Abstract
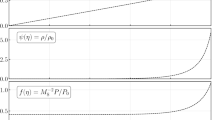
A simple approximate theory is used to estimate the optimal power of a stationary lumped source of energy in a supersonic flow and its minimal distance from a body, which provide for a significant reduction of energy consumption required for the advance of the body. Similarity laws are formulated for the conversion of the numerical or experimental results to other conditions. Numerical simulation is performed of the incidence of hypersonic flow on a blunt body with and without energy release. The calculations are performed in application to the described new experiments in flow past a model and in measuring the drag in a hypersonic shock tunnel at Mach 10 in the presence or absence of a powerful arc source of energy. Descriptive patterns are given of flow and space distributions of gasdynamic quantities. The calculated shapes of waves agree well with schlieren photographs, and the calculated value of drag force — with the measured value. It is demonstrated numerically that, under close-to-optimal conditions, the drag may be reduced by a factor of approximately five, and the total energy consumption required to overcome this drag — by a factor of four.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Oswatitsch, K., Propulsion with heating at Supersonic Speed, Report 90, Deutsche Versuchsanstalt for Luft- und Raumfahrt, 1959.
Investigation of Gas Flows with Heat Input in the Vicinity of the External Surface of a Flying Vehicle, Obzor BNTI TsAGI (A Review by the Office of Scientific-and-Technical Information of Central Inst. of Aerohydrodynamics), 1971, no. 347.
J.P. Reding D.M. Jesmen (1983) J. Spacecr. Rockets 20 IssueID3 452 Occurrence Handle1983JSpRo..20..452R
P.Yu. Georgievskii V.A. Levin (1987) Supersonic Flow past Volume Sources of Energy Release Mekhzanika. Sovremennye problemy Izd. MGU (Moscow State Univ.) Moscow 93
V.V. Vlasov V.G. Grudnitskii V.N. Rygalin (1995) Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk Mekh. Zhidk. Gaza 2 142
L.N. Myrabo Yu. P. Raizer M.N. Shneider (1998) Teplofiz. Vys. Temp. 36 IssueID2 304
P.Yu. Georgievskii V.A. Levin (1998) Unsteady-State Effects in Supersonic Flow behind a Pulsating High-Power Source of Energy Proc. 9 th Int. Conf. on Methods in Aerophysical Research Izd. ITPM RAN (Inst. of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Russ. Acad. Sci. Novosibirsk 58
Levin, V.A. and Terent’eva, L.V., Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk Mekh. Zhidk. Gaza, 1993, no. 2, p. 110.
P.Yu. Georgievskii V.A. Levin (1993) Khim. Fiz. 10 IssueID12 1414
V.Yu. Borzov I.V. Rybka A.S. Yur’ev (1992) Inzh. Fiz. Zh. 63 IssueID6 659
D. Riggins H.F. Nelson E. Johnson (1999) AIAA J. 37 IssueID4 460 Occurrence Handle10.2514/2.756
V.A. Levin V.B. Gromov N.E. Afonina (2000) Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 41 IssueID25 171 Occurrence Handle1074.80500
R. Takaki M.-S. Liou (2002) AIAA J. 40 IssueID3 501
P. Tretyakov A. Garanin V. Kraynev et al. (1996) Proc. 8 th Int. Conf. on Methods in Aerophysical Research Izd. ITPM RAN (Inst. of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Russ. Acad. Sci.) Novosibirsk 200
Knight, D., Kuchinskiy, V., Kuranov, A., and Sheikin, E., AIAA Paper 2003-0525, 2003.
Myrabo, L.N. and Raizer, Yu.P., AIAA Paper 942551, 1994.
S.W. Kandebo (1995) Aviat. Week Space Technol. 142 IssueID20 66
G.G. Chernyi (1957) Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 112 213 Occurrence Handle87438
Ya.B. Zel’dovich Yu.P. Raizer (1966) Fizika udarnylh voln i vysokotemperaturnykh gidrodinamicheskikh yavlenii Fizmatgiz Moscow
A. Safe (1965) New Investigations in the Field of Hypersonic Gas Flows Gazovaya dinamika kosmicheskikh apparatov Mir Moscow 184
Bracken, R.M., Myrabo, L.N., Nagamatsu, H.T., Meloney, E.D., and Schneider, M.N., AIAA Paper 2001–2734, 2001.
Hartley, C.S., Portwood, T.W., Filipelli, M.V. et al., AIAA Paper 2004–0035, 2004.
Girgis, I.G., Shneider, M.N., Macheret, S.O. et al., AIAA Paper 2002–0129, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Teplofizika Vysokikh Temperatur, Vol. 42, No. 6, 2004, pp. 890–899.
Original Russian Text Copyright © 2004 by L. N. Myrabo, Yu. P. Raizer, M. N. Shneider, and R. Bracken.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myrabo, L.N., Raizer, Y.P., Shneider, M.N. et al. Reduction of drag and energy consumption during energy release preceding a blunt body in supersonic flow. High Temp 42, 901–910 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10740-005-0035-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10740-005-0035-2