Abstract
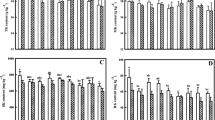
Soybean-maize rotation is a profitable cropping system and is used under rain fed conditions in north China. Since crop yields have been reported to decrease when K fertilizers are not used, we analyzed the productivity trends, soil-exchangeable and non-exchangeable K contents, and K balance in a continuous cropping experiment conducted in an area with an alfisol soil in the Liaohe River plain, China. The trial, established in early 1990 and continued till 2007, included 8 combinations of recycled manure and N, P, and K fertilizers. In the unfertilized plot, the yields of soybean and maize were 1,486 and 4,124 kg ha−1 respectively (mean yield over 18 years). The yields of both soybean and maize increased to 2,195 and 7,476 kg ha−1, respectively, in response to the application of inorganic N, P, and K fertilizers. The maximum yields of soybean (2,424 kg ha−1) and maize (7,790 kg ha−1) were obtained in the plots under treatment with N, P, and K fertilizers and recycled manure. K was one of the yield-limiting macronutrients: regular K application was required to make investments in the application of other mineral nutrients profitable. The decrease in the yields of soybean and maize owing to the absence of K application averaged 400 and 780 kg ha−1, respectively. Soybean seed and maize grain yields significantly increased with the application of recycled manure. For both these crops, the variation coefficients of grain were lower with treatments that included recycled manure than without treatment. After 18 years, the soil-exchangeable and non-exchangeable K concentrations decreased; the concentrations in the case of treatments that did not include K fertilizers were not significantly different. Treatment with N, P, and K fertilizers appreciably improved the fertility level of the soil, increased the concentration of soil-exchangeable K, and decreased the non-exchangeable K concentration. In soils under treatment with N, P, and K fertilizers and recycled manure, the soil-exchangeable and non-exchangeable K levels in the 0–20 cm-deep soil layer increased by 34% and 2%, respectively, over the initial levels. Both soil-exchangeable and non-exchangeable K concentrations were the highest with on treatment with N, P, and K fertilizers and recycled manure, followed by treatment with N, P, and K fertilizers. These concentrations were lowest in unfertilized soils; the other treatments yielded intermediate results. The results showed a total removal of K by the crops, and the amount removed exceeded the amount of K added to the soil; in treatments that did not include K fertilizers, a net negative K balance was observed, from 184 to 575 kg ha−2. The combined use of N, P, and K fertilizers and recycled manure increased the K content of the 0–20 cm-deep soil layer by 125% compared to the increase obtained with the application of N, P, and K fertilizers alone. The results clearly reveal that current mineral fertilizer applications are inadequate; instead, the annual application of recycled manure along with N, P, and K fertilizers could sustain future yields and soil productivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MM, Shaheed SM, Kubota D, Masunaga T, Wakatsuki T (1997) Soil degradation during the period 1961–1995 in Bangladesh .1. Carbon and nitrogen. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 43:863–878
Anon (1986) Analysis of agricultural materials, reference book 427, 3rd edn. HMSO, London
Bhattacharyya R, Prakash V, Kundu S, Ghosh BN, Srivastva AK, Gupta HS (2006) Potassium balance as influenced by farmyard manure application under continuous soybean–wheat cropping system in a Typic Haplaquept. Geoderma 137:155–160. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.08.006
Cai ZC, Qin SW (2006) Crop yield, N use efficiency and environmental impact of a long-term fertilization experiment in fluvor aquic soil in north China. Acta Pedol Sin 43:885–891
Dobermann A, Cassman KG, Sta Cruz PC, Adviento MAA, Pampolino MF (1996) Fertilizer inputs, nutrient balance, and soil nutrient-supplying power in intensive, irrigated rice systems. III. Phosphorus. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 46:111–125. doi:10.1007/BF00704311
