Abstract
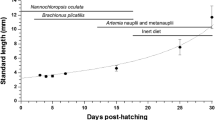
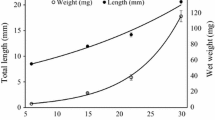
Digestive enzymatic activity and growth performance on tropical gar (Atractosteus tropicus) larvae fed Artemia nauplii (LF), frozen adult Artemia (AB), an artificial diet (AF) with 46% protein and 16% lipids and a starvation group (SG) from first feeding (5 days after hatching—5 DAH) to 34 DAH were studied. All larvae under starvation (SG) died at 15 DAH. By the end of the experimental period, morphological variables (total length, wet weight and specific growth rate) were significant in larvae fed AF compared to LF and AB. All enzymes studied in the experiment were present since the start of exogenous feeding (including pepsin) and the enzymatic activity varied with the diets. Low levels of enzymatic activity were observed until the 29 DAH; however, after this moment, there was a significant increase (eightfold), particularly for the AF treatment. In vitro protein digestibility tests performed with enzymatic extracts showed that artificial diets with 52% protein and 14% lipids were better digested by larvae before 30 DAH, while diets with 45% protein and 11% lipids were better digested after this age. Taking into account the better growth performance, higher enzymatic activity and better protein digestibility obtained, artificial diets can be used since the start of exogenous feeding on tropical gar larvae, as in other lepisosteids.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera C, Mendoza R, Rodríguez G, Márquez G (2002) Morphological description of alligator gar and tropical gar larvae, with an emphasis on growth indicators. Trans Am Fish Soc 131:899–909
Alarcon FJ, Moyano FJ, Diaz M, Fernandez-Diaz C, Yúfera M (1999) Optimization of the protein fraction of microcapsules used in feeding of marine fish larvae using in vitro digestibility techniques. Aquac Nutr 5:107–113
Anson ML (1938) The estimation of pepsin, trypsin, papain and cathepsin with hemoglobin. J Gen Physiol 22:79–89
Baragi V, Lovell RT (1986) Digestive enzyme activities in striped bass from first feeding through larval development. Trans Am Fish Soc 115:478–484
Barrows FT (2000) Larval feeds: two methods for production of on-size, microbound particles. Glob Aquaculture Advocate 3(1):61–63
Bassompierre M, Larsen KL, Zimmermann W, McLean E (1998) Comparison of chemical, electrophoretic and in vitro digestion methods for predicting fish meal nutritive quality. Aquac Nutr 4:232–239
Bernfeld P (1951) Amylases (alpha) and (beta). In: Colowick S, Kaplan N (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 149–158
Blaxter JHS, Hempel G (1963) The influence of egg size on herring larvae. J Cons Perm Int Explor Mer 28:211–240
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buddington RK (1985) Digestive secretions of lake sturgeon, Acipenser fulvescens, during early development. J Fish Biol 26:715–723
Buddington RK, Doroshov SI (1986) Development of digestive secretions in white sturgeon juveniles (Acipenser transmontanus). Comp Biochem Physiol 83A:233–238
Castro-Mejia J, Espindola-Ronquillo Y, Castro-Mejia G, Cremiux-Grimaldi JC (2009) Efecto de dos dietas proteicas en el crecimiento y sobrevivencia de prejuveniles de Atractosteus tropicus Gill, 1863 (Pejelagarto). BIOCYTE 2(8):77–88
Chen BN, Qin JG, Carragher JF, Clarke SM, Kumar MS, Hutchinson WG (2007) Deleterious effects of food restrictions in yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi during early development. Aquaculture 271:326–335
Clay TA (2009) Growth, survival, and cannibalism rates of alligator gar Atractosteus spatula in recirculating aquaculture systems. Dissertation, Nicholls State University
Comabella Y, Mendoza R, Aguilera C, Carrillo O, Hurtado A, García-Galano T (2006) Digestive enzyme activity during early larval development of the Cuban gar Atractosteus tristoechus. Fish Physiol Biochem 32:147–157
CONAPESCA (2008) Comisión Nacional de Acuacultura y Pesca, Anuario Estadístico de Acuacultura y Pesca. Mazatlán, Sinaloa, México: CONAPESCA_SAGARPA, pp 213
Conceicao LEC, Aragao C, Richard N, Engrola S, Gavaia P, Mira S, Dias J (2010) Novel methodologies in marine fish larval nutrition. Fish Physiol Biochem 36:1–16
Dabrowski K, Krumschnabel G, Paukku M, Labanowski J (1992) Cyclic growth and activity of pancreatic enzymes in alevins of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.). J Fish Biol 40:511–521
Erlanger FE, Kokoswky N, Cohen W (1961) The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:271–278
