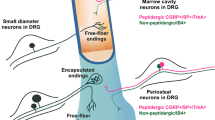
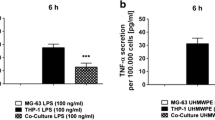
Abstract
Alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (αCGRP) and substance P (SP) are functionally correlated sensory neuropeptides deeply involved in bone homeostasis. However, they are usually studied individually rather than as an organic whole. To figure out whether they are interdependent, we firstly recorded the real-time αCGRP and SP levels in aging bone and healing fracture, which revealed a moderate to high level of αCGRP coupled with a low αCGRP/SP ratio in an anabolic state, and a high level of αCGRP coupled with a high αCGRP/SP ratio in a catabolic state, suggesting the importance of αCGRP/SP ratio in driving aging and healing scenarios. During facture healing, increase in αCGRP/SP ratio by adding αCGRP led to better callus formation and faster callus remodeling, while simultaneous addition of αCGRP and SP resulted in hypertrophic callus and delayed remodeling. The characteristics in inflammation and osteoclast activation further confirmed the importance of high αCGRP/SP ratio during catabolic bone remodeling. In vitro assays using different mixtures of αCGRP-SP proved that the osteogenic potential of the mixtures depended mostly on αCGRP, while their effects on osteoclasts and neutrophils relied on both peptides. These results demonstrated that αCGRP and SP were spatiotemporally interdependent. The αCGRP/SP ratio may be more important than the dose of a single neuropeptide in managing age-related and trauma-related bone diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam C, Llorens A, Baroukh B, Cherruau M, Saffar JL (2000) Effects of capsaicin-induced sensory denervation on osteoclastic resorption in adult rats. Exp Physiol 85(1):62–66
Assas MB (2021) Anti-migraine agents from an immunological point of view. J Transl Med 19(1):23
Augustyniak D, Roszkowiak J, Wiśniewska I, Skała J, Gorczyca D, Drulis-Kawa Z (2018) Neuropeptides SP and CGRP diminish the moraxella catarrhalis outer membrane vesicle- (OMV-) triggered inflammatory response of human A549 epithelial cells and neutrophils. Mediators Inflamm 2018:4847205
Bhatia M, Saluja AK, Hofbauer B, Frossard JL, Lee HS, Castagliuolo I et al (1998) Role of substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor in acute pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(8):4760–4765
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313(5997):54–56
Burbach JP (2011) What are neuropeptides? Methods Mol Biol 789:1–36
Charles A, Pozo-Rosich P (2019) Targeting calcitonin gene-related peptide: a new era in migraine therapy. Lancet 394(10210):1765–1774
Chen D, Liu P, Li M, Zhang C, Gao Y, Guo Y (2022) Nacre-mimetic hydroxyapatite/chitosan/gelatin layered scaffolds modifying substance P for subchondral bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym 291:119575
Chen ZH, Wu JJ, Guo DY, Li YY, Chen MN, Zhang ZY et al (2023) Physiological functions of podosomes: from structure and function to therapy implications in osteoclast biology of bone resorption. Ageing Res Rev 85:101842
Choi JE, Di Nardo A (2018) Skin neurogenic inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 40(3):249–259
Chow SK, Wong CH, Cui C, Li MM, Wong RMY, Cheung WH (2022) Modulating macrophage polarization for the enhancement of fracture healing, a systematic review. J Orthop Translat 36:83–90
Claes L, Recknagel S, Ignatius A (2012) Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8(3):133–143
Cowie AM, Moehring F, O’Hara C, Stucky CL (2018) Optogenetic inhibition of CGRPα sensory neurons reveals their distinct roles in neuropathic and incisional pain. J Neurosci 38(25):5807–5825
Dansereau MA, Midavaine É, Bégin-Lavallée V, Belkouch M, Beaudet N, Longpré JM et al (2021) Mechanistic insights into the role of the chemokine CCL2/CCR2 axis in dorsal root ganglia to peripheral inflammation and pain hypersensitivity. J Neuroinflammation 18(1):79
Douglas SD, Leeman SE (2011) Neurokinin-1 receptor: functional significance in the immune system in reference to selected infections and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1217:83–95
D’Souza SM, MacIntyre I, Girgis SI, Mundy GR (1986) Human synthetic calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibits bone resorption in vitro. Endocrinology 119(1):58–61
Duda GN, Geissler S, Checa S, Tsitsilonis S, Petersen A, Schmidt-Bleek K (2023) The decisive early phase of bone regeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol 19(2):78–95
