Abstract
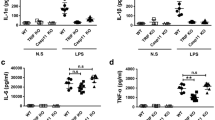
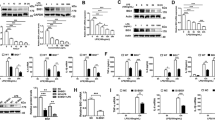
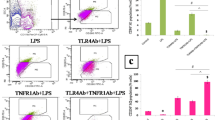
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK1) is a key regulatory protein in TLR/IL1R-mediated cell activation during inflammatory response. Studies indicated that pending on the nature of the used inflammatory model, downregulation of IRAK1 may be beneficial or detrimental. However, the role of IRAK1 in affecting outcome in polymicrobial sepsis is unknown. We tested this question using an IRAK1-deficient mouse strain and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) procedure, which is a clinically relevant rodent septic model. Sepsis-induced mortality was markedly lower in IRAK1-deficient mice (35 %) compared to WT (85 %). Sepsis-induced increases in blood IL-6 and IL-10 levels were blunted at 6 h post-CLP in IRAK1 deficiency compared to WT, but cytokine levels were similar at 20 h post-CLP. Sepsis-induced blood granulocytosis and depletion of splenic B cells were also blunted in IRAK1-deficient mice as compared to WT. Analysis of TLR-mediated cytokine responses by IRAK1-deficient and WT macrophages ex vivo indicated a TLR4-dependent downregulation of IL-6 and IL1β in IRAK1 deficiency, whereas TLR2-dependent responses were unaffected. TLR7/8-mediated IL-6, IL1β, and IL-10 production was also blunted in IRAK1 macrophages as compared to WT. The study shows that IRAK1 deficiency impacts multiple TLR-dependent pathways and decreases early cytokine responses following polymicrobial sepsis. The delayed inflammatory response caused by the lack of IRAK1 expression is beneficial, as it manifests a marked increased chance of survival after polymicrobial sepsis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
- PMN:
-
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils
- BM:
-
Bone marrow
References
Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature Reviews Immunology 4: 499–511.
Gottipati, S., N.L. Rao, and W.P. Fung-Leung. 2008. IRAK1: A critical signaling mediator of innate immunity. Cellular Signalling 20: 269–276.
Janssens, S., and R. Beyaert. 2003. Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members. Molecular Cell 11: 293–302.
Thomas, J.A., J.L. Allen, M. Tsen, T. Dubnicoff, J. Danao, X.C. Liao, Z. Cao, and S.A. Wasserman. 1999. Impaired cytokine signaling in mice lacking the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase. Journal of Immunology 163: 978–984.
Tiwari, R.L., V. Singh, A. Singh, and M.K. Barthwal. 2011. IL-1R-associated kinase-1 mediates protein kinase Cdelta-induced IL-1beta production in monocytes. Journal of Immunology 187: 2632–2645.
Huang, Y., T. Li, D.C. Sane, and L. Li. 2004. IRAK1 serves as a novel regulator essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-10 gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 51697–51703.
Uematsu, S., S. Sato, M. Yamamoto, T. Hirotani, H. Kato, F. Takeshita, M. Matsuda, C. Coban, K.J. Ishii, T. Kawai, O. Takeuchi, and S. Akira. 2005. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 plays an essential role for Toll-like receptor (TLR)7- and TLR9-mediated interferon-{alpha} induction. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 201: 915–923.
Liu, Y.C., D.P. Simmons, X. Li, D.W. Abbott, W.H. Boom, and C.V. Harding. 2012. TLR2 signaling depletes IRAK1 and inhibits induction of type I IFN by TLR7/9. Journal of Immunology 188: 1019–1026.
Thomas, J.A., M.F. Tsen, D.J. White, and J.W. Horton. 2002. IRAK contributes to burn-triggered myocardial contractile dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology 283: H829–H836.
Thomas, J.A., S.B. Haudek, T. Koroglu, M.F. Tsen, D.D. Bryant, D.J. White, D.F. Kusewitt, J.W. Horton, and B.P. Giroir. 2003. IRAK1 deletion disrupts cardiac Toll/IL-1 signaling and protects against contractile dysfunction. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology 285: H597–H606.
Deng, C., C. Radu, A. Diab, M.F. Tsen, R. Hussain, J.S. Cowdery, M.K. Racke, and J.A. Thomas. 2003. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 regulates susceptibility to organ-specific autoimmunity. Journal of Immunology 170: 2833–2842.
