Abstract
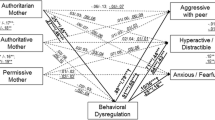
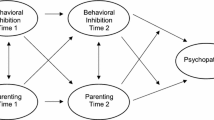
Behavioral inhibition (BI) is characterized by a pattern of extreme social reticence, risk for internalizing behavior problems, and possible protection against externalizing behavior problems. Parenting style may also contribute to these associations between BI and behavior problems (BP). A sample of 113 children was assessed for BI in the laboratory at 14 and 24 months of age, self-report of maternal parenting style at 7 years of age, and maternal report of child internalizing and externalizing BP at 4, 7, and 15 years. Internalizing problems at age 4 were greatest among behaviorally inhibited children who also were exposed to permissive parenting. Furthermore, greater authoritative parenting was associated with less of an increase in internalizing behavior problems over time and greater authoritarian parenting was associated with a steeper decline in externalizing problems. Results highlight the importance of considering child and environmental factors in longitudinal patterns of BP across childhood and adolescence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Integrative Guide to the 1991 CBCL/4–18, YSR, and TRF Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychology.
Achenbach, T. M. (2001). Child behavior checklist for ages 6 to 18. Burlington: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families.
American Psychological Association. (2007). APA Dictionary of Psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Angold, A., Costello, E. J., & Erkanli, A. (1999). Comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 40, 57–87. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00424.
Bar-Haim, Y., Fox, N.A., Benson, B., Guyer, A.E., Williams, A., Nelson, E.E., Perez-Edgar, K., Pine, D.S., & Ernst, M. Neural correlates of reward processing in adolescents with a history of shyness and inhibited temperament. Psychological Science, in press.
Baumrind, D. (1967). Child care practices anteceding three patterns of preschool behavior. Genetic Psychology Monographs, 75, 43–88.
Baumrind, D. (1971). Current patterns of parental authority. Developmental Psychology, 4, 1–103. doi:10.1037/h0030372.
Baumrind, D. (1991). The influence of parenting styles on adolescent competence and substance use. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 11, 56–95. doi:10.1177/0272431691111004.
Bell, R. Q. (1968). A reinterpretation of the direction of effects in studies of socialization. Psychological Review, 75, 81–95. doi:10.1037/h0025583.
Biederman, J., Hirshfeld-Becker, D. R., Rosenbaum, J. F., Herot, C., Friedman, D., Snidman, N., et al. (2001). Further evidence of association between behavioral inhibition and social anxiety in children. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 1673–1679. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.158.10.1673.
Bongers, I. L., Koot, H. M., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2003). The normative development of child and adolescent problem behavior. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 112, 179–192. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.112.2.179.
Broidy, L. M., Nagin, D. S., Tremblay, R. E., Bates, J. E., Brame, B., Dodge, K. A., et al. (2003). Developmental trajectories of childhood disruptive behaviors and adolescent delinquency: a six-site, cross-national study. Developmental Psychology, 39, 222–245. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.39.2.222.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (2005). Making human beings human: Bioecological perspectives on human development. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Calkins, S. D., & Degnan, K. A. (2006). Temperament in early development. In R. Ammerman (Ed.), Comprehensive Handbook of Personality and Psychopathology, Vol 3: Child Psychopathology. New York: Wiley.
Calkins, S. D., Fox, N. A., & Marshall, T. R. (1996). Behavioral and physiological antecendents of inhibited and uninhibited behavior. Child Development, 67, 523–540. doi:10.2307/1131830.
Caspi, A., Moffitt, T. E., Newman, D. L., & Silva, P. A. (1996). Behavioral observations at age 3 years predict adult psychiatric disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 53, 1033–1039.
Chronis-Tuscano, A., Degnan, K.A., Pine, D., Perez-Edgar, K., Diaz, Y., Raggi, V.L., & Fox, N.A. Stable, Early Maternal Report of Behavioral Inhibition Predicts Lifetime Social Anxiety Disorder in Adolescence. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, in press.
Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (1998). Perspectives on research and practice in developmental psychopathology. In W. Damon, I. E. Sigel & K. A. Renninger (Eds.), Handbook of Child Psychology (5th ed., pp. 479–583). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Cook, W. L., & Kenny, D. A. (2005). The actor-partner interdependence model: A model of bidirectional effects in developmental studies. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29, 101–109. doi:10.1080/01650250444000405.
Coplan, R. J., Wilson, J., Frohlick, S. L., & Zelenski, J. (2006). A person-oriented analysis of behavioral inhibition and behavioral activation in children. Personality and Individual Differences, 41, 917–927. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2006.02.019.
Darling, N., & Steinberg, L. (1993). Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychological Bulletin, 113, 487–496. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.113.3.487.
Degnan, K. A., Calkins, S. D., Keane, S. P., & Hill-Soderlund, A. L. (2008). Profiles of disruptive behavior across early childhood: Contributions of frustration reactivity, physiological regulation, and maternal behavior. Child Development, 79, 1357–1376. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01193.x.
