Abstract
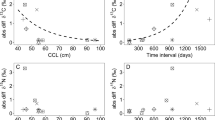
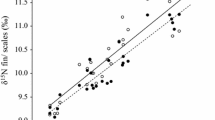
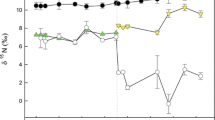
Investigations into trophic ecology and aquatic food web resolution are increasingly accomplished through stable isotope analysis. The incorporation of dietary and metabolic changes over time results in variations in isotope signatures and turnover rates of producers and consumers at tissue, individual, population and species levels. Consequently, the elucidation of trophic relationships in aquatic systems depends on establishing standard isotope values and tissue turnover rates for the level in question. This study investigated the effect of diet and food quality on isotopic signatures of four mussel tissues: adductor muscle, gonad, gill and mantle tissue from the brown mussel Perna perna. In the laboratory, mussels were fed one of the two isotopically distinct diets for 3 months. Although not all results were significant, overall δ13C ratios in adductor, mantle and gill tissues gradually approached food source signatures in both diets. PERMANOVA analyses revealed significant changes over time in tissue δ13C (mantle and gill) with both diets and in δ15N (all tissues) and C:N ratios (mantle and gill) for one diet only. The percentage of replaced carbon isotopes were calculated for the 3 month period and differed among tissues and between diets. The tissue with the highest and lowest amount of replaced isotopes over 81 days were mantle tissue on the kelp diet (33.89%) and adductor tissue on the fish food diet (4.14%), respectively. Percentages could not be calculated for any tissue in either diet for δ15N due to the lack of significant change in tissue nitrogen. Fractionation patterns in tissues for both diets can be linked to nutritional stress, suggesting that consumer isotopic signatures are strongly dependent on food quality, which can significantly affect the degree of isotopic enrichment within a trophic level.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle, N. & M. Malzahn, 2007. Interspecific and nutrient-dependent variations in stable isotope fractionation: experimental studies simulating pelagic multitrophic systems. Plant Animal Interactions 154: 291–303.
Adams, T. S. & R. W. Sterner, 2000. The effect of dietary nitrogen content on trophic level 15N enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 601–607.
Aldridge, D. W., W. D. Russel-Hunter & D. E. Buckley, 1983. Age-related differential catabolism in the snail, Viviparous georgianus, and its significance in the bioenergetics of sexual dimorphism. Canadian Journal of Zoology 64: 340–346.
Ambrose, S. & L. Norr, 1993. Carbon isotopic evidence for routing of dietary protein to bone collagen, and whole diet to bone apatite carbonate: purified diet growth experiments. In Lambert, J. & G. Grupe (eds), Molecular Archaeology of Prehistoric Human Bone. Springer-Verlag, Berlin: 1–37.
Anderson, M. J., 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology 26: 32–46.
Augley, J., M. Huxham, F. M. Fernandes, A. R. Lyndon & A. Bury, 2007. Carbon stable isotopes in estuarine sediments and their utility as migration markers for nursery studies in the Firth of Forth and Forth Estuary, Scotland. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 72: 648–656.
Badalamenti, F., G. D’Anna, J. K. Pinnegar & N. V. C. Polunin, 2002. Size-related trophodynamic changes in three target fish species recovering from intensive trawling. Marine Biology 141: 561–570.
Bayne, B. & A. Hawkins, 1990. Filter feeding in bivalve molluscs: controls on energy balance. In Mellinger, J. (ed.), Animal Nutrition and Transport Processes. 1 Nutrition in Wild and Domestic Animals. Karger, Basel: 70–83.
Bearhop, S., S. Waldron, S. C. Votier & R. W. Furness, 2002. Factors that influence assimilation rates and fractionation of nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes in avian blood and feathers. Physiological and Biochemical Zoology 75: 451–458.
Bearhop, S., C. E. Adams, S. Waldron, R. A. Fuller & H. Macleod, 2004. Determining trophic niche width: a novel approach using stable isotope analysis. Journal of Animal Ecology 73: 1007–1012.
