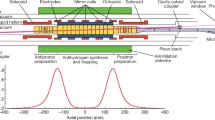
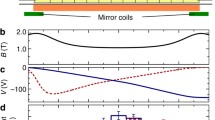
Abstract
Detailed comparisons of antihydrogen with hydrogen promise to be a fruitful test bed of fundamental symmetries such as the CPT theorem for quantum field theory or studies of gravitational influence on antimatter. With a string of recent successes, starting with the first trapped antihydrogen and recently resulting in the first measurement of a quantum transition in anti-hydrogen, the ALPHA collaboration is well on its way to perform such precision comparisons. We will discuss the key innovative steps that have made these results possible and in particular focus on the detailed work on positron and antiproton preparation to achieve antihydrogen cold enough to trap as well as the unique features of the ALPHA apparatus that has allowed the first quantum transitions in anti-hydrogen to be measured with only a single trapped antihydrogen atom per experiment. We will also look at how ALPHA plans to step from here towards more precise comparisons of matter and antimatter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madsen, N.: Cold antihydrogen: a new frontier in fundamental physics. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. A. 368, 3671–3682 (2010)
Shore, G.M.: Strong equivalence, Lorentz and CPT violation, anti-hydrogen spectroscopy and gamma-ray burst polarimetry . Nucl. Phys. B 717, 86–118 (2005)
Maury, S.: The antiproton decelerator: AD. Hyp. Int. 109, 43–52 (1997)
Amoretti, M., et al.: (ATHENA), production and detection of cold antihydrogen atoms. Nature 419, 456–459 (2002)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), trapped antihydrogen. Nature 468, 673–676 (2010)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), confinement of antihydrogen for 1,000 seconds. Nat. Phys. 7, 558–564 (2011)
Amole, C., et al.: (ALPHA), resonant quantum transitions in trapped antihydrogen atoms. Nature 483, 439–443 (2012)
ALPHA Collab, Charman, A.E.: Description and first application of a new technique to measure the gravitational mass of antihydrogen. Nat. Comm. 4, 1785 (2013)
Madsen, N., et al.: (ATHENA), spatial distribution of cold antihydrogen formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 033403, 94 (2005)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), compression of antiproton clouds for antihydrogen trapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 203401 (2008)
Eggleston, D.L., et al.: Parallel energy analyzer for pure electron plasma devices. Phys. Fluids. B. 4, 3432–3439 (1992)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), antiproton, positron, and electron imaging with a microchannel plate/phosphor detector. Rev. Sci. Inst. 80, 123701 (2009)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), evaporative cooling of antiprotons to cryogenic temperatures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 013003 (2010)
Fajans, J., et al.: Effects of extreme magnetic quadrupole fields on penning traps and the consequences for antihydrogen trapping
Fajans, J., Madsen, N., Robicheaux, F.: Critical loss radius in a Penning trap subject to multipole fields. Phys. Plas. 15, 032108 (2008)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), autoresonant excitation of antiproton plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 025002 (2011)
Amole, C., et al.: (ALPHA), experimental and computational study of the injection of antiprotons into a positron plasma for antihydrogen production. Phys. Plas. 20, 043510 (2011)
Bertsche, W., et al.: (ALPHA), a magnetic trap for antihydrogen confinement. Nucl. Inst. Meth. A. 566, 746–756 (2006)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), antihydrogen annihilation reconstruction with the ALPHA silicon detector. Nucl. Inst. Meth. A 684, 73–81 (2012)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), search for trapped antihydrogen. Phys. Lett. B 695, 95–104 (2011)
Andresen, G.B., et al.: (ALPHA), discriminating between antihydrogen and mirror-trapped antiprotons in a minimum-B trap. New. J. Phys. 14, 015010 (2012)
Oelert, W., Eriksson, T., Belochitskii, P., Tranquille, G.: AD performance and its extension towards ELENA. Hyp. Int. 213, 227–236 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Low Energy Antiproton Physics (LEAP 2013) held in Uppsala, Sweden, 10-15 June, 2013
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, N., for the ALPHA collaboration. ALPHA: antihydrogen and fundamental physics. Hyperfine Interact 228, 37–45 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-014-1031-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-014-1031-x