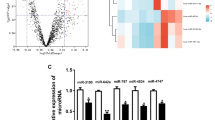
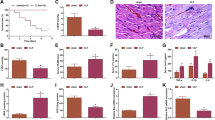
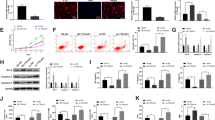
Abstract
Sepsis is an infectious disease that seriously endangers human health. It usually leads to myocardial injury which seriously endangers to the health of human beings. H19 has been confirmed to play key roles in various diseases, including sepsis. However, its function in the progression of sepsis-induced myocardial injury remains largely unknown. H9C2 cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to mimic sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vitro. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were detected by MTT assay and flow cytometry, respectively. In addition, gene and protein expression levels in H9C2 cells were measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blotting. The levels of inflammatory cytokines in H9C2 cell supernatants were tested by ELISA. JC-1 staining was performed to observe the mitochondrial membrane potential level in H9C2 cells. H19 and SORBS2 were downregulated in H9C2 cells following LPS treatment, while miR-93-5p was upregulated. Moreover, LPS-induced cell growth inhibition and mitochondrial damage were significantly reversed by overexpression of H19. In addition, H19 upregulation notably suppressed LPS-induced inflammatory responses in H9C2 cells. Moreover, H19 sponged miR-93-5p to promote SORBS2 expression. Overall, H19 suppressed sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulation of the miR-93-5p/SORBS2 axis. H19 attenuated the development of sepsis-induced myocardial injury in vitro via modulation of the miR-93-5p/SORBS2 axis. Thus, H19 could serve as a potential target for the treatment of sepsis-induced myocardial injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- SORBS2:
-
sorbin and SH3 domain-containing 3
- MiR-93-5p:
-
microRNA-93-5p
- LncRNA H19:
-
long noncoding RNA H19
- FBS:
-
foetal bovine serum
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- cTnT:
-
cardiac troponin T
- TNF-α:
-
tumour necrosis factor-α
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1β
References
Candel, F.J., M. Borges Sa, S. Belda, G. Bou, J.L. Del Pozo, O. Estrada, et al. 2018. Current aspects in sepsis approach. Turning things around. Revista espanola de quimioterapia : publicacion oficial de la Sociedad Espanola de Quimioterapia. 31 (4): 298–315.
Rhee, C., M.V. Murphy, L. Li, R. Platt, and M. Klompas. 2015. Centers for disease C, et al. comparison of trends in sepsis incidence and coding using administrative claims versus objective clinical data. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 60 (1): 88–95.
Prescott, H.C., T.M. Cope, F.C. Gesten, T.A. Ledneva, M.E. Friedrich, T.J. Iwashyna, T.M. Osborn, C.W. Seymour, and M.M. Levy. 2018. Reporting of sepsis cases for performance measurement versus for reimbursement in New York state. Critical care medicine. 46 (5): 666–673.
Faix, J.D. 2013. Biomarkers of sepsis. Critical reviews in clinical laboratory sciences. 50 (1): 23–36.
Souto FO, Castanheira FVS, Trevelin SC, Lima BHF, Cebinelli GCM, Turato WM, et al. Liver X receptor activation impairs neutrophil functions and aggravates sepsis. The Journal of infectious diseases. 2019.
Li D, Cheng Y, Yu J, Jia Y, Liu B, Xia Y, et al. Thrombo-inflammatory prognostic score improves qSOFA for risk stratification in patients with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. 2019.
Rello, J., F. Valenzuela-Sanchez, M. Ruiz-Rodriguez, and S. Moyano. 2017. Sepsis: A review of advances in management. Advances in therapy. 34 (11): 2393–2411.
Cui, C., D. Zhai, L. Cai, Q. Duan, L. Xie, and J. Yu. 2018. Long noncoding RNA HEIH promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis via counteracting miR-939 mediated transcriptional repression of Bcl-xL. Cancer research and treatment : official journal of Korean Cancer Association. 50 (3): 992–1008.
Muret, K., C. Klopp, V. Wucher, D. Esquerre, F. Legeai, F. Lecerf, et al. 2017. Long noncoding RNA repertoire in chicken liver and adipose tissue. Genetics, Selection, Evolution: GSE 49 (1): 6.
Wu, Z.Y., M. Trenner, R.A. Boon, J.M. Spin, and L. Maegdefessel. 2019. Long noncoding RNAs in key cellular processes involved in aortic aneurysms. Atherosclerosis. 292: 112–118.