Bode, A., M. T. Alvarez-Ossorio & M. Varela, 2006. Phytoplankton and macrophyte contributions to littoral food webs in the Galician upwelling estimated from stable isotopes. Marine Ecological Progress Series 318: 89–102.
Bodin, N., F. Le Loc’h, C. Hily, X. Caisey, D. Latrouite & M.-A. Le Guellec, 2007. Variability of stable isotope signatures (δ13C and δ15N) in two spider crab populations (Maja brachydactyla) in Western Europe. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 343: 149–157.
Breese, W. P., E. Millemann & R. E. Dimick, 1963. Stimulation of spawning in the mussels, Mytilus edulis Linnaeus and Mytilus californianus Conrad, by Kraft mill effluent. Biological Bulletin 125: 197–205.
Cranford, P. J. & P. S. Hill, 1999. Seasonal variation in food particle utilization by the suspension-feeding bivalve molluscs Mytilus edulis and Placopecten magellanicus. Marine Ecological Progress Series 190: 223–239.
Crespo, C. A. & J. Espinosa, 1990. Nutrient storage cell isolation from mantle tissue of Mytilus galloprovincialis: glucose release and glycogen content. Revista Española de Fisiología 46: 241–246.
DeNiro, M. J. & S. Epstein, 1977. A mechanism of carbon isotope fractionation associated with lipid synthesis. Science 197: 261–263.
DeNiro, M. J. & S. Epstein, 1978. Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 42: 495–506.
DeNiro, M. J. & S. Epstein, 1981. Influence of diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 45: 341–351.
Deudero, S., M. Cabanellas, A. Blanco & S. Tejada, 2009. Stable isotope fractionation in the digestive gland, muscle and gills tissues of the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 368: 181–188.
Doucett, R. R., R. K. Booth, G. Power & R. S. McKinley, 1999. Effects of the spawning migration on the nutritional status of anadromous Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): insights from stable-isotope analysis. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 56: 2172–2180.
Dunton, K. H. & D. M. Schell, 1987. Dependence of consumers on macroalgal (Laminaria solidungula) carbon in an arctic kelp community: δ13C evidence. Marine Biology 93: 615–625.
Frazer, T., R. Ross, L. Quetin & J. Montoya, 1997. Turnover of carbon and nitrogen during growth of larval krill, Euphausia superba Dana: a stable isotope approach. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 212: 259–275.
Fredriksen, S., 2003. Food web studies in a Norwegian kelp forest based on stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) analysis. Marine Ecological Progress Series 260: 71–81.
Freites, L., U. Labarta & M. J. Fernandez-Reiriz, 2002. Evolution of fatty acid profiles of subtidal and rocky shore mussel seed (Mytilus galloprovincialis Link.). Influence of environmental parameters. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 268: 185–204.
Fry, B. & C. Arnold, 1982. Rapid 13C/12C turnover during growth of brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus). Oecologia 54: 200–204.
Fry, B. & E. B. Sherr, 1984. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contributions in Marine Science 27: 13–17.
Fry, B., P. L. Mumford, F. Tam, D. D. Fox, G. L. Warren, K. E. Havens & A. D. Steinman, 1999. Trophic position and individual feeding histories of fish from Lake Okeechobee, Florida. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 56: 590–600.
Gabbott, P. A. & K. Peek, 1991. Cellular biochemistry of the mantle tissue of the mussel Mytilus edulis L. Aquaculture 94: 165–176.
Gaebler, O. H., T. G. Vitti & R. Vukmirovich, 1966. Isotope effects in metabolism of 14N and 15N from unlabeled dietary proteins. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 44: 1249–1257.
Gannes, L. Z., D. M. O’Brien & C. Martinez del Rio, 1997. Stable isotopes in animal ecology: assumptions, caveats, and a call for more laboratory experiments. Ecology 78: 1271–1276.
Gardner, J. P. A., 2002. Effects of seston variability on the clearance rate and absorption efficiency of the mussels Aulacomya maoriana, Mytilus galloprovincialis and Perna canaliculus from New Zealand. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 268: 83–101.