Ejaz A, LoGerfo FW, Pradhan L (2011) Diabetic neuropathy and heart failure: role of neuropeptides. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e26
Gajda M, Litwin JA, Cichocki T, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D (2005) Development of sensory innervation in rat tibia: co-localization of CGRP and substance P with growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43). J Anat 207(2):135–144
Gao Z, Liu Y, Zhang L, Yang Z, Lv L, Wang S et al (2022) Nociceptor neurons are involved in the host response to escherichia coli urinary tract infections. J Inflamm Res 15:3337–3353
Grasman JM, Kaplan DL (2017) Human endothelial cells secrete neurotropic factors to direct axonal growth of peripheral nerves. Sci Rep 7(1):4092
Grässel SG (2014) The role of peripheral nerve fibers and their neurotransmitters in cartilage and bone physiology and pathophysiology. Arthritis Res Ther 16(6):485
Guo Y, Chen H, Jiang Y, Yuan Y, Zhang Q, Guo Q et al (2020) CGRP regulates the dysfunction of peri-implant angiogenesis and osseointegration in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Bone 139:115464
He H, Chai J, Zhang S, Ding L, Yan P, Du W et al (2016) CGRP may regulate bone metabolism through stimulating osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Mol Med Rep 13(5):3977–3984
Hu R, Li YJ, Li XH (2016) An overview of non-neural sources of calcitonin gene-related peptide. Curr Med Chem 23(8):763–773
Hukkanen M, Konttinen YT, Santavirta S, Paavolainen P, Gu XH, Terenghi G et al (1993) Rapid proliferation of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves during healing of rat tibial fracture suggests neural involvement in bone growth and remodelling. Neuroscience 54(4):969–979
Jia S, Zhang SJ, Wang XD, Yang ZH, Sun YN, Gupta A et al (2019) Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances osteogenic differentiation and recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats. Exp Ther Med 18(2):1039–1046
Joos GF, Germonpre PR, Kips JC, Peleman RA, Pauwels RA (1994) Sensory neuropeptides and the human lower airways: present state and future directions. Eur Respir J 7(6):1161–1171
Kim SH, Kim JE, Kim SH, Jung Y (2017) Substance P/dexamethasone-encapsulated PLGA scaffold fabricated using supercritical fluid process for calvarial bone regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 11(12):3469–3480
Kim DJ, Moon JY, Kim SM, Seo JW, Lee YH, Jung SW et al (2020) Substance P Improves renal ischemia reperfusion injury through modulating immune response. Front Immunol 11:600
Knox AM, McGuire AC, Natoli RM, Kacena MA, Collier CD (2021) Methodology, selection, and integration of fracture healing assessments in mice. J Orthop Res 39(11):2295–2309
Langenkamp E, Molema G (2009) Microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity: general concepts and pharmacological consequences for anti-angiogenic therapy of cancer. Cell Tissue Res 335(1):205–222
Leal EC, Carvalho E, Tellechea A, Kafanas A, Tecilazich F, Kearney C et al (2015) Substance P promotes wound healing in diabetes by modulating inflammation and macrophage phenotype. Am J Pathol 185(6):1638–1648
Leroux A, Paiva Dos Santos B, Leng J, Oliveira H, Amédée J (2020) Sensory neurons from dorsal root ganglia regulate endothelial cell function in extracellular matrix remodelling. Cell Commun Signal 18(1):162
Li J, Kreicbergs A, Bergström J, Stark A, Ahmed M (2007) Site-specific CGRP innervation coincides with bone formation during fracture healing and modeling: a study in rat angulated tibia. J Orthop Res 25(9):1204–1212
Li H, Qu J, Zhu H, Wang J, He H, Xie X et al (2021) CGRP regulates the age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:675503
Lin T, Quellier D, Lamb J, Voisin T, Baral P, Bock F et al (2021) Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced nociceptor activation increases susceptibility to infection. PLoS Pathog 17(5):e1009557
Lv L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhang T, Li S (2014) Healing of periodontal defects and calcitonin gene related peptide expression following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats. J Mol Histol 45(3):311–320
Lv T, Liang W, Li L, Cui X, Wei X, Pan H et al (2019) Novel calcitonin gene-related peptide/chitosan-strontium-calcium phosphate cement: Enhanced proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 107(1):19–28
M G E B, Dosh L, Haidar H, Gerges A, Baassiri S, Leone A, et al. (2022) Nerve growth factor and burn wound healing: Update of molecular interactions with skin cells. Burns.