Fang, K., C. Hu, X. Zhang, Y. Hou, D. Gao, Z. Guo, and L. Li. 2019. LncRNA ST8SIA6-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in breast cancer through the p38 MAPK ssignalling pathway. Carcinogenesis.
Rao, N., X. Wang, J. Xie, J. Li, Y. Zhai, X. Li, et al. 2019. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting advanced glycation end product-activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Stem Cells International 2019: 2751475.
Hu, H., J. Wu, X. Yu, J. Zhou, H. Yu, and L. Ma. 2019. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 enhances the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes through autophagy inhibition by regulating TSC2-mTOR signaling. Biological Research 52 (1): 58.
Luo, Y., L. Huang, W. Luo, S. Ye, and Q. Hu. 2019. Genomic analysis of lncRNA and mRNA profiles in circulating exosomes of patients with rheumatic heart disease. Biology open. 8: bio045633.
Xue, P., J. Zhao, A. Zheng, L. Li, H. Chen, W. Tu, N. Zhang, Z. Yu, Q. Wang, and M. Gu. 2019. Chrysophanol alleviates myocardial injury in diabetic db/db mice by regulating the SIRT1/HMGB1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 18 (6): 4406–4412.
Xing, P.C., P. An, G.Y. Hu, D.L. Wang, and M.J. Zhou. 2020. LncRNA MIAT promotes inflammation and oxidative stress in sepsis-induced cardiac injury by targeting miR-330-5p/TRAF6/NF-kappaB axis. Biochemical Genetics 58: 783–800.
Zhu, Y., A. Sun, T. Meng, and H. Li. 2020. Protective role of long noncoding RNA CRNDE in myocardial tissues from injury caused by sepsis through the microRNA-29a/SIRT1 axis. Life Sciences 255: 117849.
Zhang, B.F., H. Jiang, J. Chen, Q. Hu, S. Yang, X.P. Liu, et al. 2019. LncRNA H19 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury and maladaptive cardiac remodelling by regulating KDM3A. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine.
Cui, C., X. Chen, W. Du, L. Jing, L. Shi, D. Xia, et al. 2020. Correlations of inflammation, oxidative stress and prognosis with expression of LncRNA H19 in rats with sepsis-evoked lung injury. Panminerva Medica.
Wang, X., Y. Zhang, S. Han, Y. Yin, C. Chen, H. Chen, et al. 2019. LncRNA H19 inhibits kidney injury in sepsis rats through MAPK pathway. Minerva Medica.
Fang, Y., J. Hu, Z. Wang, H. Zong, L. Zhang, R. Zhang, et al. 2018. LncRNA H19 functions as an aquaporin 1 competitive endogenous RNA to regulate microRNA-874 expression in LPS sepsis. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 105: 1183–1191.
Valera, V.A., R. Parra-Medina, B.A. Walter, P. Pinto, and M.J. Merino. 2020. microRNA expression profiling in young prostate cancer patients. Journal of Cancer 11 (14): 4106–4114.
Hua, Q., Y. Chen, Y. Liu, M. Li, Q. Diao, H. Xue, H. Zeng, L. Huang, and Y. Jiang. 2019. Circular RNA 0039411 is involved in neodymium oxide-induced inflammation and antiproliferation in a human bronchial epithelial cell line via sponging miR-93-5p. Toxicological Sciences 170 (1): 69–81.
Zhang, S., Y. He, C. Liu, G. Li, S. Lu, Q. Jing, X. Chen, H. Ma, D. Zhang, Y. Wang, D. Huang, P. Tan, J. Chen, X. Zhang, Y. Liu, and Y. Qiu. 2020. miR-93-5p enhances migration and invasion by targeting RGMB in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Journal of Cancer 11 (13): 3871–3881.
JF OS, Neylon A, McGorrian C, Blake GJ. 2016. miRNA-93-5p and other miRNAs as predictors of coronary artery disease and STEMI. International Journal of Cardiology 224: 310–316.
Liu, J., M. Jiang, S. Deng, J. Lu, H. Huang, Y. Zhang, et al. 2018. miR-93-5p-containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 11: 103–115.
Yan, B., Z. Peng, and C. Xing. 2019. SORBS2, mediated by MEF2D, suppresses the metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibitiing the c-Abl-ERK signaling pathway. American Journal of Cancer Research 9 (12): 2706–2718.