Galgani F, Nagayama F (1986) Characteristic of digestive proteolysis of crabs Portunus triberculatus, Portunus sanguinolentus and Charybdis japonica. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52:2183–2188
Hernández U (1999) Punto crítico de no-retorno en larvas de pejelagarto Atractosteus tropicus (Gill, 1863). Dissertation, Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco
Hjelmeland K, Pedersen BH, Nielssen EM (1988) Trypsin content in intestines of herring larvae, Clupea harengus, ingesting inert polystrene spheres or live crustacea prey. Mar Biol 98:331–335
Hoque M, Takemura A, Takano K (1998) Annual changes in oocyte development and serum vitellogenin level in the rabbitfish Siganus canaliculatus (Park) in Okinawa, Southern Japan. Fisheries Sci 64(1):44–51
Lauff M, Hofer R (1984) Proteolytic enzymes in fish development and the importance of dietary enzymes. Aquaculture 37:335–346
Lazo J, Mendoza R, Holt J, Aguilera C, Arnold C (2007) Characterization of digestive enzymes during larval development of red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus). Aquaculture 265(1–4):194–205
Maldonado EC, Ponce JT (1991) Aprovechamiento de peces forrajeros en la alimentación del pejelagarto Atractosteus tropicus Gill en jaulas flotantes en el Estado de Tabasco, México. Universidad y Ciencia 8(15):77–90
Márquez H (1998) Efectos de la temperatura en el desarrollo de embriones y en crecimiento de las larvas de pejelagarto Atractosteus tropicus bajo condiciones de Laboratorio. Dissertation, Universidad Juárez Autónoma de Tabasco. Tabasco
Martínez I, Moyano FJ, Fernández-Díaz C, Yúfera M (1999) Digestive enzyme activity during larvla development of Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis). Fish Physiol Biochem 21:317–323
Mendoza R, Aguilera C, Rodriguez G, González M, Castro R (2002) Morphophysiological studies on alligator gar (Atractosteus spatula) larval development as a basis for their culture and repopulation of their natural habitats. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 12:133–142
Mendoza R, Aguilera C, Ferrara A (2008a) Gar biology and culture: status and prospects. Aquacult Res 39:748–763
Mendoza R, Aguilera C, Carron L, Montemayor J, Gonzalez M (2008b) Weaning of Alligator Gar (Atractosteus spatula) larvae to artificial diets. Aquac Nutr 14:223–231
Moyano FJ, Diaz M, Alarcon FJ, Sarasquete MC (1996) Characterization of digestive enzyme activity during larval development of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Fish Physiol Biochem 15:121–130
Munilla R, Saborido F (1996) Digestive enzymes in marine species I. Proteinase activities in gut from redfish (Sebastes mentella), seabream (Sparus aurata) and turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Comp Biochem Physiol 113B:395–402
Munilla R, Stark R (1989) Protein digestion in early turbot larvae Scophthalmus maximuis (L.). Aquaculture 81:315–327
Nguyen HQ, Reinertsen H, Wold P, Tran TM, Kjørsvik E (2010) Effects of early weaning strategies on growth, survival and digestive enzyme activities in cobia (Rachycentron canadum L.) larvae. Aquacult Int. doi:10.1007/s10499-010-9341-8
Oozeki Y, Bailey KM (1995) Ontogenetic development of digestive enzyme activities in larval walleye Pollock, Theragra chalcogramma. Mar Biol 112:177–186
Shan X, Huang W, Cao L, Wu Y (2008) Advances in studies of the effects of starvation on growth and development of fish larvae. J Ocean Univ China 7(3):319–326
Steel R, Torrie J (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Tanaka M (1971) Studies on the structure and function of the digestive system in teleost larvae-iii. development of the digestive system during postlarval stage. Japanese J Ichtiol 18(4):164–174
Walter HE (1984) Proteinases: methods with haemoglobin, casein and azocoll as substrates. In: Bergmeyer J, Grad M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 5. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, Germany, pp 270–277
Zambonino JL, Cahu CL (2007) Dietary modulation of some digestive enzymes and metabolic processes in developing marine fish: applications to diet formulation. Aquaculture 268:98–105
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Programa de Apoyo a la Investigación Científica y Tecnológico (Ref: PAICYT CN1100-06) for financing the Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguilera, C., Mendoza, R., Iracheta, I. et al. Digestive enzymatic activity on Tropical gar (Atractosteus tropicus) larvae fed different diets. Fish Physiol Biochem 38, 679–691 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9550-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-011-9550-8