Abstract
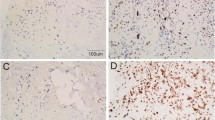
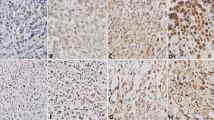
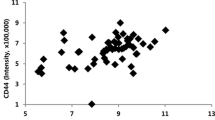
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression patterns of IGF2 and IMP3 in osteosarcoma as well as its relationship with angiogenesis in the tumor. IGF2 and IMP3 expression was detected by immunohistochemical staining in the serial sections of the osteosarcoma. The impacts of IGF2 and IMP3 expression patterns on tumor angiogenesis were evaluated by statistics. The IGF2 and IMP3 staining had different expression patterns in different osteosarcoma. Twelve out of the sixty-four cases of conventional osteosarcoma showed nuclear staining patterns, and twenty-nine showed cytoplasmic staining of IGF2 and IMP3 simultaneously. On the other hand, fourteen cases showed nuclear IGF2 staining but cytoplasmic IMP3 expression, and nine cases showed nuclear IMP3 staining and cytoplasmic IGF2 expression. Twenty-eight out of forty-seven cases of parosteal osteosarcoma showed nuclear IGF2 and IMP3 expression, nine showed cytoplasmic IGF2 and IMP3 expression simultaneously. Seven out of forty-seven cases of parosteal osteosarcoma expressed IGF2 with nuclear staining but expressed IMP3 with cytoplasmic staining. Meanwhile, three cases expressed IGF2 with cytoplasmic staining but expressed IMP3 with nuclear staining. Similar to the parosteal osteosarcoma, the periosteal osteosarcoma expressed IGF2 and IMP3 mainly with nuclear staining simultaneously, forty out of fifty-five cases of periosteal osteosarcoma did that. Five out of fifty-five cases expressed IGF2 and IMP3 with cytoplasmic staining at the same time. Four cases showed nuclear IGF2 staining and cytoplasmic IMP3 staining. In the parosteal and periosteal osteosarcoma, there was no significant difference in IGF and IMP3 expression patterns (P = 0.216). However, compared with conventional osteosarcoma, the parosteal and periosteal osteosarcoma showed significant difference in IMP3 and IGF2 expression (P = 0.016, P = 0.023). IGF2 and IMP3 expression patterns were positive correlation in the different osteosarcoma (r = 0.1021, P = 0.032). The Microvessel density (MVD) in osteosarcoma with IGF2 and IMP3 cytoplasmic staining was more than that with nuclear expression of IGF2 and IMP3, and the difference was significant (P = 0.024). Moreover, the conventional osteosarcoma with cytoplasmic IGF and IMP3 showed more MVD than parosteal and periosteal osteosarcoma with cytoplasmic IGF and IMP3, and the difference was significant (P = 0.035). IGF2 and IMP3 had different expression patterns, which might be associated with angiogenesis. However, cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of IGF2 and IMP3 might play different roles in the angiogenesis of osteosarcoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alitalo K, Carmeliet P (2002) Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 1(3):219–227
Al-Romaih K, Somers GR, Bayani J (2007) Modulation by decitabine of gene expression and growth of osteosarcoma U2OS cells in vitro and in xenografts: identification of apoptotic genes as targets for demethylation. Cancer Cell Int 7:14
Amit D, Tamir S, Birman T, Gofrit ON, Hochberg A (2011) Development of targeted therapy for bladder cancer mediated by a double promoter plasmid expressing diphtheria toxin under the control of IGF2–P3 and IGF2–P4 regulatory sequences. Int J Clin Exp Med 4(2):91–102
Avnet S, Sciacca L, Salerno M, Gancitano G, Cassarino MF, Longhi A, Zakikhani M, Carboni JM, Gottardis M, Giunti A, Pollak M, Vigneri R, Nicola B (2009) Insulin receptor isoform A and insulin-like growth factor II as additional treatment targets in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Res 69(6):2443–2452
Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A (1993) Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75:73–82
Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B (1997) The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1332(3):F105–F126
Bautista CM, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1991) Isolation of a novel insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human bone: a potential candidate for fixing IGFII in human bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:756–763
Beasley NJ, Prevo R, Banerji S et al (2002) Intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 62(5):1315–1320