Zhao, L., W. Wang, S. Huang, Z. Yang, L. Xu, Q. Yang, X. Zhou, J. Wang, Q. Shen, C. Wang, X. le, M. Feng, N. Zhou, W.B. Lau, B. Lau, S. Yao, T. Yi, X. Wang, X. Zhao, Y. Wei, and S. Zhou. 2018. The RNA binding protein SORBS2 suppresses metastatic colonization of ovarian cancer by stabilizing tumor-suppressive immunomodulatory transcripts. Genome Biology 19 (1): 35.
Li, C., F. Liu, S. Liu, H. Pan, H. Du, J. Huang, et al. 2020. Elevated myocardial SORBS2 and the underlying implications in left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy. EBioMedicine. 53: 102695.
Wang, H., Y. Bei, S. Shen, P. Huang, J. Shi, J. Zhang, et al. 2016. miR-21-3p controls sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 94: 43–53.
Sun, F., W. Yuan, H. Wu, G. Chen, Y. Sun, L. Yuan, W. Zhang, and M. Lei. 2020. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-192-5p/XIAP axis. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood, N.J.) 245 (7): 620–630.
Guo, Y., J. Ni, S. Chen, M. Bai, J. Lin, G. Ding, Y. Zhang, P. Sun, Z. Jia, S. Huang, L. Yang, and A. Zhang. 2018. MicroRNA-709 mediates acute tubular injury through effects on mitochondrial function. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN. 29 (2): 449–461.
Essandoh, K., X. Wang, W. Huang, S. Deng, G. Gardner, X. Mu, Y. Li, E.G. Kranias, Y. Wang, and G.C. Fan. 2019. Tumor susceptibility gene 101 ameliorates endotoxin-induced cardiac dysfunction by enhancing Parkin-mediated mitophagy. The Journal of biological chemistry. 294 (48): 18057–18068.
Zhang J, Wang L, Xie W, Hu S, Zhou H, Zhu P, et al. Melatonin attenuates ER stress and mitochondrial damage in septic cardiomyopathy: A new mechanism involving BAP31 upregulation and MAPK-ERK pathway. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2019.
Denning, N.L., M. Aziz, S.D. Gurien, and P. Wang. 2019. DAMPs and NETs in sepsis. Frontiers in immunology. 10: 2536.
Harrington, J.S., A.M.K. Choi, and K. Nakahira. 2017. Mitochondrial DNA in sepsis. Current opinion in critical care. 23 (4): 284–290.
Supinski GS, Schroder EA, Callahan LA. Mitochondria and critical illness. Chest. 2019.
Liu, Y., W. Yang, X. Sun, L. Xie, Y. Yang, M. Sang, and R. Jiao. 2019. SS31 ameliorates sepsis-induced heart injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation. 42 (6): 2170–2180.
Wang, Y.P., J. Liu, D. Liu, X.D. Wang, A.M. Bian, D.Z. Fang, and X.B. Hui. 2019. MiR-532-5p acts as a tumor suppressor and inhibits glioma cell proliferation by targeting CSF1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 23 (20): 8964–8970.
Huang, M.C., Y.H. Chou, H.P. Shen, S.C. Ng, Y.C. Lee, Y.H. Sun, C.F. Hsu, S.F. Yang, and P.H. Wang. 2019. The clinicopathological characteristic associations of long non-coding RNA gene H19 polymorphisms with uterine cervical cancer. Journal of Cancer. 10 (25): 6191–6198.
Liu ZZ, Tian YF, Wu H, Ouyang SY, Kuang WL. LncRNA H19 promotes glioma angiogenesis through miR-138/HIF-1alpha/VEGF axis. Neoplasma. 2019.
Ye, Y., A. Shen, and A. Liu. 2019. Long non-coding RNA H19 and cancer: A competing endogenous RNA. Bulletin du cancer. 106: 1152–1159.
Bi, Y., Y. Fu, S. Wang, X. Chen, and X. Cai. 2019. Schizandrin A exerts anti-tumor effects on A375 cells by down-regulating H19. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research = Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas 52 (10): e8385.
Safi, R., T. Mohsen-Kanson, G. Nemer, B. Dekmak, N. Rubeiz, M. El-Sabban, et al. 2019. Loss of ferrochelatase is protective against colon cancer cells: Ferrochelatase a possible regulator of the long noncoding RNA H19. Journal of gastrointestinal oncology. 10 (5): 859–868.
Wu, H., L. Liu, and J.M. Zhu. 2019. MiR-93-5p inhibited proliferation and metastasis of glioma cells by targeting MMP2. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences. 23 (21): 9517–9524.
Liu, Z.M., X.L. Yang, F. Jiang, Y.C. Pan, and L. Zhang. 2019. Matrine involves in the progression of gastric cancer through inhibiting miR-93-5p and upregulating the expression of target gene AHNAK. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.
