Abstract
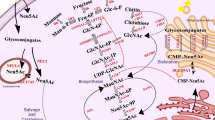
The bifunctional enzyme UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase (GNE) catalyzes the first two committed steps in sialic acid synthesis. Non-allosteric GNE gene mutations cause the muscular disorder GNE myopathy (also known as hereditary inclusion body myopathy), whose exact pathology remains unknown. Increased knowledge of GNE regulation, including isoform regulation, may help elucidate the pathology of GNE myopathy. While eight mRNA transcripts encoding human GNE isoforms are described, we only identified two mouse Gne mRNA transcripts, encoding mGne1 and mGne2, homologous to human hGNE1 and hGNE2. Orthologs of the other human isoforms were not identified in mice. mGne1 appeared as the ubiquitously expressed, major mouse isoform. The mGne2 encoding transcript is differentially expressed and may act as a tissue-specific regulator of sialylation. mGne2 expression appeared significantly increased the first 2 days of life, possibly reflecting the high sialic acid demand during this period. Tissues of the knock-in Gne p.M712T mouse model had similar mGne transcript expression levels among genotypes, indicating no effect of the mutation on mRNA expression. However, upon treatment of these mice with N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc, a Gne substrate, sialic acid precursor, and proposed therapy for GNE myopathy), Gne transcript expression, in particular mGne2, increased significantly, likely resulting in increased Gne enzymatic activities. This dual effect of ManNAc supplementation (increased flux through the sialic acid pathway and increased Gne activity) needs to be considered when treating GNE myopathy patients with ManNAc. In addition, the existence and expression of GNE isoforms needs consideration when designing other therapeutic strategies for GNE myopathy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A. avenae :
-
Acidovorax avenae
- B2M:
-
β2 microglobulin
- BLAST:
-
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool
- B. subtilis :
-
Bacillus subtilis
- CDM:
-
Consensus Data Mining
- CMP:
-
Cytidine monophosphate
- DMRV:
-
Distal Myopathy with Rimmed Vacuoles
- DYRK2:
-
Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 2
- E:
-
Embryonic day
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
- FDM:
-
Fragment Database Mining
- GCNA:
-
N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase
- GlcNAc:
-
N-acetylglucosamine
- GNE:
-
UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase
- GOR:
-
Garnier-Osguthorpe-Robson
- H. arsenicoxydans :
-
Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans
- HIBM:
-
Hereditary Inclusion Body Myopathy
- His:
-
Histidine
- H. sapiens :
-
Homo sapiens
- Min:
-
Minutes
- ManNAc:
-
N-acetylmannosamine
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Neu5Ac:
-
N-acetylneuraminic acid
- OMIM:
-
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
- P:
-
Postnatal day
- P. carotovorum :
-
Pectobacterium carotovorum
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- Pdb:
-
Protein databank
- PRPP:
-
Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate
- PSIPRED:
-
Protein Structure Initiative Prediction
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- SGK1:
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1
- S. gordonii :
-
Streptococcus gordonii
- T. maritime :
-
Thermotoga maritima
- UDP:
-
Uridine diphosphate
- VAV1:
-
Vav-family member of guanine nucleotide exchange factors
References
Hinderlich, S., Stasche, R., Zeitler, R., Reutter, W.: A bifunctional enzyme catalyzes the first two steps in N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis of rat liver. Purification and characterization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24313–24318 (1997)
Eisenberg, I., Avidan, N., Potikha, T., Hochner, H., Chen, M., Olender, T., Barash, M., Shemesh, M., Sadeh, M., Grabov-Nardini, G., Shmilevich, I., Friedmann, A., Karpati, G., Bradley, W.G., Baumbach, L., Lancet, D., Asher, E.B., Beckmann, J.S., Argov, Z., Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S.: The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nat. Genet. 29, 83–87 (2001)
Kornfeld, S., Kornfeld, R., Neufeld, E.F., O'Brien, P.J.: The feedback control of sugar nucleotide biosynthesis in liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 52, 371–379 (1964)
Seppala, R., Lehto, V.P., Gahl, W.A.: Mutations in the human UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene define the disease sialuria and the allosteric site of the enzyme. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64, 1563–1569 (1999)
Chen, X., Varki, A.: Advances in the biology and chemistry of sialic acids. ACS Chem. Biol. 5, 163–176 (2010)
Varki, N.M., Varki, A.: Diversity in cell surface sialic acid presentations: implications for biology and disease. Lab. Invest. 87, 851–857 (2007)
