Abstract
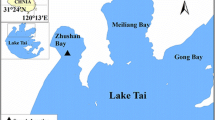
To understand the effect of hydrodynamical process on water phosphorus concentration, wind, wave, and several water quality indices were observed in Meiliang Bay, a shallow and eutrophic bay locates in north of Lake Taihu. During the 7 day observation period, wind speed and significant wave height were recorded more than 3 h per day, and water samples were collected in five water-depth layers once a day. Hydrodynamical disturbance had no significant correlationship with the water quality at the top layer when the significant wave height was smaller than 30 cm, but it significantly increased suspended solids (SS) concentration of the bottom water layer. Concentrations of nutrients showed no positive correlationship with SS concentration in the water body. Intensive sediment resuspension may not have occurred when the hydrodynamic stress on sediment was only a little higher than the critical stress for sediment resuspension. A new method for confirming the critical stress for intensive sediment resuspension and nutrient release still needs to be developed. The range of the water quality indices was quite high during the seven days of observation. High variation seems to be a common character of large shallow lakes like Taihu.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalderink, R. H., L. Lijklema, J. Breukelman, W. Raaphorts & A. G. Brinkman, 1984. Quantification of wind-induced resuspension in a shallow lake. Water Science & Technology 17: 903–914.
Carper, G. L. & R. W. Bachmann, 1984. Wind Resuspension of Sediments in a Prairie Lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 41: 1763–1767.
Chen, W. M. & A. Nauwerck, 1996. A note on composition and feeding of the crustacean zooplankton of Lake Taihu, Jiangsu Province, China. Limnologia 26: 275–279.
Chen, W. M., Y. W. Chen, X. Y. Gao & I. Yoshida, 1997. Eutrophication of Lake Taihu and its control. Agricultural Engineering Journal 6(2): 109–120.
Chen, Y. W., B. Q. Qin, K. Teubner & M. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis- domination in a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Dokulil, M., W. Chen & Q. Cai, 2000. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: the Tai Hu example. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management 3: 81–94.
Fan, C. X., L. Zhang & W. C. Qu, 2001. Lake sediment resuspension and caused phosphate release - a simulation study. Journal of Environmental Sciences 13: 406–410.
Fan, C. X., L. Zhang, B. Q. Qin, S. M. Wang, W. P. Hu & C. Zhang, 2004. Estimation on dynamic release of phosphorus from wind-induced suspended particulate matter in Lake Taihu. Science in China Series D 47: 710–719.
Gunatilaka, A., 1982. Phosphate adsorption kinetics of resuspended sediments in a shallow lake, Neusiedlersee, Austria. Hydrobiologia 91: 293–298.
Hu, W. P, J. Salomonsen, F. L. Xu & P. M. Pu, 1998. A model for the effects of water hyacinths on water quality in an experiment of physico-biological engineering in Lake Taihu, China. Ecological Modelling 107: 171–188.
Kristensen, P. M., M. Søondergåard & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Resuspension in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 228: 101–109.
Li, W. C. & Q. X. Yang, 1995. Wetland utilization in Lake Taihu for fish faming and improvement of lake water quality. Ecological Engineering 5: 107–121.
Linge, K. L. & C. E. Oldham, 2004. Control mechanisms for dissolved phosphorus and arsenic in a shallow lake. Applied Geochemistry 19: 1377–1389.
Luettich, R. A., D. R. F. Harleman & L. Somlódy, 1990. Dynamic behaviour of suspended sediment concentrations in a shallow lake perturbed by episodic wind events. Limnology & Oceanography 35: 1050–1067.
McNaught, D. C., W. M. Chen & H. J. Cai, 1997. Grazing on a Microcystis bloom by cladocerans and copepods in Tai Lake. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung fur Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 26: 550–552.
Pu, P. M., W. P. Hu, J. S. Yan, G. X. Wang & C. H. Hu, 1998. A physico-ecological engineering experiment for water treatment in a hypertrophic lake in China. Ecological Engineering 10: 179–190.
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu, W. M. Chen, C. X. Fan, J. Ji, Y. W. Chen, X. Y. Gao, L. Y. Yang, G. Gao, W. Y. Huang, J. H. Jiang, C. Zhang, Y. B. Liu & Z. Y. Zhou, 2000. Studies on the hydrodynamic processes and related factors in Meiliang Bay, Northern Taihu Lake, China. Journal of Lake Sciences 12: 327–334 (in Chinese).
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu, G. Gao, L. C. Luo & J. S. Zhang, 2004. Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chinese Science Bulletin 49: 54–64.
Qin, B. Q., P. Z. Xu, Q. L. Wu & L. C. Luo, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Qu, W. C., M. Dickman & S. M. Wang, 2001. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in sediments of Taihu Lake, China. Hydrobiologia 450: 83–89.
Søondergåard, M., P. Kristensen & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228: 91–99.
Wang, J. J., 2004. Effect of biogeochemistry processes of new born surface caused by sludge dredging on the internal loading recovery in a lake. Master thesis of Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Zhu, G. W., G. Gao, B. Q. Qin, L. Zhang & L. C. Luo, 2003. Geochemical characteristics of phosphorus in sediments of a large shallow lake. Advances in Water Science 14: 714–719 (in Chinese).
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin & G. Gao, 2004. Vertical distribution of the concentrations of phosphorus and suspended solid in Lake Taihu affected by wind-induced wave. Advances in Water Science 15: 775–780 (in Chinese).
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin, L. Zhang, L. C. Luo, X. J. Sun, D. L. Hong, Y. J. Gao & R. Xie, 2005a. Study on the effects of wave on nutrients releasing of sediments from Lake Taihu by flume experiments. Journal of Lake Sciences, 17(1): 61–68 (in Chinese).
Zhu, G. W., B. Q. Qin & G. Gao, 2005b. Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 577–582.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX1-SW-12) and Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40673078, 40573062). We also would like to thank Chen Weimin, Hu Weiping, Zhang Fabing, Ji Jiang, Qian Rongshu, Song Yuzhi, Yang Liuyan, Zhang Xiaofeng, Yang Longyuan for their help on field observation, sampling and chemical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, G., Qin, B., Gao, G. et al. Effects of hydrodynamics on phosphorus concentrations in water of Lake Taihu, a large, shallow, eutrophic lake of China. Hydrobiologia 581, 53–61 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0519-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0519-z