Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate corneal endothelial cell changes following uncomplicated phacoemulsification in diabetic patients with PEX, compared with diabetic patients and non-diabetic patients with PEX.
Methods
This prospective, comparative, non-randomized cohort study included 61 eyes of 61 patients who were diagnosed as having senile cataract. Patients were divided into three groups: Group (1) included 19 eyes of patients with DM and PEX, group (2) included 22 eyes of diabetic patients, and group (3) included 20 eyes of patients with PEX. All included patients had uncomplicated phacoemulsification with IOL implantation. Patients were examined by non-contact specular microscopy (NIDEK, CEM-530, Japan), preoperatively and postoperatively at regular follow-up periods (one, three, and six months postoperatively) with analysis of the endothelial cell density, percentage of hexagonal cells, CV, and CCT.
Results
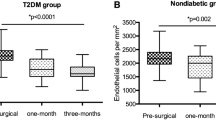
By the end of follow-up period, there was a statistically significant reduction in ECD and HEX with a significant increase in CV and CCT in group one (DM-PEX). In group two (DM), a statistically significant decrease in ECD and HEX with a significant increase in CCT was reported, while in group three (PEX), the only significant difference was found in the form of ECD reduction.
Conclusion
Patients with DM and PEX had significant changes regarding ECD, CV, HEX, and CCT which were more pronounced than in patients with DM only or PEX only. More attention should be paid while operating on diabetic patients with PEX to save corneal endothelium and decrease postoperative complications.
Study registration number
The study was retrospectively registered (16 July 2021) on ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04965168).
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Abbreviations
- PEX:
-
Pseudo-exfoliation syndrome
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- ECD:
-
Endothelial cell density
- CCT:
-
Central corneal thickness
- LOCS III:
-
Lens opacity classification system III
- HbA1c:
-
Hemoglobin A1c
- IOL:
-
Intra-ocular lens
- SPSS:
-
Statistical package for social sciences
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- HEX:
-
Percentage of hexagonality
- HC%:
-
Hexagonal cell percent
References
Storr-Paulsen A, Singh A, Jeppesen H, Norregaard JC, Thulesen J (2014) Corneal endothelial morphology and central thickness in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Acta Ophthalmol 92(2):158–160
Elhawy E, Kamthan G, Dong CQ, Danias J (2012) Pseudoexfoliation syndrome, a systemic disorder with ocular manifestations. Hum Genomics 6(1):22
Zheng X, Shiraishi A, Okuma S, Mizoue S, Goto T, Kawasaki S et al (2011) In vivo confocal microscopic evidence of keratopathy in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(3):1755–1761
Hayashi K, Manabe S, Yoshimura K, Kondo H (2013) Corneal endothelial damage after cataract surgery in eyes with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. J Cataract Refract Surg 39(6):881–887
Demircan S, Atas M, Yurtsever Y (2015) Effect of torsional mode phacoemulsification on cornea in eyes with/without pseudoexfoliation. Int J Ophthalmol 8(2):281–287
Wirbelauer C, Anders N, Pham DT, Wollensak J (1998) Corneal endothelial cell changes in pseudoexfoliation syndrome after cataract surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 116(2):145–149
Kaljurand K, Teesalu P (2007) Exfoliation syndrome as a risk factor for corneal endothelial cell loss in cataract surgery. Ann Ophthalmol (Skokie) 39(4):327–333
Kristianslund O, Pathak M, Østern AE, Drolsum L (2020) Corneal endothelial cell loss following cataract surgery in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome: a 2-year prospective comparative study. Acta Ophthalmol 98(4):337–342
Hegazi R, El-Gamal M, Abdel-Hady N, Hamdy O (2015) Epidemiology of and risk factors for type 2 diabetes in egypt. Ann Glob Health 81(6):814–820
Fernández-Muñoz E, Zamora-Ortiz R, Gonzalez-Salinas R (2019) Endothelial cell density changes in diabetic and nondiabetic eyes undergoing phacoemulsification employing phaco-chop technique. Int Ophthalmol 39(8):1735–1741
Gonen T, Sever O, Horozoglu F et al (2012) Endothelial cell loss: biaxial small-incision torsional phacoemulsification versus biaxial small-incision longitudinal phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg 38:1918–1924