Gorokhova, E. & S. Hansson, 1999. An experimental study on variations in stable carbon and nitrogen isotope fractionation during growth of Mysis mixta and Neomysis integer. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 56: 2203–2210.
Griffiths, C. L. & P. A. R. Hockey, 1987. A model describing the interactive roles of predation, competition and tidal elevation structuring mussel populations. South African Journal of Marine Science 5: 547–556.
Gu, B., D. M. Schell & V. Alexander, 1994. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic analysis of the plankton food web in a subarctic lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 51: 1338–1344.
Haubert, D., R. Langel, S. Scheu & L. Ruess, 2005. Effects of food quality, starvation and life stage on stable isotope fractionation in Collembola. Pedobiologia 49: 229–237.
Hawkins, A. J. S., B. L. Bayne & A. J. Day, 1986. Protein turnover, physiological energetics and heterozygosity in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis: the basis of variable age-specific growth. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 229: 161–176.
Hendriks, I. E., L. A. V. Duren & P. M. J. Herman, 2003. Effect of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids on reproductive output and larval growth of bivalves. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 296: 199–213.
Hesslein, R. H., K. A. Hallard & P. Ramlal, 1993. Replacement of sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen in tissue of growing broad whitefish (Coregonus nasus) in response to a change in diet traced by δ34S, δ13C and δ15N. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 50: 2071–2076.
Hill, J., C. McQuaid & S. Kaehler, 2006. Biogeographic and nearshore/offshore trends in isotope ratios of intertidal mussels and their food sources around the coast of southern Africa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 318: 63–73.
Hobson, K. A., 1999. Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: a review. Oecologia 120: 314–326.
Hobson, K. A. & R. G. Clark, 1992. Assessing avian diets using stable isotopes. II. Factors influencing diet-tissue fractionation. Condor 94: 189–197.
Hobson, K. A. & R. G. Clark, 1993. Turnover of 13C in cellular and plasma fractions of blood: implications for nondestructive sampling in avian dietary studies. Auk 110: 638–641.
Hobson, K. A. & L. I. Wassenaar, 1997. Linking breeding and wintering grounds of neotropical migrant songbirds using stable hydrogen isotopic analysis of feathers. Oecologia 109: 142–148.
Hobson, K. A., R. T. Alisauskas & R. G. Clark, 1993. Stable nitrogen isotope enrichment in avian tissues due to fasting and nutritional stress: implications for isotopic analysis of diet. Condor 94: 181–188.
Hobson, K., A. Fisk, N. Karnovsky, M. Holst, J. Gagnon & M. Fortier, 2002. A stable isotope (δ13C, δ15N) model for the North Water food web: implications for evaluating trophodynamics and the flow of energy and contaminants. Deep-Sea Research Part II 49: 5131–5150.
Iglesias, J. I. P. & E. Navarro, 1991. Energetics of growth and reproduction in cockles (Cerastoderma edule): seasonal and age-dependent variations. Marine Biology 111: 359–368.
Kendall, C., 1998. Tracing nitrogen sources and cycling in catchments. In Kendall, C. & J. J. McDonnell (eds), Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology. Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam: 519–576.
Kendall, C. & D. H. Doctor, 2003. Stable isotope applications in hydrologic studies. In Drever, J. I. (ed), Treatise on Geochemistry Vol. 5. Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam: 319–364.
Kreeger, D. A. & R. I. E. Newell, 2001. Seasonal utilization of different seston carbon sources by the ribbed mussel, Geukenseia demissa (Dillwyn) in a mid-Atlantic salt marsh. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 260: 71–91.
Libby, W. F., R. Berger, J. F. Mead, G. V. Alexander & J. F. Ross, 1964. Replacement rates for human tissue from atmospheric radiocarbon. Science 146: 1170–1172.
Livingstone, D. R. & S. V. Farrar, 1984. Tissue and subcellular distribution of enzyme activities of mixed-function oxygenase and benzo(a) pyrene metabolism in the common mussel Mytilus edulis L. Science of the Total Environment 39: 209–235.
Lombraña, M., P. Suárez & F. San Juan, 2005. Two forms of a-amylase in mantle tissue of Mytilus galloprovincialis: purification and molecular properties of form II. Comparative and Biochemical Physiology B 142: 56–66.