Degnan, K. A., & Fox, N. A. (2007). Behavioral inhibition and anxiety disorders: Multiple levels of a resilience process. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 729–746. doi:10.1017/S0954579407000363.
Degnan, K. A., Henderson, H. A., Fox, N. A., & Rubin, K. H. (2008). Predicting social wariness in middle childhood: The Moderating Roles of Child Care History, Maternal Personality and Maternal Behavior. Social Development, 17, 471–487. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9507.2007.00437.x.
Fox, N. A., Henderson, H. A., & Marshall, P. J. (2001a). The biology of temperament: An integrative approach. In C. A. Nelson & M. Luciana (Eds.), The handbook of developmental cognitive neuroscience (pp. 631–645). Cambridge, MA: Springer.
Fox, N. A., Henderson, H. A., Rubin, K. H., Calkins, S. D., & Schmidt, L. A. (2001b). Continuity and discontinuity of behavioral inhibition and exuberance: Psychophysiological and behavioral influences across the first four years of life. Child Development, 72, 1–21. doi:10.1111/1467-8624.00262.
Gilliom, M., & Shaw, D. S. (2004). Codevelopment of externalizing and internalizing problems in early childhood. Development and Psychopathology, 16, 313–333. doi:10.1017/S0954579404044530.
Guyer, A. E., Nelson, E. E., Perez-Edgar, K., Hardin, M. G., Roberson-Nay, R., Monk, C. S., et al. (2006). Striatal functional alteration in adolescents characterized by early childhood behavioral inhibition. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 6399–6405. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0666-06.2006.
Hastings, P. D., Rubin, K. H., & DeRose, L. (2005). Links among gender, inhibition, and parental socialization in the development of prosocial behavior. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 51, 467–493. doi:10.1353/mpq.2005.0023.
Kagan, J. (2001). Temperamental contributions to affective and behavioral profiles in childhood. In S. G. Hoffmann & P. M. Dibartolo (Eds.), From social anxiety to social phobia: Multiple perspectives (pp. 216–234). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Kagan, J., Reznick, J. S., Clarke, C., Snidman, N., & Garcia-Coll, C. (1984). Behavioral inhibition to the unfamiliar. Child Development, 55, 2212–2225. doi:10.2307/1129793.
Kimonis, E. R., Frick, P. J., Boris, N. W., Smyke, A. T., Cornell, A. H., Farrell, J. M., et al. (2006). Callous-unemotional features, behavioral inhibition, and parenting: independent predictors of aggression in a high-risk preschool sample. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 15, 745–756. doi:10.1007/s10826-006-9047-8.
LeDoux, J. E., Iwata, J., Cicchetti, P., & Reis, D. J. (1988). Different projections of the central amygdaloid nucleus mediate autonomic and behavioral correlates of conditioned fear. The Journal of Neuroscience, 8, 2517–2529.
Leve, L. D., Kim, H. K., & Pears, K. C. (2005). Childhood temperament and family environmanet as predictors of internalizing and externalizing trajectories from ages 5 to 17. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33, 505–520. doi:10.1007/s10802-005-6734-7.
Little, R. J., & Rubin, D. B. (eds). (1987). Statistical analysis with missing data. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Lonigan, C. J., Phillips, B. M., & Hooe, E. S. (2003). Relations of positive and negative affectivity to anxiety and depression in children: Evidence from a latent variable longitudinal study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71, 465–481. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.71.3.465.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent-child interaction. In P. H. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Socialization, personality and social development (Vol. 4, pp. 1–101). New York: Wiley.
McLeod, B. D., Wood, J. J., & Weisz, J. R. (2007). Examining the association between parenting and childhood anxiety: A meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review, 27, 155–172. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2006.09.002.
Mills, R. S. L., & Rubin, K. H. (1993). Socialization factors in the development of social withdrawal. In K. H. Rubin & J. Asendorpf (Eds.), Social withdrawal, inhibition, and shyness in childhood. Hillsdale, N.J.: Erlbaum.
Moffitt, T. E., Caspi, A., Dickson, N., Silva, P., & Stanton, W. (1996). Childhood-onset versus adolescent-onset antisocial conduct problems in males: Natural history from ages 3 to 18 years. Development and Psychopathology, 8, 399–424. doi:10.1017/S0954579400007161.
Pérez-Edgar, K., Roberson-Nay, R., Hardin, M. G., Poeth, K., Guyer, A. E., Nelson, E. E., et al. (2007). Attention alters neural responses to evocative faces in behaviorally inhibited adolescents. NeuroImage, 35, 1538–1546. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.006.
Pine, D. S., Cohen, E., Cohen, P., & Brook, J. S. (2000). Social phobia and the persistence of conduct problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 41, 657–665. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00652.
Propper, C., & Moore, G. A. (2006). The influence of parenting on infant emotionality: A multi-level psychobiological perspective. Developmental Review, 26, 427–460. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2006.06.003.