Dobermann A, Witt C, Dawe D, Abdulrachman S, Gines HC, Nagarajan R, Satawathananont S, Son TT, Tan CS, Wang GH, Chien NV, Thoa VTK, Phung CV, Stalin P, Muthukrishnan P, Ravi V, Babu M, Chatuporn S, Sookthongsa J, Sun Q, Fu R, Simbahan GC, Adviento MAA (2002) Site-specific nutrient management for intensive rice cropping systems in Asia. Field Crops Res 74:37–66. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00197-6
Guan YX, Dai JY, Xu SC (1997) Effects of soil drought during flowering and rewatering on plant compensative growth and yield of maize. Acta Agron Sin 23(6):740–745
Jagadamma S, Lal R, Hoeft RG, Nafziger ED, Adee EA (2008) Nitrogen fertilization and cropping system impacts on soil properties and their relationship to crop yield in the central Corn Belt, USA. Soil Tillage Res 98:120–129. doi:10.1016/j.still.2007.10.008
Jones JB (1973) Soil testing in the United States. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 4:307–322. doi:10.1080/00103627309366451
Jouany C, Colomb B, Bosc M (1996) Long-term effects of potassium fertilization on yields and fertility status of calcareous soils of Southwest France. Eur J Agron 5:287–294. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(96)02042-4
Kong XB, Zhang FG, Wei Q, Xu Y, Hui JG (2006) Influence of land use change on soil nutrients in an intensive agricultural region of North China. Soil Tillage Res 88:85–94. doi:10.1016/j.still.2005.04.010
Liu EK, Zhao BQ, Hu CH, Li XY, Li YT (2007) Effects of long-term nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer applications on maize yield and soil fertility. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 13:789–794
Liu SP, Nie XT, Zhang HC, Dai QG, Huo ZY, Xu K (2006) Effects of tillage and straw returning on soil fertility and grain yield in a wheat-rice double cropping system. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 22:48–51
Liu XJ, Wang JC, Lu SH, Zhang FS, Zeng XZ, Ai YW, Peng SB, Christie P (2003) Effects of non-flooded mulching cultivation on crop yield, nutrient uptake and nutrient balance in rice–wheat cropping systems. Field Crops Res 83:297–311. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(03)00079-0
Liu RL, Jin JY, Wu RG, Liang MZ (2000) Study on the characteristics of potassium cycling in different soil–crop systems in northern China. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 2:123–132
Ma JY, Li KJ, Cao CY, Zheng CL (2007) Effect of long-term located organic-inorganic fertilizer application on fluvo-aquic soil fertility and crop yield. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 13(2):236–241
Mengel K, Rahmatullah K (1994) Exploitation of potassium by various crop species from primary minerals in soils rich in micas. Biol Fertil Soils 17:75–79. doi:10.1007/BF00418676
Mussgnug F, Becker M, Son TT, Buresh R, Vlek PLG (2006) Yield gaps and nutrient balances in intensive, rice-based cropping systems on degraded soils in the Red River Delta of Vietnam. Field Crops Res 98:127–140. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.012
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium carbonate. US Department of Agriculture, Circular no. 939, p 19
Quemener J (1986) Important factors in potassium balance sheets. In: Laudelout H (ed) Nutrient balances and the need for potassium. I.·P. I, Bern, pp 41–72
Regmi AP, Ladha JK, Pathak H, Pasuquin E, Bueno C, Dawe D, Hobbs PR, Joshy D, Maskey SL, Pandey SP (2002) Yield and soil fertility trends in a 20-year rice–rice–wheat experiment in Nepal. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:857–867
Sayre JD (1948) Mineral accumulation in corn. Plant Physiol 23:267–281
Shen SM (1998) Soil fertility in China. Chinese Agricultural Press, Beijing
Singh M, Singh VP, Reddy D (2002a) Potassium balance and release kinetics under continuous rice–wheat cropping system in Vertisol. Field Crops Res 77:81–91. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00206-4
Singh M, Tripathi AK, Reddy D (2002b) Potassium balance and release kinetics of non-exchangeable K in a Typic Haplustert as influenced by cattle manure application under a soybean–wheat system. Aust J Soil Res 40:533–541. doi:10.1071/SR00064