Mapp PI, Walsh DA (2012) Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8(7):390–398
Mapp PI, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, Hargin E, Walsh DA (2012) A role for the sensory neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide in endothelial cell proliferation in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 166(4):1261–1271
Mi J, Xu J, Yao H, Li X, Tong W, Li Y et al (2021) Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances distraction osteogenesis by increasing angiogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A 27(1–2):87–102
Mi J, Xu JK, Yao Z, Yao H, Li Y, He X et al (2022) Implantable electrical stimulation at dorsal root ganglions accelerates osteoporotic fracture healing via calcitonin gene-related peptide. Adv Sci 9(1):e2103005
Moattari CR, Granstein RD (2021) Neuropeptides and neurohormones in immune, inflammatory and cellular responses to ultraviolet radiation. Acta Physiol 232(1):e13644
Mu C, Hu Y, Hou Y, Li M, He Y, Shen X et al (2020) Substance P-embedded multilayer on titanium substrates promotes local osseointegration via MSC recruitment. J Mater Chem B 8(6):1212–1222
Naot D, Musson DS, Cornish J (2019) The activity of peptides of the calcitonin family in bone. Physiol Rev 99(1):781–805
Offley SC, Guo TZ, Wei T, Clark JD, Vogel H, Lindsey DP et al (2005) Capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons contribute to the maintenance of trabecular bone integrity. J Bone Miner Res 20(2):257–267
Park JH, Kim S, Hong HS, Son Y (2016) Substance P promotes diabetic wound healing by modulating inflammation and restoring cellular activity of mesenchymal stem cells. Wound Repair Regen 24(2):337–348
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Baddal B, Haarsma R, O’Seaghdha M, Yang NJ, Blake KJ et al (2018) Blocking neuronal signaling to immune cells treats streptococcal invasive infection. Cell 173(5):1083-1097.e1022
Russell FA, King R, Smillie SJ, Kodji X, Brain SD (2014) Calcitonin gene-related peptide: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 94(4):1099–1142
Schou WS, Ashina S, Amin FM, Goadsby PJ, Ashina M (2017) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: a systematic review. J Headache Pain 18(1):34
Serra MC, Bazzoni F, Della Bianca V, Greskowiak M, Rossi F (1988) Activation of human neutrophils by substance P. Effect on oxidative metabolism, exocytosis, cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and inositol phosphate formation. J Immunol 141(6):2118–2124
Shi Z, Wang S, Deng J, Gong Z (2022) Neural peptide α-CGRP coregulated angiogenesis and osteogenesis via promoting the cross-talk between mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial cells. Biomed Res Int 2022:1585840
Sohn SJ (2005) Substance P upregulates osteoclastogenesis by activating nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclast precursors. Acta Otolaryngol 125(2):130–133
Springer J, Geppetti P, Fischer A, Groneberg DA (2003) Calcitonin gene-related peptide as inflammatory mediator. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 16(3):121–130
Steinhoff MS, von Mentzer B, Geppetti P, Pothoulakis C, Bunnett NW (2014) Tachykinins and their receptors: contributions to physiological control and the mechanisms of disease. Physiol Rev 94(1):265–301
Sterner-Kock A, Braun RK, van der Vliet A, Schrenzel MD, McDonald RJ, Kabbur MB et al (1999) Substance P primes the formation of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 65(6):834–840
Sun S, Diggins NH, Gunderson ZJ, Fehrenbacher JC, White FA, Kacena MA (2020) No pain, no gain? The effects of pain-promoting neuropeptides and neurotrophins on fracture healing. Bone 131:115109
Takahashi N, Matsuda Y, Sato K, de Jong PR, Bertin S, Tabeta K et al (2016) Neuronal TRPV1 activation regulates alveolar bone resorption by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via CGRP. Sci Rep 6:29294
Tanabe T, Otani H, Zeng XT, Mishima K, Ogawa R, Inagaki C (1996) Inhibitory effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on substance-P-induced superoxide production in human neutrophils. Eur J Pharmacol 314(1–2):175–183
Tang P, Duan C, Wang Z, Wang C, Meng G, Lin K et al (2017) NPY and CGRP inhibitor influence on ERK pathway and macrophage aggregation during fracture healing. Cell Physiol Biochem 41(4):1457–1467
Tao R, Qu Z, Zhang K, Chen J, Wang X, Deng Y (2022) Substance P modulates BMSCs migration for tissue repair through NK-1R/CXCR4/p-Akt signal activation. Mol Biol Rep 49(3):2227–2236
Tepper SJ (2018) History and review of anti-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) therapies: from translational research to treatment. Headache 58(Suppl 3):238–275
Tuo Y, Guo X, Zhang X, Wang Z, Zhou J, Xia L et al (2013) The biological effects and mechanisms of calcitonin gene-related peptide on human endothelial cell. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 33(2):114–123
