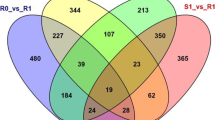
Abstract
Plasmopara viticola is the oomycete that causes downy mildew in grapevines. Varying levels of resistance to P. viticola across grape cultivars allowed quantitative trait loci to be identified. The Rpv3 locus is located at chromosome 18, in a region enriched in TIR-NBS-LRR genes, and the phenotype associated is a high hypersensitive response. In this work, we aimed to identify candidate genes associated with resistance to downy mildew on the Rpv3 locus and to evaluate their transcriptional profiles in a susceptible and a resistant grapevine cultivar after challenging with P. viticola. Candidate genes were identified by in silico functional enrichment tests. Many predicted genes associated with resistance to diseases were found at the Rpv3 locus. In total, seventeen genes were evaluated by RT-qPCR. Differences in the steady-state expression of these genes were observed between the two cultivars. Four genes were found to be expressed only in Villard Blanc, suggesting their association to the hypersensitivity reaction. Aiming to assist marker assisted-selection for downy mildew resistance, we show the efficient use of a set of SSR markers. Furthermore, from on a set of forty-one Rpv3-located SNPs, whose segregation was tested in the populations studied, the two segregating markers, Rpv3_15 and Rpv3_33, were considered efficient for downy mildew resistance identification. This study presents a genomic characterization of the Rpv3 locus, confirms its involvement in resistance against P. viticola infection and presents promising biotechnological tools for the selection of young resistant individuals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolfo G, Ercolano MR (2015) Plant innate immunity multicomponent model. Front Plant Sci 6:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00987
Anonymous (1983) Descriptor list for grapevine varieties and Vitis species 452. Organization Internacional de la Vigne et du Vin (OIV), Paris
Belkhadir Y, Subramaniam R, Dangl JL (2004) Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR proteins and their partners. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.05.009
Bellin D, Peressotti E, Merdinoglu D et al (2009) Resistance to Plasmopara viticola in grapevine “Bianca” is controlled by a major dominant gene causing localised necrosis at the infection site. Theor Appl Genet 120:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1167-2
Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2015) Signaling mechanisms in pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Mol Plant 8:521–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.022
Blasi P, Blanc S, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S et al (2011) Construction of a reference linkage map of Vitis amurensis and genetic mapping of Rpv8, a locus conferring resistance to grapevine downy mildew. Theor Appl Genet 123:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1565-0
Blum M, Waldner M, Gisi U (2010) A single point mutation in the novel PvCesA3 gene confers resistance to the carboxylic acid amide fungicide mandipropamid in Plasmopara viticola. Fungal Genet Biol 47:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2010.02.009
Bove F, Rossi V (2020) Components of partial resistance to Plasmopara viticola enable complete phenotypic characterization of grapevine varieties. Sci Rep 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57482-0
Brilli M, Asquini E, Moser M et al (2018) A multi-omics study of the grapevine-downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola) pathosystem unveils a complex protein coding- and noncoding-based arms race during infection. Sci Rep 8:757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19158-8
Brun LA, Le Corff J, Maillet J (2003) Effects of elevated soil copper on phenology, growth and reproduction of five ruderal plant species. Environ Pollut 122:361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00312-3
Cabezas JA, Cervera MT, Ruiz-García L et al (2006) A genetic analysis of seed and berry weight in grapevine. Genome 49:1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1139/G06-122
Canaguiera A, Grimplet J, Di Gaspero G et al (2017) A new version of the grapevine reference genome assembly (12X.v2) and of its annotation (VCost.v3). Genom Data 14:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gdata.2017.09.002
Costantini L, Battilana J, Lamaj F et al (2008) Berry and phenology-related traits in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): from quantitative Trait Loci to underlying genes. BMC Plant Biol 8:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-38
Creste S, Tulmann Neto A, Figueira A (2001) Detection of single sequence repeat polymorphisms in denaturing polyacrylamide sequencing gels by silver staining. Plant Mol Biol Report 19:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772828
Cus F, Basa Cesnik H, Velikonja Bolta S, Gregorcic A (2010) Pesticide residues and microbiological quality of bottled wines. Food Control 21:150–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.04.010
da Falavigna V, S, Porto DD, Buffon V, et al (2014) Differential transcriptional profiles of dormancy-related genes in ppple buds. Plant Mol Biol Report 32:796–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0690-0
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G (2003) Nucleotide binding site/leucine-rich repeats, Pto-like and receptor-like kinases related to disease resistance in grapevine. Mol Genet Genom 269:612–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0884-5
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G, Adam-Blondon A-F, Testolin R (2007) Linkage maps of grapevine displaying the chromosomal locations of 420 microsatellite markers and 82 markers for R-gene candidates. Theor Appl Genet 114:1249–1263
Di Gaspero G, Copetti D, Coleman C et al (2012) Selective sweep at the Rpv3 locus during grapevine breeding or downy mildew resistance. Theor Appl Genet 124:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1703-8
Díez-Navajas AM, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Greif C, Merdinoglu D (2008) Nonhost versus host resistance to the grapevine downy mildew, Plasmopara viticola, studied at the tissue level. Phytopathology 98:776–780
Doligez A, Bouquet A, Danglot Y et al (2002) Genetic mapping of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) applied to the detection of QTLs for seedlessness and berry weight. Theor Appl Genet 105:780–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0951-z
Dry IB, Feechan A, Anderson C et al (2010) Molecular strategies to enhance the genetic resistance of grapevines to powdery mildew. Aust J Grape Wine Res 16:94–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0238.2009.00076.x
Durrant WE, Dong X (2004) Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:185–209. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.42.040803.140421
Eisenmann B, Czemmel S, Ziegler T et al (2019) Rpv3-1 mediated resistance to grapevine downy mildew is associated with specific host transcriptional responses and the accumulation of stilbenes. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1935-3
Erwin DC, Ribeiro OK (1996) Phytophthora diseases worldwide. American Phytopathological Society (APS Press), St, Paul, Minnesota
Figueira D (2013) Cabernet Sauvignon a casta sagrada. In: Prazeres do vinho. http://www.dfwines.com.br/public/pdf/midia/002.pdf.
