Abstract
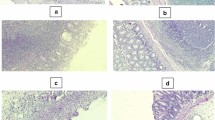
Euterpe oleracea Mart., commonly known as açaí, has been demonstrated to exhibit significantly antioxidant and inflammatory activities in experimental models. These effects of the hydroalcoholic extract from the açaí seed (ASE) were investigated in TNBS-induced (2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid) acute colitis model in rats. Wistar rats (180–220 g) were orally pretreated with saline (0.3 mL), ASE (10, 30 and 100 mg/kg) and dexamethasone (control group, 1 mg/kg) once daily for 3 days starting before TNBS instillation. On day 3 after TNBS, the animals were euthanized, the portion of distal colon was collected and washed with 0.9% saline for macroscopy and histological evaluation, glutathione (GSH) and malonyldialdehyde (MDA) levels, myeloperoxidase (MPO) and catalase (CAT) activity, nitrate and nitrite (NO3/NO2) concentration, pro-inflammatory cytokines levels and intestinal barrier integrity. We also evaluated Toll-like Receptor 4/cyclooxygenase-2/nuclear factor kappa B expression as a possible mechanism related to the ASE effects. Treatment with ASE 100 mg/kg decreased significantly macroscopic and microscopic damage induced by TNBS. In addition, MPO activity, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) and IL-1β (interleukin 1) levels were reduced in rats with colitis. ASE 100 mg/kg restored GSH and MDA levels, CAT activity, NO3/NO2 concentration and improved the intestinal barrier integrity in the TNBS group. ASE 100 mg/kg significantly reduced TNBS-induced expression of the TLR4, COX-2 and NF-κB p65. ASE 100 mg/kg improved macroscopy and histological parameters, inflammation, intestinal barrier integrity and nitric and oxidative stress through the TLR-4/COX-2/NF-κB pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleyard CB, Wallace JL (1995) Reactivation of hapten-induced colitis and its prevention by anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Physiol 269:119–125
Bourgonje AR, von Martels JZ, Bulthuis ML, van Londen M, Faber KN, Dijkstra G, van Goor H (2019) Crohn’s disease in clinical remission is marked by systemic oxidative stress. Front Physiol 10:499. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00499
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Investig Dermatol 78:206–209
Brito TV, Neto JP, Prudêncio RS, Batista JA, Júnior JS, Silva RO, Franco AX, Aragão KS, Soares PMG, Souza MHLP, Chaves LS, Freitas ALP, Medeiros JVR, Barbosa ALR (2014) Sulfated-polysaccharide fraction extracted from red algae Gracilaria birdiae ameliorates trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 66:1161–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12231
Brito TV, Barros FC, Silva RO, Júnior GJD, Júnior JSC, Franco AX, Souza MH (2016) Sulfated polysaccharide from the marine algae Hypnea musciformis inhibits TNBS-induced intestinal damage in rats. Carbohydr Polym 151:957–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.047
Brito TV, Júnior GJD, da Cruz Júnior JS, Silva RO, da Silva Monteiro CE, Franco AX, Vasconcelos DFP, Oliveira JS, Costa DVS, Carneiro TB, Duarte ASG, Souza MHLP, Soares PMG, Barbosa ALR (2020) Gabapentin attenuates intestinal inflammation: role of PPAR-gamma receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172974
Broad A, Kirby JA, Jones DE (2007) Toll-like receptor interactions: tolerance of MyD88-dependent cytokines but enhancement of MyD88-independent interferon-β production. Immunology 120:103–111
Cao SG, Chen R, Wang H, Lin LM, Xia XP (2018) Cryptotanshinone inhibits prostaglandin E2 production and COX-2 expression via suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in LPS-stimulated Caco-2 cells. Microb Pathog 116:313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.12.027
Capaldo CT, Nusrat A (2009) Cytokine regulation of tight junctions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:864–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.027
da Costa GF, Grings M, Nunes NS, Pinto FO, Garcez TNA, Visioli F, Paz AH (2017) Antioxidant properties of mesenchymal stem cells against oxidative stress in a murine model of colitis. Biotechnol Lett 39:613–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2272-3
de Carvalho LR, de Brito TV, Júnior JSDC, Júnior GJD, de Aguiar MD, Sousa SG, Silva RO, Silva FRP, Vasconcelos DFP, Véras LMC, Leite JRSA, Martins DS, Martins CS, Oliveira JS, Barbosa ALR (2018) Epiisopiloturine, an imidazole alkaloid, reverses inflammation and lipid peroxidation parameters in the Crohn disease model induced by trinitrobenzenosulfonic acid in Wistar rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.090
de Lima Yamaguchi KK, Pereira LFR, Lamarão CV, Lima ES, da Veiga-Junior VF (2015) Amazon acai: Chemistry and biological activities: a review. Food Chem 179:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.055
de Moura RS, Pires KMP, Ferreira TS, Lopes AA, Nesi RT, Resende AC, Valenca SS (2011) Addition of açaí (Euterpe oleracea) to cigarettes has a protective effect against emphysema in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 49:855–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.12.007
de Moura RS, Ferreira TS, Lopes AA, Pires KM, Nesi RT, Resende AC, Souza PJ, Silva AJ, Borges RM, Porto LC, Valenca SS (2012) Effects of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açaí) extract in acute lung inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in the mouse. Phytomedicine 19:262–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2011.11.004
