabtia L. by response surface methodology. Carbohyd Polym 115:701–706
Ge L, Wang P, Mou H (2011) Study on saccharification techniques of seaweed wastes for the transformation of ethanol. Renew Energy 36:84–89
Gohi B, Zeng HY, Pan AD (2016) Optimization and characterization of chitosan enzymolysis by pepsin. Bioeng (Basel) 3(3):17
Hosseini Koupaie E, Dahadha S, Bazyar Lakeh AA, Azizi A, Elbeshbishy E (2019) Enzymatic pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced biomethane production-a review. J Environ Manag 233:774–784
Jun-Hong L, Ru Y, Fu-Mei W, Qi Z, Hui C (2014) Technology optimization of enzymolysis of burmuda grass. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 7:2411–2415
Liu Z, Li X, Xie W, Deng H (2017) Extraction, isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from industrial kelp (Laminaria japonica) waste. Carbohyd Polym 173:353–359
María ER-G, Ceri WJ, Gardiner PHE (2000) The application of dealginated seaweed as a cation exchanger foron-line preconcentration and chemical speciation of trace metals. J Anal Atom Spectrom 15:1009–1013
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Najafabadi AH, Malekzadeh M, Jalilian F, Vossoughi M, Pazuki G (2015) Effect of various carbon sources on biomass and lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris during nutrient sufficient and nitrogen starvation conditions. Bioresour Technol 180:311–317
Palanisamy M, Iniyakumar M, Elaiyaraju P, Mukund S, Uthandi S, Sivasubramanian V (2017) Effect of application of algal biochar on soil enzymes. J Alg Biom Util 8:1–9
Panthapulakkal S, Sain M (2013) Optimization of microwave assisted alkaline extraction of xylan from birch wood using response surface methodology. J Mater Sci Chem Eng 01:38–50
Pearce NJG, Hartley S, Perkins WT, Dinelli E, Edyvean RGJ, Priestman G, Bachman R, Sandlands L (2007) Dealginated seaweed for the bioremediation of mine waters in mid-wales: results of field trials from the “BIOMAN” EU life environment project. In: Cidu R and Frau F (eds) Proceedings of IMWA symposium. Cagliari, Italy. pp 243–247
Tang X, Dai L, Tang Y, Sun W (2014) Study on optimization of bagasse hemicellulose enzymolysis with response surface analysis. J Sust Bioenerg Syst 04:249–259
Tseng CK (2001) Algal biotechnology industries and research activities in China. J Appl Phycol 13:375–380
Wang YQ, Wu ZF, Ke G, Yang M (2014) An effective vacuum assisted extraction method for the optimization of labdane diterpenoids from Andrographis paniculata by response surface methodology. Molecules 20:430–445
Wu X, Leung DYC (2011) Optimization of biodiesel production from camelina oil using orthogonal experiment. Appl Energy 88:3615–3624
Yeh AI, Huang YC, Chen SH (2010) Effect of particle size on the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Carbohyd Polym 79:192–199
Yu KL, Lau BF, Show PL, Ong HC, Ling TC, Chen WH, Ng EP, Chang JS (2017) Recent developments on algal biochar production and characterization. Bioresour Technol 246:2–11
Yue H, Sun Y, Jing H, Zeng S, Ouyang H (2014) The analysis of Laminaria japonica industry and international trade situation in China. In: Xu S (ed) Proceedings of selected articles of 2013 world agricultural outlook conference. Springer, Berlin, pp 39–51
Zarei M, Niaei A, Salari D, Khataee A (2010) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of peroxi-coagulation of textile dye solution using carbon nanotube-PTFE cathode. J Hazard Mater 173:544–551
Zhang J, Jia S, Liu Y, Wu S, Ran J (2011) Optimization of enzyme-assisted extraction of the Lycium barbarum polysaccharides using response surface methodology. Carbohyd Polym 86:1089–1092
Zheng S, He M, Jiang J, Zou S, Yang W, Zhang Y, Deng J, Wang C (2016a) Effect of kelp waste extracts on the growth and lipid accumulation of microalgae. Bioresour Technol 201:80–88
Zheng S, Jiang J, He M, Zou S, Wang C (2016b) Effect of kelp waste extracts on the growth and development of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.). Sci Rep 6:38683
Zheng S, He M, Sui Y, Gebreluel T, Zou S, Kemuma ND, Wang C (2017) Kelp waste extracts combined with acetate enhances the biofuel characteristics of Chlorella sorokiniana. Bioresour Technol 225:142–150
Funding
This work is supported by the Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Resource Utilization, Collaborative Innovation Center for Jiangsu Marine Bio-Industry Technology, National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770436).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gebreluel, T., He, M., Zheng, S. et al. Optimization of enzymatic degradation of dealginated kelp waste through response surface methodology. J Appl Phycol 32, 529–537 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01894-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01894-7