Wang Y, Xia Y, Liu X et al (2012) Comparison of bimanual and micro-coaxial phacoemulsification with torsional ultrasound. Acta Ophthalmol 90:184–187
Sollosy M (2004) Incidence of the uveal pseudoexfoliation syndrome in patients with diabetes mellitus. Oftalmologia 48(1):76–80
Psilas KG, Stefaniotou MJ, Aspiotis MB (1991) Pseudoexfoliation syndrome and diabetes mellitus. Acta Ophthalmol 69(5):664–666
Manaviat MR, Rashidi M (2010) Pseudoexfoliation syndrome in diabetic patients. Iran J Diabetes Obes 2(1):7–11
Wang Y, Zhou Q, Xie L (2014) Diabetic keratopathy: new progresses and challenges. Chin J Ophthalmol 50(1):69–72
Yang R, Sha X, Zeng M, Tan Y, Zheng Y, Fan F (2011) The influence of phacoemulsification on corneal endothelial cells at varying blood glucose levels. Eye Sci 26(2):91–95
Hugod M, Storr-Paulsen A, Norregaard JC, Nicolini J, Larsen AB, Thulesen J (2011) Corneal endothelial cell changes associated with cataract surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cornea 30(7):749–753
Khan A, Kose S, Jharwal MK, Meena A, Sharma A (2016) Comparison of corneal endothelial cell counts in patients with controlled diabetes mellitus (type 2) and non-diabetics after phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation. Int Mulspec J Health 2(6):14–22
Elbassiouny O, Khalil A, Al Nahrawy O, Rashid A (2017) Corneal endothelial changes in correlation with corneal thickness after phacoemulsification among diabetic patients. Adv Ophthalmol Vis Syst 7(1):1–5
Østern AE, Drolsum L (2012) Corneal endothelial cells 6–7 years following cataract surgery in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol 90:408–411
Benetz B et al (2011) Specular microscopy. In: Krachmer J, Mannis M, Holland E (eds) Cornea. Elsevier Mosby, Philadelphia, pp 178–198
Budiman B (2020) Comparison of endothelial cell density, morphological changes and central corneal thickness after phacoemulsification between diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Open Ophthalmol J 14(1):15–20
Sahu P, Das G, Agrawal S et al (2017) Comparative evaluation of corneal endothelium in diabetic patients undergoing phacoemulsification. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 24:195–201
Lee JS, Lee JE, Choi HY, Oum BS, Cho BM (2005) Corneal endothelial cell change after phacoemulsification relative to the severity of diabetic retinopathy. J Cataract Refract Surg 31:742–749
Tang Y, Chen X, Zhang X, Tang Q, Liu S, Yao K (2017) Clinical evaluation of corneal changes after phacoemulsification in diabetic and non-diabetic cataract patients, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 7(1):14128
Taşlı NG, Icel E, Karakurt Y, Ucak T, Ugurlu A, Yilmaz H, Akbas EM (2020) The findings of corneal specular microscopy in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Ophthalmol 20(1):214
Morikubo S, Takamura Y, Kubo E, Tsuzuki S, Akagi Y (2004) Corneal changes after small-incision cataract surgery in patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Ophthalmol 122:966–969
El-Agamy A, Alsubaie S (2017) Corneal endothelium and central corneal thickness changes in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ophthalmol 11:481–486
Funding
No financial support was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors (MSM, IAN, and HRA) participated in this work through all its stages. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ophthalmology Department, Minia University, El‑Minia, Egypt.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the local research ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Research Ethics Committee “FMREC” (Approval No: 691:11/2020), and was adherent to the tents of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent to participate was obtained from all of the participants in current study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, M.SD., Omar, I.A.N. & AttaAllah, H.R. Evaluation of the corneal thickness and endothelial changes following uncomplicated phacoemulsification in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with pseudo-exfoliation syndrome by specular microscopy. Int Ophthalmol 43, 4773–4780 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02877-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02877-x