Abstract
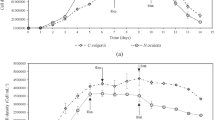
The microalga Nannochloropsis sp. was cultured under different initial population densities (IPDs) ranging from 0.11 to 9.09 g L−1. The IPD affected the biomass and lipid accumulation significantly. The algal cultured with higher IPD resulted higher biomass concentration (up to 13.07 g L−1) in 10 days growth. The biomass productivity with 0.98 g L−1 IPD was 0.75 g L−1 d−1 which was higher than that of other IPDs. For IPDs ranging from 0.11 to 0.98 g L−1, with the increase of IPD, the biomass productivity increased, while for IPD over 0.98 g L−1, the biomass productivity decreased. Lipid content of the algal culture started with 0.11 g L−1 IPD reached to 42 % of dry weight. But with the increase of IPD, the lipid content decreased. Lipid composition was analyzed using thin layer chromatography coupled with flame ionization detection (TLC/FID). Seven lipid classes were identified and quantified. The main reserve lipid, triacylglyceride (TAG), accumulated under all different IPD conditions. However, with the increasing IPD values, TAG content decreased from 59.1 to 23.5 % of the total lipids. Based on these results, to obtain the maximal biomass productivity and lipid productivity of Nannochloropsis sp. in mass cultivation systems, it is necessary to select an appropriate IPD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Boussiba S, Vonshak A, Cohen Z (1987) Lipid and biomass production by the halotolerant microalga Nannochloropsis salina. Biomass 12:37–47
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Chrismadha T, Borowitzka MA (1994) Effect of cell-density and irradiance on growth, proximate composition and eicosapentaenoic acid production of Phaeodactylum tricornutum grown in a tubular photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 6:67–74
Collos Y, Mornet F, Sciandra A (1999) An optical method for the rapid measurement of micromolar concentrations of nitrate in marine phytoplankton cultures. J Appl Phycol 11:179–184
Converti A, Casazza AA, Ortiz EY (2009) Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on the growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Chem Eng Process 48:1146–1151
Emdadi D, Berland B (1989) Variation in lipid class composition during batch growth of Nannochloropsis salina and Pavlova lutheri. Mar Chem 26:215–225
Fang X, Wei C, Cai ZL (2004) Effects of organic carbon sources on cell growth and eicosapentaenoic acid content of Nannochloropsis sp. J Appl Phycol 16:499–503
Goksan T, Durmaz Y, Gokpinar S (2003) Effects of light path lengths and initial culture density on the cultivation of Chaetoceros muelleri (Lemmermann, 1898). Aquaculture 217:431–436
Guschina IA, Harwood JL (2006) Lipids and lipid metabolism in eukaryotic algae. Prog Lipid Res 45:160–186
Hodgson PA, Henderson RJ, Sargent JR (1991) Patterns of variation in the lipid class and fatty acid composition of Nannochloropsis oculata (Eustigmatophyceae) during batch culture. 1. The growth-cycle. J Appl Phycol 3:169–181
Hu HH, Gao KS (2006) Response of growth and fatty acid compositions of Nannochloropsis sp. to environmental factors under elevated CO2 concentration. Biotechnol Lett 28:987–992
Hu Q, Guterman H, Richmond A (1996) A flat inclined modular photobioreactor for outdoor mass cultivation of photoautotrophs. Biotechnol Bioeng 51:51–60
Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Jarvis E (2008) Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant J 54:621–639
Kaewpintong K, Shotipruk A, Powtongsook S (2007) Photoautotrophic high-density cultivation of vegetative cells of Haematococcus pluvialis in airlift bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 98:288–295
Lubian LM, Montero O, Moreno-Garrido I (2000) Nannochloropsis (Eustigmatophyceae) as source of commercially valuable pigments. J Appl Phycol 12:249–255
Richmond A, Zou N (1999) Efficient utilisation of high photon irradiance for mass production of photoautotrophic micro-organisms. J Appl Phycol 11:123–127
Richmond A, Zhang CW, Zarmi Y (2003) Efficient use of strong light for high photosynthetic productivity: interrelationships between the optical path, the optimal population density and cell-growth inhibition. Biomol Eng 20:229–236
Rodolfi L, Zittelli GC, Bassi N (2009) Microalgae for oil: strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:100–112
Suen Y, Hubbard JS, Holzer G (1987) Total lipid production of the green-alga Nannochloropsis sp. Qii under different nitrogen regimes. J Phycol 23:289–296
Zittelli GC, Lavista F, Bastianini A (1999) Production of eicosapentaenoic acid by Nannochloropsis sp cultures in outdoor tubular photobioreactors. J Biotechnol 70:299–312
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the project “High efficient breeding and cultivation technology for energy microalgae (2011BAD14B01)” of National Key Technologies R&D Program from Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the project of “High efficient cultivation technology for energy microalgae” by the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Liu, T. et al. Effects of initial population density (IPD) on growth and lipid composition of Nannochloropsis sp.. J Appl Phycol 24, 1623–1627 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9825-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9825-1