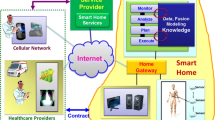
Abstract
One major challenge to successful aging is the capability to preserve health, or from another perspective to avoid disease. Unfortunately, a large percentage of the elderly people are living with chronic diseases or disabilities. Home care technologies and other emerging technologies have the potential to play a major role in home-based health care approach. The advent of sensor technology, in addition to telecom industry has made this possible. The main goal of the presented research in this paper is to develop a cost-effective user-friendly telehealth system to serve the elderly and disabled people in the community. The research also aims at utilizing the state-of-the-art advances in medical instrumentation technology to establish a continuous communication link between patients and caregivers and allow physicians to offer help when needed. Hence, we are presenting here an integrated user-friendly model of a smart home which provides telemedicine for elderly at home. The general problem addressed in this paper is that of offering a smart environment which monitors the elderly continuously as he moves around at home, and sends an emergency call for help in case of an occurrence of an accident or a severe health problem. The paper focuses on implementation details and practical considerations of integrating the diverse technologies into a working system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crilly, P. B., Arakawa, E. T., Hedden, D. L., & Ferrell, T. L. (1997). An integrated pulse oximeter system for telemedicine applications. IEEE Proceedings of Instrumentation and measurement Technology Conference, 1, 102–104.
Deni, H., Muratore, D. M., & Malkin, R. A. (2005). Development of a pulse oximeter analyzer for the developing world. IEEE Proceedings of 31st Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, pp. 227–228.
Dhem, J. F., & Feyt, N. (2001). Hardware and software symbiosis helps smart card evolution. IEEE Micro, 21(issue 6), 14–25.
Dresher, R. P., & Mendelson, Y. (2006). A new reflectance pulse oximeter housing to reduce contact pressure effects. IEEE Proceedings of 32nd Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference, pp. 49–50.
Hansmann, U., Merk, L., Nicklous, M. S., & Stober, T. (2003). Pervasive computing. New York: Springer.
Hung, K., Zhang, Y. T., & Tai, B. (2004). Wearable medical devices for tele-home healthcare. IEEE Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of Engineering Medicine and Biology Society, 2, 5384–5387.
Johnston, W. S., & Mendelson, Y. (2004). Extracting breathing rate information from a wearable reflectance pulse oximeter sensor. IEEE Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the Engineering Medicine and Biology Society, 2, 5388–5391.
Lin, K. J., Yu, T., & Shih, C. Y. (2005). The design of a personal and Intelligent pervasive-commerce system architecture. IEEE proceedings of the second international workshop on mobile commerce and services, pp. 163–173.
Lopera, J. M., Diaz, J., Prieto, M. J., & Nuno, F. (2002). Pulse oximeter for homecare. Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference and Annual Fall meeting of the Biomedical Engineering Society EMBS/BMED Conference, 2, 1738–1739.
Lukowicz, P., Anliker, U., Ward, J., Troster, G., Hirt, E., & Neufelt, C. (2002). AMON: A wearable medical computer for high risk patients. Proceedings of 6th international symposium on wearable computers, pp. 133–134.
Oliver, N., & Mangas, F. F. (2005). HealthGear: A real-time wearable system for monitoring and analyzing physiological signals. Technical report MSR-TR-2005-182.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge the support of King Fahad university Petroleum and Minerals for its support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raad, M.W., Yang, L.T. A ubiquitous smart home for elderly. Inf Syst Front 11, 529–536 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-008-9119-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-008-9119-y