Bjorndahl M, Renhai Cao L, Nissen J, Clasper S, Johnson LA, Xue Y, Zhou Z, Jackson D, Hansen AJ, Cao Y (2005) Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 induce lymphangiogenesis in vivo. PNAS 102(43):15593–15598
Cao Y (2005) Opinion: emerging mechanisms of tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 5(9):735–743
Chava S, Mohan V, Shetty PJ, et al. (2011) Immunohistochemical evaluation of p53, FHIT, and IGF2 gene expression in esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 10 June 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01213.x. [Epub ahead of print]
Che W, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Huang Q, Osawa M, Ohta S, Yoshizumi M, Glassman M, Lee JD, Yan C, Berk BC, Abe J (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1 enhances inflammatory responses in endothelial cells: role of Gab1 and MEKK3 in TNF-alpha-induced c-Jun and NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression. Circ Res 90(11):1222–1230
Chen ST, Jeng YM, Chang CC, Chang HH, Huang MC, Juan HF, Hsu CH, Lee H, Liao YF, Lee YL, Hsu WM, Lai HS (2011) Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 expression predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with neuroblastoma. Cancer Sci. 14 September 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02100.x. [Epub ahead of print]
Clemmons DR (1997) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and their role in controlling IGF actions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8(1):45–62
Cullen KJ, Yee D, Sly WS, Perdue J, Hampton B, Lippman ME, Rosen N (1990) Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and function in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50(1):48–53
Dadras SS, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Velasco P, Nguyen L, Vora A, Muzikansky A, Jahnke K, Hauschild A, Hirakawa S, Mihm MC, Detmar M (2005) Tumor lymphangiogenesis predicts melanoma metastasis to sentinel lymph nodes. Mod Pathol 18(9):1232–1242
Do SI, Kim YW, Park HR, Park YK (2008) Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA binding protein 3 (IMP3) in osteosarcoma. Oncol Res 17(6):269–272
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3(6):453–458
Fletcher CDM, Unni KK, Mertens F (eds) (2002) World health organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IARC Press, Lyon
Flossmann-Kast BB, Jehle PM, Hoeflich A, Adler G, Lutz MP (1998) Src stimulates insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-dependent cell proliferation by increasing IGF-I receptor number in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 58(16):3551–3554
Fokas E, Kamlah F, Hänze J, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Rose F, An HX (2010) EphA2 blockade enhances the anti-endothelial effect of radiation and inhibits irradiated tumor cell-induced migration of endothelial cells. Thorac Cancer 1:153–162
Guerra FK, Eijan AM, Puricelli L, Alonso DF, de Kier Joffe EB, Kornblihgtt AR, Charreau EH, Elizalde PV (1996) Varying patterns of expression of insulin-like growth factors I and II and their receptors in murine mammary adenocarcinomas of different metastasizing ability. Int J Cancer 65:812–820
Guo YS, Jin GF Jr, Townsend CM, Zhang T, Sheng HM, Beauchamp RD, Thompson JC (1995) Insulin-like growth factor II expression in carcinoma in colon cell lines: implications for autocrine actions. J Am Coll Surg 181:145–154
Hermanto U, Zong CS, Wang LH (2000) Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase selectively inhibits cell proliferation in human breast cancer cells displaying enhanced insulin-like growth factor I-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Cell Growth Differ 11:655–664
Jenkins PJ, Bustin SA (2004) Evidence for a link between IGF-I and cancer. Eur J Endocrinol 151(Suppl 1):S17–S22
Kappel CC, Velez-Yanguas MC, Hirschfeld S, Helman LJ (1994) Human osteosarcoma cell lines are dependent on insulin-like growth factor I for in vitro growth. Cancer Res 54:2803–2807
Kasperk C, Fitzsimmons R, Strong D, Mohan S, Jennings J, Wergedal J, Baylink D (1990) Studies of the mechanism by which androgens enhance mitogenesis and differentiation in bone cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 71(5):1322–1329
Kasperk CH, Faehling K, Bo¨rcso¨k I, Ziegler R (1996) Effects of androgens on subpopulations of the human osteosarcoma cell line SaOS2. Calcif Tissue Int 58:376–382