Lorrain, A., Y. Paulet, L. Chauvaud, N. Savoye, A. Donval & C. Saout, 2002. Differential δ13C and δ15N signatures among scallop tissues: implications for ecology and physiology. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 275: 47–61.
Lubet, P., P. Herlin, M. Mathieu & F. Collin, 1978. Tissue de réserve et cycle sexuel chez les Lamellibranches. Haliotis 7: 59–62.
Mann, K., 1988. Production and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine and coastal marine ecosystems. Limnology Oceanography 33: 910–930.
McArdle, B. H. & M. J. Anderson, 2001. Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance based redundancy analysis. Ecology 82: 290–297.
McCutchan, J. H. Jr., W. M. Lewis Jr., C. Kendall & C. C. McGrath, 2003. Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102: 378–390.
McQuaid, C. & T. Lindsay, 2000. Effect of wave exposure on growth and mortality rates of the mussel Perna perna: bottom-up regulation of intertidal populations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 206: 147–154.
Minagawa, M. & E. Wada, 1984. Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between 15N and animal age. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 8: 1135–1140.
Murry, B. A., J. M. Farrell, M. A. Teece & P. M. Smyntek, 2006. Effect of lipid extraction on the interpretation of fish community trophic relationships determined by stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 63: 2167–2172.
Nagy, K. A., 1987. Field metabolic rate and food requirement scaling in mammals and birds. Ecological Monographs 57: 111–128.
Navarro, E., J. I. P. Iglesias, A. Perez, U. Labarta & R. Beiras, 1991. The physiological energetics of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk) from different cultivation rafts in the Rfa de Arosa (Galicia, N.W. Spain). Aquaculture 94: 197–212.
Newell, R. & J. G. Field, 1983. The contribution of bacteria and detritus to carbon and nitrogen flow in a benthic community. Marine Biology Letters 4: 23–36.
Newell, R. I. E. & S. J. Jordan, 1983. Preferential ingestion of organic material by the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Marine Ecology Progress Series 13: 47–53.
Newell, R. C., S. E. Shumway, T. L. Cucci & R. Selvin, 1989. The effects of natural seston particle size and type of feeding rates, feeding selectivity and food resource availability for the mussel Mytilus edulis Linneaus, 1758 at bottom culture sites in Maine. Journal of Shellfish Research 8: 187–196.
Oelbermann, K. & S. Scheu, 2002. Stable isotope enrichment (δ15N and δ13C) in a generalist predator (Pardosa lugubris, Araneae: Lycosidae): effects of prey quality. Oecologia 130: 337–344.
Olive, P. J. W., J. K. Pinnegar, N. V. C. Polunin, G. Richards & R. Welch, 2003. Isotope trophic-step fractionation: a dynamic equilibrium model. Journal of Animal Ecology 72: 608–617.
Peterson, C. H., 1983. A concept of quantitative reproductive senility: application to the hard clam, Mercenaria mercenaria (L.). Oecologia 58: 164–168.
Prins, T. C., A. C. Smaal & A. J. Pouwer, 1991. Selective ingestion of phytoplankton by the bivalves Mytilus edulis L. and Cerastoderma edule (L.). Hydrobiological Bulletin 25: 93–100.
Ram, J. L., G. W. Crawford, J. U. Walker, J. J. Mojares, N. Patel, P. P. Fong & K. Kyozuka, 1993. Spawning in the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha): activation by internal or external application of serotonin. Journal of Experimental Zoology 265: 587–598.
Rouillon, G. & E. Navarro, 2003. Differential utilization of species of phytoplankton by the mussel Mytilus edulis. Acta Oecologica 24: S299–S305.
Russel-Hunter, W. D., 1970. Aquatic productivity: an introduction to some basic aspects of biological oceanography and limnology. MacMillan Co., New York, NY: 352.
Schmidt, O., C. M. Scrimgeour & J. P. Curry, 1999. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios in body tissue and mucus of feeding and fasting earthworms (Lumbricus festivus). Oecologia 118: 9–15.