Huang, W., Y. Yang, J. Wu, Y. Niu, Y. Yao, J. Zhang, et al. 2019. Circular RNA cESRP1 sensitises small cell lung cancer cells to chemotherapy by sponging miR-93-5p to inhibit TGF-beta signalling. Cell death and differentiation.
Li, J.P., Y. Xiang, L.J. Fan, A. Yao, H. Li, and X.H. Liao. 2019. Long noncoding RNA H19 competitively binds miR-93-5p to regulate STAT3 expression in breast cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 120 (3): 3137–3148.
Han, L., C. Huang, and S. Zhang. 2019. The RNA-binding protein SORBS2 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma tumourigenesis and metastasis by stabilizing RORA mRNA. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 39 (11): 2190–2203.
Ma, N., J. Pan, X. Ye, B. Yu, W. Zhang, and J. Wan. 2019. Whole-transcriptome analysis of APP/PS1 mouse brain and identification of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks to investigate AD pathogenesis. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids. 18: 1049–1062.
Wang, L., L.F. Song, X.Y. Chen, Y.L. Ma, J.F. Suo, J.H. Shi, and G.H. Chen. 2019. MiR-181b inhibits P38/JNK signaling pathway to attenuate autophagy and apoptosis in juvenile rats with kainic acid-induced epilepsy via targeting TLR4. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 25 (1): 112–122.
Fredriksson-Lidman, K., C.M. Van Itallie, A.J. Tietgens, and J.M. Anderson. 2017. Sorbin and SH3 domain-containing protein 2 (SORBS2) is a component of the acto-myosin ring at the apical junctional complex in epithelial cells. PLoS One 12 (9): e0185448.
Ichikawa, T., M. Kita, T.S. Matsui, A.I. Nagasato, T. Araki, S.H. Chiang, T. Sezaki, Y. Kimura, K. Ueda, S. Deguchi, A.R. Saltiel, and N. Kioka. 2017. Vinexin family (SORBS) proteins play different roles in stiffness-sensing and contractile force generation. Journal of cell science. 130 (20): 3517–3531.
Teyra, J., H. Huang, S. Jain, X. Guan, A. Dong, Y. Liu, W. Tempel, J. Min, Y. Tong, P.M. Kim, G.D. Bader, and S.S. Sidhu. 2017. Comprehensive analysis of the human SH3 domain family reveals a wide variety of non-canonical specificities. Structure. 25 (10): 1598–1610 e3.
Fan, J., Y.C. Zhang, D.F. Zheng, M. Zhang, H. Liu, M. He, et al. 2019. IL-27 is elevated in sepsis with acute hepatic injury and promotes hepatic damage and inflammation in the CLP model. Cytokine. 127: 154936.
Zhuang, Y.T., D.Y. Xu, G.Y. Wang, J.L. Sun, Y. Huang, and S.Z. Wang. 2017. IL-6 induced lncRNA MALAT1 enhances TNF-alpha expression in LPS-induced septic cardiomyocytes via activation of SAA3. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences. 21 (2): 302–309.
Qu, Y., Q. Sun, X. Song, Y. Jiang, H. Dong, W. Zhao, et al. 2019. Helix B surfacepeptide reduces sepsis-induced kidney injury via PI3K/Akt pathway. Nephrology.
Funding
We thank the support of the funding obtained from Chenzhou Bureau of Science and Technology (ZDYF2020095 and ZDYF201941).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: Bin Shan, Liang-Xian Luo.
Study concepts: Bin Shan.
Study design: Bin Shan, Liang-Xian Luo.
Definition of intellectual content: Bin Shan, Jia-Yan Li.
Literature research: Bin Shan, Jia-Yan Li, Ya-Jiang Liu.
Experimental studies: Ya-Jiang Liu, Xiao-Bin Tang, Zheng Zhou.
Data acquisition: Bin Shan, Zheng Zhou.
Data analysis: Xiao-Bin Tang, Zheng Zhou.
Statistical analysis: Xiao-Bin Tang, Zheng Zhou.
Manuscript preparation: Bin Shan, Liang-Xian Luo.
Manuscript editing: Bin Shan, Liang-Xian Luo.
Manuscript review: Bin Shan, Liang-Xian Luo.
All the authors approved for the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
The informed consent was obtained from the study participants.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, B., Li, JY., Liu, YJ. et al. LncRNA H19 Inhibits the Progression of Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury via Regulation of the miR-93-5p/SORBS2 Axis. Inflammation 44, 344–357 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01340-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01340-8