Jacob, C.O., J. Zhu, D.L. Armstrong, M. Yan, J. Han, X.J. Zhou, J.A. Thomas, A. Reiff, B.L. Myones, J.O. Ojwang, K.M. Kaufman, M. Klein-Gitelman, D. McCurdy, L. Wagner-Weiner, E. Silverman, J. Ziegler, J.A. Kelly, J.T. Merrill, J.B. Harley, R. Ramsey-Goldman, L.M. Vila, S.C. Bae, T.J. Vyse, G.S. Gilkeson, P.M. Gaffney, K.L. Moser, C.D. Langefeld, R. Zidovetzki, and C. Mohan. 2009. Identification of IRAK1 as a risk gene with critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 6256–6261.
Swantek, J.L., M.F. Tsen, M.H. Cobb, and J.A. Thomas. 2000. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase modulates host responsiveness to endotoxin. Journal of Immunology 164: 4301–4306.
Albrecht, V., T.P. Hofer, B. Foxwell, M. Frankenberger, and L. Ziegler-Heitbrock. 2008. Tolerance induced via TLR2 and TLR4 in human dendritic cells: Role of IRAK-1. BMC Immunology 9: 69.
Xiong, Y., F. Qiu, W. Piao, C. Song, L.M. Wahl, and A.E. Medvedev. 2011. Endotoxin tolerance impairs IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 and TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 activation, K63-linked polyubiquitination and assembly of IRAK1, TNF receptor-associated factor 6, and IkappaB kinase gamma and increases A20 expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 286: 7905–7916.
Verdrengh, M., J.A. Thomas, and O.H. Hultgren. 2004. IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 mediates protection against Staphylococcus aureus infection. Microbes and Infection 6: 1268–1272.
Ebong, S., D. Call, J. Nemzek, G. Bolgos, D. Newcomb, and D. Remick. 1999. Immunopathologic alterations in murine models of sepsis of increasing severity. Infection and Immunity 67: 6603–6610.
Remick, D.G., D.E. Newcomb, G.L. Bolgos, and D.R. Call. 2000. Comparison of the mortality and inflammatory response of two models of sepsis: Lipopolysaccharide vs. cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 13: 110–116.
Remick, D.G., and P.A. Ward. 2005. Evaluation of endotoxin models for the study of sepsis. Shock 24(Suppl 1): 7–11.
Baker, C.C., I.H. Chaudry, H.O. Gaines, and A.E. Baue. 1983. Evaluation of factors affecting mortality-rate after sepsis in a murine cecal ligation and puncture model. Surgery 94: 331–335.
Chandra, R., S. Federici, Z.H. Nemeth, B. Horvath, P. Pacher, G. Hasko, E.A. Deitch, and Z. Spolarics. 2011. Female X-chromosome mosaicism for NOX2 deficiency presents unique inflammatory phenotype and improves outcome in polymicrobial sepsis. Journal of Immunology 186: 6465–6473.
Nemeth, Z.H., B. Csoka, J. Wilmanski, D. Xu, Q. Lu, C. Ledent, E.A. Deitch, P. Pacher, Z. Spolarics, and G. Hasko. 2006. Adenosine A2A receptor inactivation increases survival in polymicrobial sepsis. Journal of Immunology 176: 5616–5626.
Wilmanski, J., M. Siddiqi, E.A. Deitch, and Z. Spolarics. 2005. Augmented IL-10 production and redox-dependent signaling pathways in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient mouse peritoneal macrophages. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 78: 85–94.
Chandra, R., E. Villanueva, E. Feketova, G.W. Machiedo, G. Hasko, E.A. Deitch, and Z. Spolarics. 2008. Endotoxemia down-regulates bone marrow lymphopoiesis but stimulates myelopoiesis: the effect of G6PD deficiency. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 83: 1541–1550.
Deitch, E.A. 2005. Rodent models of intra-abdominal infection. Shock 24(Suppl 1): 19–23.
Dejager, L., I. Pinheiro, E. Dejonckheere, and C. Libert. 2011. Cecal ligation and puncture: the gold standard model for polymicrobial sepsis? Trends in Microbiology 19: 198–208.
Remick, D.G., G.R. Bolgos, J. Siddiqui, J. Shin, and J.A. Nemzek. 2002. Six at six: interleukin-6 measured 6 h after the initiation of sepsis predicts mortality over 3 days. Shock 17: 463–467.