Schwarcz, H. P., 1991. Some theoretical aspects of isotope paleodiet studies. Journal of Archaeological Science 18: 261–275.
Sholto-Douglas, A. D., J. G. Field, A. G. James & N. J. van der Merwe, 1991. 13C/12C and 15N/14N isotope ratios in the Southern Benguela Ecosystem: indicators of food web relationships among different size-classes of plankton and pelagic fish; differences between fish muscle and bone collagen tissues. Marine Ecology Progress Series 78: 23–31.
Shumway, S. E., T. L. Cucci, R. C. Newell & C. M. Yentsch, 1985. Particle selection, ingestion and absorption in filter-feeding bivalves. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 91: 77–92.
Sotiropoulos, M., W. Tonn & L. Wassenaar, 2004. Effects of lipid extraction on stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses of fish tissues: potential consequences for food web studies. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 13: 155–160.
Stuart, V., M. I. Lucas & R. C. Newell, 1981. Heterotrophic utilization of particulate matter from the kelp Laminaria pallida. Marine Ecology Progress Series 4: 337–348.
Suárez, M. P., C. Alvarez, P. Molist & F. San Juan, 2005. Particular aspects of gonadal cycle and seasonal distribution of gametogenic stages of Mytilus galloprovincialis, cultured in the Estuary of Vigo. Journal of Shellfish Research 24: 531–540.
Sukhotin, A. A. & H.-O. Pörtner, 2001. Age-dependence of metabolism in mussels Mytilus edulis (L.) from the White Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 251: 53–72.
Sweeting, C. J., S. Jennings & N. V. C. Polunin, 2005. Variance in isotopic signatures as a descriptor of tissue turnover and degree of omnivory. Functional Ecology 19: 777–784.
Thompson, R. C. & J. E. Ballou, 1956. Studies of metabolic turnover with tritium as a tracer. V. The predominantly non-dynamic state of body constituents in the rat. Journal of Biological Chemistry 223: 795–809.
Tieszen, L. L., T. W. Boutton, K. G. Tesdahl & N. A. Slade, 1983. Fractionation and turnover of stable carbon isotopes in animal tissues: implications for δ13C analysis of diet. Oecologia 57: 32–37.
Vahl, O., 1973. Efficiency of particle retention in Chlamys islandica (O.F. Müller). Astarte 6: 21–25.
Valiela, I., 1995. Marine Ecological Processes, 2nd ed. Springer, New York, 686 pp.
Vander Zanden, M. & J. Rasmussen, 2001. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 2061–2066.
Vanderklift, M. A. & S. Ponsard, 2003. Sources of variation in consumer-diet δ15N enrichment: a meta-analysis. Oecologia 136: 169–182.
Vizzini, S. & A. Mazzola, 2003. Seasonal variations in the stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios (13C/12C and 15N/14N) of primary producers and consumers in a western Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Marine Biology 142: 1009–1018.
Ward, J. E. & S. E. Shumway, 2004. Separating the grain from the chaff: particle selection in suspension-and deposit-feeding bivalves. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 300: 83–130.
Widdows, J., P. Fieth & C. Worrall, 1979. Relationships between seston, available food and feeding activity in the common mussel Mytilus edulis. Marine Biology 50: 195–207.
Wong, W. & S. G. Cheung, 1999. Feeding behaviour of the green mussel, Perna viridis (L.): responses to variation in seston quantity and quantity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 236: 191–207.
Young, R. T., 1945. Stimulation of spawning in the mussel (Mytilus californianus). Ecology 26: 58–69.
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to both Hydribiologia’s reviewers who provided constructive comments that have significantly improved the manuscript. Thanks as well to Prof. M. Villet and Dr. F. Porri, Rhodes University, South Africa for providing statistical help and direction, and to J. Lanham for isotopic analysis at the Stable Light Isotope Unit, University of Cape Town, South Africa. This study is based upon research supported by the South African Research Chairs Initiative of the Department of Science and Technology and National Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: M. Power
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, J.M., McQuaid, C.D. Effects of food quality on tissue-specific isotope ratios in the mussel Perna perna . Hydrobiologia 635, 81–94 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9865-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9865-y