Abstract
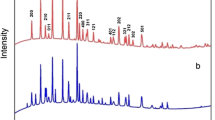
The spherical LiFePO4/C and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C powders were successfully prepared from spherical FePO4 via a simple uniform-phase precipitation method at normal pressure, using FeCl3 and H3PO4 as the reactants. The FePO4, LiFePO4/C, and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C powders were characterized by scanning electron microscopies (SEM), powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS), and tap-density testing. The uniform spherical particles produced are amorphous, but they were crystallized to FePO4 after calcining above 400 °C. Due to the homogeneity of the basic FePO4, the final products, LiFePO4/C and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C, are also significantly uniform and the particle size is of about 1 μm in diameter. The tap-density of the spherical LiFePO4/C and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C are 1.75 and 1.77 g cm−3, respectively, which are remarkably higher than the non-spherical LiFePO4 powders (the tap-density is 1.0–1.3 g cm−3). The excellent specific capacities of 148 and 157 mAh g−1 with a rate of 0.1 C are achieved for the LiFePO4/C and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C, respectively. Comparison of the cyclic voltammograms of LiFePO4/C and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C shows enhanced redox current and reversibility for the sample substituting Mg on the Fe site. LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4/C exhibits better high-rate and cycle performances than the un-substituted LiFePO4/C.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:1188
Yamada A, Chung SC, Hinokuma K (2001) J Electrochem Soc 148:A224
Ravet N, Chouinard Y, Magnan JF, Besner S, Gauthier M, Armand M (2001) J Power Sources 97/98:503
Huang H, Yin SC, Nazar LF (2001) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 4:A170
Chen Z, Dahn JR (2002) J Electrochem Soc 149:A1184
Hu Y, Doeff MM, Kostecki R, Fiñones R (2004) J Electrochem Soc 151:A1279
Belharouak I, Johnson C, Amine K (2005) Electrochem Commun 7:983
Chung SY, Blocking JT, Chiang YM (2002) Nat Mater 1:123
Yamada A, Yonemura M, Takei Y, Sonoyama N, Kanno R (2005) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8:A55
Sun YK, Bae YC, Myung ST (2005) J Appl Electrochem 35:151
Ying J, Jiang C, Wan C (2004) J Power Sources 129:264
Ying J, Lei M, Jiang C, Wan C, He X, Li J, Wang L, Ren J (2006) J Power Sources 158:543
He P, Wang H, Qi L, Osaka T (2006) J Power Sources 158:529
Shi SQ, Liu LJ, Ouyang CY, Wang DS, Wang Z, Chen L, Huang X (2003) Phys Rev B 68:195108
Liu H, Cao Q, Fu LJ, Li C, Wu YP, Wu HQ (2006) Electrochem Commun 8:1553
Zhang M, Jiao LF, Yuan HT, Wang YM, Guo J, Zhao M, Wang W, Zhou XD (2006) Solid State Ionics 177:3309
Barker J, Saidi MY, Swoyer JL (2003) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 6:A53
Wang GX, Bewlay S, Yao J, Ahn JH, Dou SX, Liu HK (2004) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 7:A503
Wang D, Li H, Shi S, Huang X, Chen L (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:2955
Hong J, Wang C, Kasavajjula U (2006) J Power Sources 162:1289
Wang C, Hong J (2007) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 10:A65
Wilhelmy RB, Matijević E (1987) Colloids Surf 22:111
Springsteen LL, Matijević E (1989) Colloid Polym Sci 267:1007
Kandori K, Nakashima H, Ishikawa T (1993) J Colloid Interface Sci 160:499
Kandori K, Kuwae T, Ishikawa T (2006) J Colloid Interface Sci 300:225
Scaccia S, Carewska M, Wisniewski P, Prosini PP (2003) Mater Res Bull 38:1155
Wang YQ, Wang JL, Yang J, Nuli JN (2006) Adv Funct Mater 16:2135
Franger S, Cras FL, Bourbon C, Rouault H (2002) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 5:A231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Zhang, X. & Hong, L. Preparation and electrochemical properties of spherical LiFePO4 and LiFe0.9Mg0.1PO4 cathode materials for lithium rechargeable batteries. J Appl Electrochem 39, 2433–2438 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9931-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-009-9931-1