Tuzmen C, Verdelis K, Weiss L, Campbell P (2018) Crosstalk between substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide during heterotopic ossification in murine Achilles tendon. J Orthop Res 36(5):1444–1455
Villalobos V, Garrido M, Reyes A, Fernández C, Diaz C, Torres VA et al (2022) Aging envisage imbalance of the periodontium: a keystone in oral disease and systemic health. Front Immunol 13:1044334
Wang L, Zhao R, Shi X, Wei T, Halloran BP, Clark DJ et al (2009) Substance P stimulates bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic activity, osteoclast differentiation, and resorption activity in vitro. Bone 45(2):309–320
Wang L, Shi X, Zhao R, Halloran BP, Clark DJ, Jacobs CR et al (2010a) Calcitonin-gene-related peptide stimulates stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and inhibits RANKL induced NF-kappaB activation, osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Bone 46(5):1369–1379
Wang XY, Guo X, Cheng JC, Mi YL, Lai PY (2010b) Involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide innervation in the promoting effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on spinal fusion without decortication. Spine 35(26):E1539-1545
Wang J, Zhou F, Zhang S, Mao M, Feng S, Wang X (2022a) Participation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in the analgesic effect of duloxetine for paclitaxel induced peripheral neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 773:136512
Wang S, Liu L, Blanco T, Ge H, Xia Y, Pang K et al (2022b) Therapeutic efficacy of topical blockade of substance P in experimental allergic red eye. Ocul Surf 26:184–190
Xie D, Xu Y, Yang Y, Hua Z, Li J, Fu G et al (2021) Sensory denervation increases potential of bisphosphonates to induce osteonecrosis via disproportionate expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1487(1):56–73
Xu J, Wang J, Chen X, Li Y, Mi J, Qin L (2020) The effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide on bone homeostasis and regeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep 18(6):621–632
Yan K, Lin Q, Tang K, Liu S, Du Y, Yu X et al (2020) Substance P participates in periodontitis by upregulating HIF-1α and RANKL/OPG ratio. BMC Oral Health 20(1):27
Ye X, Liu X (2022) Wnt16 signaling in bone homeostasis and osteoarthristis. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 13:1095711
Ye L, Xu J, Mi J, He X, Pan Q, Zheng L et al (2021) Biodegradable magnesium combined with distraction osteogenesis synergistically stimulates bone tissue regeneration via CGRP-FAK-VEGF signaling axis. Biomaterials 275:120984
Yu X, Lv L, Zhang J, Zhang T, Xiao C, Li S (2015) Expression of neuropeptides and bone remodeling-related factors during periodontal tissue regeneration in denervated rats. J Mol Histol 46(2):195–203
Yu X, Liu S, Chen H, Zhao X, Chen X, Du Y et al (2018) CGRP gene-modified rBMSCs show better osteogenic differentiation capacity in vitro. J Mol Histol 49(4):357–367
Zhang Y, Xu J, Ruan YC, Yu MK, O’Laughlin M, Wise H et al (2016) Implant-derived magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med 22(10):1160–1169
Zhang D, Ni N, Su Y, Miao H, Tang Z, Ji Y et al (2020) Targeting local osteogenic and ancillary cells by mechanobiologically optimized magnesium scaffolds for orbital bone reconstruction in canines. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(25):27889–27904
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81900978], the Chongqing medical scientific research project [Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau] [2022QNXM005] and the Chongqing medical scientific research project [Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau] [2023MSXM056]. Funding sources were not involved in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, writing of the report, or the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL: investigation, data curation, formal analysis, writing–original draft. MY: investigation, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft. ML: data curation, formal analysis, visualization. ZR: data curation, validation. XT: data curation, writing—review. JH: data curation, writing—review. BS: validation, writing—review. GF: project administration, supervision, resources. QW: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, resources. Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Chongqing Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Yu, M., Liao, M. et al. The ratio of alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide to substance P is associated with the transition of bone metabolic states during aging and healing. J Mol Histol 54, 689–702 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-023-10167-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-023-10167-0