Kern PA, Svoboda ME, Eckel RH, Van Wyk JJ (1989) Insulinlike growth factor action and production in adipocytes and endothelial cells from human adipose tissue. Diabetes 38(6):710–717
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A, Friend KE (2000) The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev 21:215–244
Lee OH, Bae SK, Bae MH, Lee YM, Moon EJ, Cha HJ, Kwon YG, Kim KW (2000) Identification of angiogenic properties of insulin-like growth factor II in in vitro angiogenesis models. Br J Cancer 82(2):385–391
Li Y, Meng G, Huang L, Guo QN (2009) Hypomethylation of the P3 promoter is associated with up-regulation of IGF2 expression in human osteosarcoma. Hum Pathol 40(10):1441–1447
Long L, Rubin R, Brodt P (1998) Enhanced invasion and liver colonization by lung carcinoma cells overexpressing the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Exp Cell Res 238(1):116–121
Neuhausen SL, Brummel S, Ding YC, et al. (2011) Genetic variation in IGF2 and HTRA1 and breast cancer risk among BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 26 July 2011. [Epub ahead of print]
Ogawa O, Eccles MR, Szeto J et al (1993) Relaxation of insulin-like growth factor II gene imprinting implicated in Wilms’ tumour. Nature 362:749–751
Ohlaaon R, Nystrom A, Pfeifer-Ohlsson S et al (1993) IGF2 is parentally imprinted during human embryogenesis and in the Beckwith-Wiedemann sindrome. Nat Genet 4:94–97
Quinn KA, Treston AM, Unsworth EJ, Miller MJ, Vos M, Grimley C, Battey J, Mulshine JL, Cuttitta F (1996) Insulin-like growth factor expression in human cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 271:11477–11483
Rainier S, Johnson LA, Dobry CJ, Ping AJ, Grundy PE, Feinberg AP (1993) Relaxation of imprinted genes in human cancer. Nature 362:747–749
Reinmuth N, Fan F, Liu W, Parikh AA, Stoeltzing O, Jung YD, Bucana CD, Radinsky R, Gallick GE, Ellis LM (2002) Impact of insulin-like growth factor receptor-I function on angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of colon cancer. Lab Invest 82(10):1377–1389
Ritter MR, Dorrell MI, Edmonds J, Friedlander SF, Friedlander M (2002) Insulin-like growth factor 2 and potential regulators of hemangioma growth and involution identified by large-scale expression analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(11):7455–7460
Rosato R, Gerland K, Jammes H, Bataille-Simoneau N, Segovia B, Mercier L, Groyer A (2001) The IGFBP-3 mRNA and protein levels are IGF-I-dependent and GH-independent in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 175(1–2):15–27
Shigematsu S, Yamauchi K, Nakajima K, Iijima S, Aizawa T, Hashizume K (1999) IGF-1 regulates migration and angiogenesis of human endothelial cells. Endocr J 46(Suppl):S59–S62
Steller MA, Delgado CH, Bartels CJ, Woodworth CD, Zou Z (1996) Overexpression of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and autocrine stimulation in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Res 56:1761–1765
Tanno S, Tanno S, Mitsuuchi Y, Altomare DA, Xiao GH, Testa JR (2001) AKT activation up-regulates insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(2):589–593
Viereck V, Siggelkow H, Pannem R, Braulke T, Scharf JG, Kübler B (2007) Alteration of the insulin-like growth factor axis during in vitro differentiation of the human osteosarcoma cell line HOS 58. J Cell Biochem 102(1):28–40
Xie Y, Skytting B, Nilsson G, Brodin B, Larsson O (1999) Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in synovial sarcoma: association with an aggressive phenotype. Cancer Res 59(15):3588–3591
Yaginuma Y, Nishiwaki K, Kitamura S, Hayashi H, Sengoku K, Ishikawa M (1997) Relaxation of insulin-like growth factor-II gene imprinting in human gynecologic tumors. Oncology (Basel) 54:502–507
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Jinan Science and Technology Bureau: independent innovation projects of university and institutes Stationed in jinan city(No. 201102060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peng Chen and Shao-jin Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Wang, Sj., Wang, Hb. et al. The distribution of IGF2 and IMP3 in osteosarcoma and its relationship with angiogenesis. J Mol Hist 43, 63–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9370-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9370-2