de Oliveira PRB, da Costa CA, Graziele F, Cordeiro VS, Santos IB, de Carvalho LC, Martins GR (2015) Euterpe oleracea Mart. derived polyphenols protect mice from diet-induced obesity and fatty liver by regulating hepatic lipogenesis and cholesterol excretion. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143721
Del Pozo-Insfran D, Brenes CH, Talcott ST (2004) Phytochemical composition and pigment stability of Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.). J Agric Food Chem 52:1539–1545
Dias MMDS, Noratto G, Martino HSD, Arbizu S, Peluzio MDCG, Talcott S, Mertens-Talcott SU (2014a) Pro-apoptotic activities of polyphenolics from açai (Euterpe oleracea Martius) in human SW-480 colon cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 66:1394–1405. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2014.956252
Dias JM, Brito TV, Magalhães DA, Silva Santos PW, Batista JA, Nascimento Dias EG, de Barros FH, Damasceno SR, Silva RO, Aragão KS, Souza MH, Medeiros JV, Barbosa AL (2014b) Gabapentin, a synthetic analogue of gamma aminobutyric acid, reverses systemic acute inflammation and oxidative stress in mice. Inflammation 37:1826–1836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9913-2
Dong L, Li J, Liu Y, Yue W, Luo X (2012) Toll-like receptor 2 monoclonal antibody or/and Toll-like receptor 4 monoclonal antibody increase counts of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06839.x
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LSA, Van De Putte LB, Lipsky PE (1998) Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J 12:1063–1073
Farre R, van Malenstein H, De Vos R, Geboes K, Depoortere I, Berghe PV, Sifrim D (2008) Short exposure of oesophageal mucosa to bile acids, both in acidic and weakly acidic conditions, can impair mucosal integrity and provoke dilated intercellular spaces. Gut 57:1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2007.141804
Friedrich M, Pohin M, Powrie F (2019) Cytokine networks in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity 50:992–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.017
Fukata M, Chen A, Klepper A, Krishnareddy S, Vamadevan AS, Thomas LS, Abreu MT (2006) Cox-2 is regulated by Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling: role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine. Gastroenterology 131:862–877
Guan G, Lan S (2018) Implications of antioxidant systems in inflammatory bowel disease. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1290179
Heinzel FR, Gres P, Boengler K, Duschin A, Konietzka I, Rassaf T, Heusch G (2008) Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and cardiomyocyte dysfunction during sustained moderate ischemia in pigs. Circ Res 103:1120–1127. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.186015
Hofma BR, Wardill HR, Mavrangelos C, Campaniello MA, Dimasi D, Bowen JM, Hughes PA (2018) Colonic migrating motor complexes are inhibited in acute tri-nitro benzene sulphonic acid colitis. PLoS ONE 13:e0199394. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199394
Kuper C, Beck FX, Neuhofer W (2012) Toll-like receptor 4 activates NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways to regulate expression of proinflammatory COX-2 in renal medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 302:F38–F46. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00590.2010
Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH, Kim DS, Cho HJ (2004) Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2 upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Eur J Neurosci 19:3375–3381
Lee SH, eun Kwon J, Cho ML (2018) Immunological pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest Res 16:26. https://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.16.1.26
Lewis WE, Harris GK, Sanders TH, White BL, Dean LL (2013) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of peanut skin extracts. Food Nutr Sci 4:22. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2013.48A003
Li JH, Yu JP, Yu HG, Xu XM, Yu LL, Liu SQ (2005) Expression and significance of nuclear factor κB p65 in colon tissues of rats with TNBS-induced colitis. World J Gastroenterol 11:1759–1763
Liang B, Chen R, Wang T, Cao L, Liu Y, Yin F, Zhu M, Fan X, Liang Y, Zhang L, Guo Y, Zhao J (2013) Myeloid differentiation factor 88 promotes growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:2905–2916. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1245
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2:17023. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maehly AC, Chance B (1954) The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal 1:357–424
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2008) Redox control of cell fate by MAP kinase: physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:1325–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.12.011
Misko TP, Schilling RJ, Salvemini D, Moore WM, Currie MG (1993) A fluorometric assay for the measurement of nitrite in biological samples. Anal Biochem 214:11–16
Rocha APM, Carvalho LCRM, Sousa MAV, Madeira SVF, Sousa PJC, Tano T, Soares de Moura R (2007) Endothelium-dependent vasodilator effect of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açaí) extracts in mesenteric vascular bed of the rat. Vasc Pharmacol 46:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2006.08.411