Remick, D.G., G. Bolgos, S. Copeland, and J. Siddiqui. 2005. Role of interleukin-6 in mortality from and physiologic response to sepsis. Infection and Immunity 73: 2751–2757.
Kotake, Y., D.R. Moore, A. Vasquez-Walden, T. Tabatabaie, and H. Sang. 2003. Antioxidant amplifies antibiotic protection in the cecal ligation and puncture model of microbial sepsis through interleukin-10 production. Shock 19: 252–256.
Hiraki, S., S. Ono, H. Tsujimoto, M. Kinoshita, R. Takahata, H. Miyazaki, D. Saitoh, and K. Hase. 2012. Neutralization of interleukin-10 or transforming growth factor-beta decreases the percentages of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in septic mice, thereby leading to an improved survival. Surgery 151: 313–322.
Toubiana, J., E. Courtine, F. Pene, V. Viallon, P. Asfar, C. Daubin, C. Rousseau, C. Chenot, F. Ouaaz, D. Grimaldi, A. Cariou, J.D. Chiche, and J.P. Mira. 2010. IRAK1 functional genetic variant affects severity of septic shock. Critical Care Medicine 38: 2287–2294.
Arcaroli, J., E. Silva, J.P. Maloney, Q. He, D. Svetkauskaite, J.R. Murphy, and E. Abraham. 2006. Variant IRAK-1 haplotype is associated with increased nuclear factor-kappaB activation and worse outcomes in sepsis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 173: 1335–1341.
Lye, E., C. Mirtsos, N. Suzuki, S. Suzuki, and W.C. Yeh. 2004. The role of interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4) kinase activity in IRAK-4-mediated signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 40653–40658.
Souto, F.O., J.C. Alves-Filho, W.M. Turato, M. Auxiliadora-Martins, A. Basile-Filho, and F.Q. Cunha. 2011. Essential role of CCR2 in neutrophil tissue infiltration and multiple organ dysfunction in sepsis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 183: 234–242.
Andrades, M., C. Ritter, M.R. de Oliveira, E.L. Streck, J.C. Fonseca Moreira, and F. Dal-Pizzol. 2011. Antioxidant treatment reverses organ failure in rat model of sepsis: role of antioxidant enzymes imbalance, neutrophil infiltration, and oxidative stress. Journal of Surgical Research 167: e307–e313.
Iwata, A., R.A. de Claro, V.L. Morgan-Stevenson, J.C. Tupper, B.R. Schwartz, L. Liu, X. Zhu, K.C. Jordan, R.K. Winn, and J.M. Harlan. 2011. Extracellular administration of BCL2 protein reduces apoptosis and improves survival in a murine model of sepsis. PLoS One 6: e14729.
Hotchkiss, R.S., K.C. Chang, P.E. Swanson, K.W. Tinsley, J.J. Hui, P. Klender, S. Xanthoudakis, S. Roy, C. Black, E. Grimm, R. Aspiotis, Y. Han, D.W. Nicholson, and I.E. Karl. 2000. Caspase inhibitors improve survival in sepsis: a critical role of the lymphocyte. Nature Immunology 1: 496–501.
Hotchkiss, R.S., K.W. Tinsley, P.E. Swanson, R.E. Schmieg, J.J. Hui, K.C. Chang, D.F. Osborne, B.D. Freeman, J.P. Cobb, T.G. Buchman, and I.E. Karl. 2001. Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive profound depletion of B and CD4(+) T lymphocytes in humans. Journal of Immunology 166: 6952–6963.
Berglund, M., J.A. Thomas, E.H. Hornquist, and O.H. Hultgren. 2008. Toll-like receptor cross-hyporesponsiveness is functional in interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1)-deficient macrophages: Differential role played by IRAK-1 in regulation of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-10 production. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 67: 473–479.
Kawagoe, T., S. Sato, K. Matsushita, H. Kato, K. Matsui, Y. Kumagai, T. Saitoh, T. Kawai, O. Takeuchi, and S. Akira. 2008. Sequential control of Toll-like receptor-dependent responses by IRAK1 and IRAK2. Nature Immunology 9: 684–691.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH-NIGMS grant GM084932.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, R., Federici, S., Bishwas, T. et al. IRAK1-Dependent Signaling Mediates Mortality in Polymicrobial Sepsis. Inflammation 36, 1503–1512 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9692-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9692-1