Querido, J. G., Warner, T. D., & Eyberg, S. M. (2002). Parenting styles and child behavior in African American families of preschool children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 31, 272–277.
Raudenbush, S. W., & Byrk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications.
Robinson, C. C., Mandleco, B., Olsen, S. F., & Hart, C. H. (1995). Authoritative, authoritarian, and permissive parenting practices: Development of a new measure. Psychological Reports, 77, 819–830.
Robinson, C. C., Mandelco, B., Olsen, S. F., & Hart, C. H. (2001). Parenting styles and dimensions questionnaire. In B. F. Perlmutter, J. Touliatos & G. W. Holdem (Eds.), Handbook of Family Measurement Techniques: Instruments and Index (pp. 319–321). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Rothbart, M.K., & Bates, J.E.(2006). Temperament. In W. Damon, R. Lerner, & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Vol 3. Social, emotional, and personality development (6th ed., pp. 99–166). New York: Wiley.
Rubin, K. H., & Burgess, K. B. (2001). Social withdrawal and anxiety. In M. W. Vasey & M. R. Dadds (Eds.), The Developmental Psychopathology of Anxiety (pp. 407–434). New York: Oxford University Press.
Rubin, K. H., & Burgess, K. (2002). Parents of aggressive and withdrawn children. In M. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of Parenting (2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 383–418). Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Rubin, K. H., Chen, X., McDougall, P., Bowker, A., & Mackinnon, J. (1995). The Waterloo Longitudinal Project: Predicting internalizing and externalizing problems in adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 751–764. doi:10.1017/S0954579400006829.
Rubin, K. H., Burgess, K. B., & Hastings, P. D. (2002). Stability and social-behavioral consequences of toddlers’ inhibited temperament and parenting behaviors. Child Development, 73, 483–495. doi:10.1111/1467-8624.00419.
Russell, A., Hart, C. H., Robinson, C. C., & Olsen, S. F. (2003). Children's sociable and aggressive behaviour with peers: A comparison of the US and Australia, and contributions of temperament and parenting styles. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 27, 74–86. doi:10.1080/01650250244000038.
Rutter, M. L. (1997). Nature-nurture integration: The example of antisocial behavior. The American Psychologist, 52, 390–398. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.52.4.390.
Sameroff, A. J., & Mackenzie, M. J. (2003). Research strategies for capturing transactional models of development: The limits of the possible. Development and Psychopathology, 15, 613–640. doi:10.1017/S0954579403000312.
Schwartz, C. E., Wright, C. I., Shin, L. M., Kagan, J., & Rauch, S. L. (2003). Inhibited and uninhibited infants "grown up": Adult amygdalar response to novelty. Science, 300, 1952–1953. doi:10.1126/science.1083703.
Steinberg, L., Lamborn, S., Darling, N., Mounts, N., & Dornbusch, S. (1994). Over-time changes in adjustment and competence among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, and neglectful families. Child Development, 65, 754–770. doi:10.2307/1131416.
Steinberg, L., Blatt-Eisengart, I., & Cauffman, E. (2006). Patterns of competence and adjustment among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, and neglectful homes: A replication in a sample of serious juvenile offenders. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 16, 47–58. doi:10.1111/j.1532-7795.2006.00119.x.
Sterba, S. K., Prinstein, M. J., & Cox, M. J. (2007). Trajectories of internalizing problems across childhood: Heterogeneity, external validity, and gender differences. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 345–366. doi:10.1017/S0954579407070174.
Thompson, A., Hollis, C., & Richards, D. (2003). Authoritarian parenting attitudes as a risk for conduct problems: Results from a British national cohort study. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 12, 84–91. doi:10.1007/s00787-003-0324-4.
Van Brakel, A. M. L., Muris, P., Bogels, S. M., & Thomassen, C. (2006). A multifactorial model for the etiology of anxiety in non-clinical adolescents: Main and interactive effects of behavioral inhibition, attachment and parental rearing. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 15, 569–579.
Van Leeuwen, K. G., Mervielde, I., Braet, C., & Bosmans, G. (2004). Child personality and parental behavior as moderators of problem behavior: Variable- and person-centered approaches. Developmental Psychology, 40, 1028–1046. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.40.6.1028.
Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2002). Reactively and proactively aggressive children: antecedent and subsequent characteristics. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 43, 495–505. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00040.
Wood, J. J., McLeod, B. D., Sigman, M., Hwang, W., & Chu, B. (2003). Parenting and childhood anxiety: theory, empirical findings, and future directions. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 44, 134–151. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health awards (MH 074454 and HD 17899) to the last author. The authors would like to thank all of the research staff who assisted in data collection and coding. Above all, we thank the children and families who participated for their invaluable time and effort over the years of the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rankin Williams, L., Degnan, K.A., Perez-Edgar, K.E. et al. Impact of Behavioral Inhibition and Parenting Style on Internalizing and Externalizing Problems from Early Childhood through Adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol 37, 1063–1075 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-009-9331-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-009-9331-3