Rodrigues RB, Lichtenthaler R, Zimmermann BF, Papagiannopoulos M, Fabricius H, Marx F, Maia JG, Almeida O (2006) Total oxidant scavenging capacity of Euterpe oleracea Mart. (acai) seeds and identification of their polyphenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 54:4162–4167
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Segal JP, Mullish BH, Quraishi MN, Acharjee A, Williams HR, Iqbal T, Marchesi JR (2019) The application of omics techniques to understand the role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756284818822250
Sgambato D, Miranda A, Ranaldo R, Federico A, Romano M (2017) The role of stress in inflammatory bowel diseases. Curr Pharm Des 23:3997–4002. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612823666170228123357
Silva RO, Oliveira FFB, Bingana RD, Arruda MO, Woodland P, Lee C, Souza MAN, Soares PMG, Santos AA, Sifrim D, Souza MHLP (2017) A novel murine model of esophageal nonerosive reflux disease: from inflammation to impairment in mucosal integrity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312:658–665. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00327.2016
Sottero B, Rossin D, Poli G, Biasi F (2018) Lipid oxidation products in the pathogenesis of inflammation-related gut diseases. Curr Med Chem 25:1311–1326. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170619104105
Strober W, Fuss IJ (2011) Proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 140:1756–1767. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.016
Sudo RT, Neto ML, Monteiro CE, Amaral RV, Resende ÂC, Souza PJ, Moura RS (2015) Antinociceptive effects of hydroalcoholic extract from Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açaí) in a rodent model of acute and neuropathic pain. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:208. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0724-2
Thompson AI, Lees CW (2011) Genetics of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17:831–848. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21375
Tong LC, Wang Y, Wang ZB, Liu WY, Sun S, Li L, Zhang LC (2016) Propionate ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Front Pharmacol 7:253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00253
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 86:271–278
Vancamelbeke M, Vermeire S (2017) The intestinal barrier: a fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:821–834. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2017.1343143
Vanheel H, Vicario M, Vanuytsel T, Oudenhove LV, Martinez C, Keita CA, Pardon N, Santos J, Söderholm DJ, Tack J, Farré R (2014) Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia. Gut 63:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303857
Wang W, Wang J (2018) Toll-Like receptor 4 (TLR4)/cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by NF-κB activation. Med Sci Monit 24:5588–5597. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.906857
Wang Z, Li R, Tan J, Peng L, Wang P, Liu J, Xiong H, Jiang B, Chen Y (2015) Syndecan-1 Acts in synergy with tight junction through Stat3 signaling to maintain intestinal mucosal barrier and prevent bacterial translocation. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21:1894–1907. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000000421
Wells JM, Brummer RJ, Derrien M, MacDonald TT, Troost F, Cani PD, Mercenier A (2016) Homeostasis of the gut barrier and potential biomarkers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312:G171–G193. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00048.2015
Wright HL, Moots RJ, Bucknall RC, Edwards SW (2010) Neutrophil function in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Rheumatology 49:1618–1631. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq045
Xie QW, Kashiwabara Y, Nathan C (1994) Role of transcription factor NF-κB/Rel in induction of nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 269:4705–4708
Yang J, Liu XX, Fan H, Tang Q, Shou ZX, Zuo DM, Deng SJ (2015) Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against experimental colitis via attenuating colon inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 10:e0140551. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140551
Zhao Y, Liu X, Qu Y, Wang L, Geng D, Chen W, Zhao X (2019) The roles of p38 MAPK → COX2 and NF-κB → COX2 signal pathways in age-related testosterone reduction. Sci Rep 9:10556. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46794-5
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação Cearense de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (Award number: 301981/2016-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by CM, HF, FS, MS, JS, ÁF, ÂR, RM, MS, PS, AB. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Carlos Monteiro and André Barbosa, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Roberto Soares de Moura is the inventor of a patent (PCT/BR0200038) that supported the development of a new patent application (PCT/BR2007/000178). The other authors state no declaration of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, C.E.d.S., Filho, H.B.d.C., Silva, F.G.O. et al. Euterpe oleracea Mart. (Açaí) attenuates experimental colitis in rats: involvement of TLR4/COX-2/NF-ĸB. Inflammopharmacol 29, 193–204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00763-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00763-x