Watts, G.D., Thorne, M., Kovach, M.J., Pestronk, A., Kimonis, V.E.: Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in chromosome 9p associated hereditary inclusion body myopathy: exclusion of GNE and three other candidate genes. Neuromuscul. Disord. 13, 559–567 (2003)
Reinke, S.O., Hinderlich, S.: Prediction of three different isoforms of the human UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. FEBS Lett. 581, 3327–3331 (2007)
Yardeni, T., Choekyi, T., Jacobs, K., Ciccone, C., Patzel, K., Anikster, Y., Gahl, W.A., Kurochkina, N., Huizing, M.: Identification, Tissue Distribution, and Molecular Modeling of Novel Human Isoforms of the Key Enzyme in Sialic Acid Synthesis, UDP-GlcNAc 2-Epimerase/ManNAc Kinase. Biochemistry 50, 8914–8925 (2011)
Huizing, M., Krasnewich, D.M.: Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: a decade of progress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1792, 881–887 (2009)
Noguchi, S., Keira, Y., Murayama, K., Ogawa, M., Fujita, M., Kawahara, G., Oya, Y., Imazawa, M., Goto, Y., Hayashi, Y.K., Nonaka, I., Nishino, I.: Reduction of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase activity and sialylation in distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 11402–11407 (2004)
Schwarzkopf, M., Knobeloch, K.P., Rohde, E., Hinderlich, S., Wiechens, N., Lucka, L., Horak, I., Reutter, W., Horstkorte, R.: Sialylation is essential for early development in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 5267–5270 (2002)
Malicdan, M.C., Noguchi, S., Nonaka, I., Hayashi, Y.K., Nishino, I.: A Gne knockout mouse expressing human GNE D176V mutation develops features similar to distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles or hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 2669–2682 (2007)
Galeano, B., Klootwijk, R., Manoli, I., Sun, M., Ciccone, C., Darvish, D., Starost, M.F., Zerfas, P.M., Hoffmann, V.J., Hoogstraten-Miller, S., Krasnewich, D.M., Gahl, W.A., Huizing, M.: Mutation in the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis causes severe glomerular proteinuria and is rescued by N-acetylmannosamine. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1585–1594 (2007)
Kakani, S., Yardeni, T., Poling, J., Ciccone, C., Niethamer, T., Klootwijk, E.D., Manoli, I., Darvish, D., Hoogstraten-Miller, S., Zerfas, P., Tian, E., Ten Hagen, K.G., Kopp, J.B., Gahl, W.A., Huizing, M.: The Gne M712T mouse as a model for human glomerulopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 1431–1440 (2012)
Malicdan, M.C., Noguchi, S., Hayashi, Y.K., Nonaka, I., Nishino, I.: Prophylactic treatment with sialic acid metabolites precludes the development of the myopathic phenotype in the DMRV-hIBM mouse model. Nat. Med. 15, 690–695 (2009)
Reinke, S.O., Lehmer, G., Hinderlich, S., Reutter, W.: Regulation and pathophysiological implications of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase (GNE) as the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis. Biol. Chem. 390, 591–599 (2009)
Garnier, J., Osguthorpe, D.J., Robson, B.: Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 120, 97–120 (1978)
Kloczkowski, A., Ting, K.L., Jernigan, R.L., Garnier, J.: Combining the GOR V algorithm with evolutionary information for protein secondary structure prediction from amino acid sequence. Proteins 49, 154–166 (2002)
Cheng, H., Sen, T.Z., Kloczkowski, A., Margaritis, D., Jernigan, R.L.: Prediction of protein secondary structure by mining structural fragment database. Polymer. (Guildf). 46(4314–4321) (2005)
Sen, T.Z., Cheng, H., Kloczkowski, A., Jernigan, R.L.: A Consensus Data Mining secondary structure prediction by combining GOR V and Fragment Database Mining. Protein Sci. 15, 2499–2506 (2006)
Bryson, K., McGuffin, L.J., Marsden, R.L., Ward, J.J., Sodhi, J.S., Jones, D.T.: Protein structure prediction servers at University College London. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, W36–38 (2005)
Yardeni, T., Eckhaus, M., Morris, H.D., Huizing, M., Hoogstraten-Miller, S.: Retro-orbital injections in mice. Lab. Anim. (NY) 40(155–160) (2011)
Yardeni, T., Ciccone, C., Hoogstraten-Miller, S., Darvish, D., Anikster, Y., Maples, P.B., Jay, C.M., Gahl, W.A., Nemunaitis, J., Huizing, M.: A Non-Viral, GNE-Lipoplex Treatment to Correct Sialylation Defects in Gne-Mutant (M712T) Mice. In: Proceedings of the American Society for Gene & Cell Therapy, Annual Meeting, Washington, DC (2010)
Schmittgen, T.D., Livak, K.J.: Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108 (2008)
Reinke, S.O., Eidenschink, C., Jay, C.M., Hinderlich, S.: Biochemical characterization of human and murine isoforms of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE). Glycoconj. J. 26, 415–422 (2009)