Srinivasa RC, Subba R, Srivastava S, Singh SP (1999a) Crop response, uptake and the efficiency of potassium in berseem and sudan grass on a Typic Haplustert. J Potassium Res 15:113–118
Srinivasa RC, Anand SM, Subba RA, Raja GV (1999b) Kinetics of non-exchangeable potassium release from a Tropaquept as influenced by long-term cropping, fertilization and manuring. Aust J Soil Res 37:317–328. doi:10.1071/S98049
Su YZ, Wang F, Suo DR, Zhang ZH, Du MW (2006) Long-term effect of fertilizer and manure application on soil-carbon sequestration and soil fertility under the wheat–wheat–maize cropping system in northwest China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 75:285–295. doi:10.1007/s10705-006-9034-x
Su YZ (2001) Potassium balance and potash application effect in cultivated lands of Gansu Province. Soils 2:73–76
Swarup A, Wanjari RH (2000) Three decades of all-Iindia co-ordinated research project on long-term fertilizer experiments to study changes in soil quality crop productivity and sustainability. Indian Institute of Soil Science, Bhopal, India
Tan DS, Jin JY, Huang SW (2007a) Effect of long-term application of K fertilizer on spring maize yield and soil K in northeast China. Sci Agric Sin 40:2234–2240
Tan DS, Jin JY, Huang SW, He P (2007b) Effect of long-term K application on corn yield and potassium forms in plough layer of black soil and meadow soil in northeast of China. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 13:850–855
Wang BR, Xu MG, Wen SL (2005) Effect of long-term fertilizers application on soil characteristics and crop growth in red soil upland. J Soil Water Conserv 19(1):97–101
Wihardjaka A, Kirk GJD, Abdulrachman S, Mamaril CP (1999) Potassium balances in rain fed lowland rice on a light-textured soil. Field Crops Res 64:237–247. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00045-3
Wood LK, De Turk EE (1940) The adsorption of potassium in soil in non replaceable forms. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 5:152–161
Xie JC, Zhou JM (1999) Progress in study on soil potassium and application of potassium fertilizers in China. Soils 31:244–254
Yang CM, Yang LZ, Yang YX, Ouyang Z (2004) Rice root growth and nutrient uptake as influenced by organic manure in continuously and alternately flooded paddy soils. Agric Water Manage 70:67–81. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2004.05.003
Yang ZM, Zhou WZ, Bao SD (1999) Comprehensive evaluation on potassium supplying potential of main soils in China. Acta Pedol Sin 36(3):377–385
Yu WT, Zhao X, Zhang L, Ma Q (2007) Contribution of long-term fertilization to crop yield. Chin J Ecol 26(12):2040–2044
Zhang DX, Han ZQ, Liu W, Gao SG, Hou DJ, Li GF, Chang LS (2005) Effect of different treatments on the space-time dynamic changes of soil nutrients by returning maize straw under different decay conditions. Chin J Soil Sci 36:360–364
Zhang SM, Hao MD, Chen L (2006) Effects of long-term fertilization on yield of wheat and soil fertility in dry 1and of Loess Plateau. Agr Res Arid Areas 24:85–89
Zhang SM, Yan H, Liu GD (1999) Soil K supplying capacity and release of non-exchangeable K in Shandong soils. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 5(3):26–31
Zhou LY, Li XD, Tang X, Lin YJ, Li ZF (2007) Effects of different application amount of N, P, K fertilizers on physiological characteristics, yield and kernel quality of peanut. Chin J Appl Ecol 18:2468–2474
Zhuang HY, Cao WX, Shen XP, Lu JF (2000) Soil nutrient balance and adjustment under intensive wheat-rice double cropping. Acta Ecol Sin 20:765–770
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the kind financial support of the Key Innovational Project in Environment and Resources Fields from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-407, KZCX2-YW-405), National Key Technology R & D Program(2006BAD05B05) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (40,701,067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, WT., Jiang, ZS., Zhou, H. et al. Effects of nutrient cycling on grain yields and potassium balance. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 84, 203–213 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9237-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9237-4