Eisenberg, I., Grabov-Nardini, G., Hochner, H., Korner, M., Sadeh, M., Bertorini, T., Bushby, K., Castellan, C., Felice, K., Mendell, J., Merlini, L., Shilling, C., Wirguin, I., Argov, Z., Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S.: Mutations spectrum of GNE in hereditary inclusion body myopathy sparing the quadriceps. Hum. Mutat. 21, 99 (2003)
Tong, Y., Tempel, W., Nedyalkova, L., Mackenzie, F., Park, H.W.: Crystal structure of the N-acetylmannosamine kinase domain of GNE. PLoS One 4, e7165 (2009)
Kurochkina, N., Yardeni, T., Huizing, M.: Molecular modeling of the bifunctional enzyme UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase and predictions of structural effects of mutations associated with HIBM and sialuria. Glycobiology 20, 322–337 (2010)
Zhao, B., Lehr, R., Smallwood, A.M., Ho, T.F., Maley, K., Randall, T., Head, M.S., Koretke, K.K., Schnackenberg, C.G.: Crystal structure of the kinase domain of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in complex with AMP PNP. Protein Sci. 16, 2761–2769 (2007)
Keppler, O.T., Hinderlich, S., Langner, J., Schwartz-Albiez, R., Reutter, W., Pawlita, M.: UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase: a regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science 284, 1372–1376 (1999)
Krause, S., Hinderlich, S., Amsili, S., Horstkorte, R., Wiendl, H., Argov, Z., Mitrani-Rosenbaum, S., Lochmuller, H.: Localization of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManAc kinase (GNE) in the Golgi complex and the nucleus of mammalian cells. Exp. Cell Res. 304, 365–379 (2005)
Ghaderi, D., Strauss, H.M., Reinke, S., Cirak, S., Reutter, W., Lucka, L., Hinderlich, S.: Evidence for dynamic interplay of different oligomeric states of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase by biophysical methods. J. Mol. Biol. 369, 746–758 (2007)
Yogev, O., Pines, O.: Dual targeting of mitochondrial proteins: mechanism, regulation and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 1012–1020 (2011)
Duncan, P.I., Raymond, F., Fuerholz, A., Sprenger, N.: Sialic acid utilisation and synthesis in the neonatal rat revisited. PLoS One 4, e8241 (2009)
Kontou, M., Weidemann, W., Bork, K., Horstkorte, R.: Beyond glycosylation: sialic acid precursors act as signaling molecules and are involved in cellular control of differentiation of PC12 cells. Biol. Chem. 390, 575–579 (2009)
Kean, E.L., Munster-Kuhnel, A.K., Gerardy-Schahn, R.: CMP-sialic acid synthetase of the nucleus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1673, 56–65 (2004)
Kershaw, D.B., Beck, S.G., Wharram, B.L., Wiggins, J.E., Goyal, M., Thomas, P.E., Wiggins, R.C.: Molecular cloning and characterization of human podocalyxin-like protein. Orthologous relationship to rabbit PCLP1 and rat podocalyxin. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 15708–15714 (1997)
Chou, H.H., Takematsu, H., Diaz, S., Iber, J., Nickerson, E., Wright, K.L., Muchmore, E.A., Nelson, D.L., Warren, S.T., Varki, A.: A mutation in human CMP-sialic acid hydroxylase occurred after the Homo-Pan divergence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95, 11751–11756 (1998)
Nemunaitis, G., Maples, P.B., Jay, C., Gahl, W.A., Huizing, M., Poling, J., Tong, A.W., Phadke, A.P., Pappen, B.O., Bedell, C., Templeton, N.S., Kuhn, J., Senzer, N., Nemunaitis, J.: Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: single patient response to GNE gene Lipoplex therapy. J. Gene Med. 12, 403–412 (2010)
Nemunaitis, G., Jay, C.M., Maples, P.B., Gahl, W.A., Huizing, M., Yardeni, T., Tong, A.W., Phadke, A.P., Pappen, B.O., Bedell, C., Allen, H., Hernandez, C., Templeton, N.S., Kuhn, J., Senzer, N., Nemunaitis, J.: Hereditary Inclusion Body Myopathy: Single Patient Response to Intravenous Dosing of GNE Gene Lipoplex. Hum. Gene Ther. 22, 1331–1341 (2011)
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the expert laboratory work of Dr. Shelley Hoogstraten-Miller, Katherine Berger, Katherine Patzel, and Adrian Astiz-Martinez. The authors thank Theresa Calhoun for her skilled assistance with mouse maintenance. We thank the HIBM Research group (Encino, CA) for providing the knock-in Gne p.M712T mouse model. This work was performed in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a PhD degree of T.Y., Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel. This study was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Human Genome Research Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, United States (T.Y., K.J., T.K.N., C.C., W.A.G., and M.H.) and Research Funds of The School of Theoretical Modeling, Chevy Chase, Maryland, United States (N.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yardeni, T., Jacobs, K., Niethamer, T.K. et al. Murine isoforms of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase/ManNAc kinase: Secondary structures, expression profiles, and response to ManNAc therapy. Glycoconj J 30, 609–618 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-012-9459-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-012-9459-1