Fischer BM, Salakhutdinov I, Akkurt M et al (2004) Quantitative trait locus analysis of fungal disease resistance factors on a molecular map of grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 108:501–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1445-3
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-fob-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 3531:275–296
Foria S, Magris G, Copetti D et al (2018) InDel markers for monitoring the introgression of downy mildew resistance from wild relatives into grape varieties. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0880-4
Foria S, Copetti D, Eisenmann B et al (2020) Gene duplication and transposition of mobile elements drive evolution of the Rpv3 resistance locus in grapevine. Plant J 101:529–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14551
Fröbel S, Zyprian E (2019) Colonization of different grapevine tissues by Pasmopara viticola — a histological study. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00951
Fröbel S, Dudenhöffer J, Töpfer R et al (2019) Transcriptome analysis of early downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola) defense in grapevines carrying the Asian resistance locus Rpv10. Euphytica 215:28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2355-z
Fung RWM, Gonzalo M, Fekete C et al (2008) Powdery mildew induces defense-oriented reprogramming of the transcriptome in a susceptible but not in a resistant grapevine. Plant Physiol 146:236–249. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.108712
Garrido L da R Sônego OR (2007) Manejo de doenças da videira. In: Manejo integrado de doenças de fruteiras. Sociedade Brasileira de Fitopatologia, Brasília, pp 65–86
Gisi U, Waldner M, Kraus N, Dubuis PH, Sierotzk H (2007) Inheritance of resistance to carboxylic acid amide (CAA) fungicides in Plasmopara viticola. Plant Pathol 56:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2006.01512.x
Götz S, García-Gómez JM, Terol J et al (2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3420–3435. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn176
Greenberg JT, Vinatzer BA (2003) Identifying type III effectors of plant pathogens and analyzing their interaction with plant cells. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5274(02)00004-8
Grenville-Briggs LJ, Van West P (2005) The biotrophic stages of oomycete-plant interactions. Adv Appl Microbiol 57:217–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(05)57007-2
Guimarâes CT, de Magalhães JV, Lanza MA, Schyster I (2009) Marcadores moleculares e suas aplicações no melhoramento genético. Inf Agropecuário 30:24–33
He C, Holme J, Anthony J (2014) SNP genotyping: the KASP assay. Methods Mol Biol 1145:75–86
IBRAVIN (2012) A Vitivinicultura Brasileira. http://www2.agricultura.rs.gov.br.2012.
INRA, IFV, SupAgro M (2013) Montpellier SupAgro. Fiche Variétale Villard Blanc B. Plant Grape. http://www.montpellier.inra.fr/
Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B et al (2007) The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06148
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–239. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05286
Jones DS, McManus PS (2017) Distinctive symptoms and signs of downy mildew on cold-climate wine grape cultivars. Plant Health Prog 18:192–195. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-01-17-0009-DG
Jones DA, Takemoto D (2004) Plant innate immunity – direct and indirect recognition of general and specific pathogen-associated molecules. Curr Opin Immunol 16:48–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2003.11.016
Kassemeyer HH, Gadoury DH, Hill G, Wilcox WF (2015) Downy mildew In: compendium of grape diseases, eds W. Wilcox, W. Gubler, and J. Uyemoto (St Paul, MN: APS Press), pp 46–52
Kortekamp A (2006) Expression analysis of defence-related genes in grapevine leaves after inoculation with a host and a non-host pathogen. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2006.01.008
Kortekamp A, Zyprian E (2003) Characterization of plasmopara-resistance in grapevine using in vitro plants. J Plant Physiol 160:1393–1400. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-01021
Lefort F, Douglas GC (1999) An efficient micro-method of DNA isolation from mature leaves of four hardwood tree species Acer, Fraxinus, Prunus and Quercus. Ann for Sci 56:259–263
Li S, Liu K, Yu S et al (2020) The process of embryo abortion of stenospermocarpic grape and it develops into plantlet in vitro using embryo rescue. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 143:389–409.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01926-y
Liang Z, Duan S, Sheng J (2019) Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses. Nat Commun 10:1190. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09135-8
Marguerit E, Boury C, Manicki A et al (2009) Genetic dissection of sex determinism, inflorescence morphology and downy mildew resistance in grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 118:1261–1278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0979-4
Mejía N, Soto B, Guerrero M et al (2011) Molecular, genetic and transcriptional evidence for a role of VvAGL11 in stenospermocarpic seedlessness in grapevine. BMC Plant Biol 11:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-57
Merdinoglu D, Wiedeman-Merdinoglu S, Coste P et al (2003) Genetic analysis of downy mildew resistance derived from Muscadinia rotundifolia. Acta Hortic 603:451–456
Moreira FM, Madini A, Marino R et al (2011) Genetic linkage maps of two interspecific grape crosses (Vitis spp.) used to localize quantitative trait loci for downy mildew resistance. Tree Genet Genom 7:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0322-x
Ocarez N, Jiménez N, Núñez R et al (2020) Unraveling the deep genetic architecture for seedlessness in grapevine and the development and validation of a new set of markers for VviAGL11-based gene-assisted selection. Genes (basel) 11:1–32
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Pinto KMS, do Nascimento LC, de Souza Gomes EC, et al (2012) Efficiency of resistance elicitors in the management of grapevine downy mildew Plasmopara viticola: Epidemiological, biochemical and economic aspects. Eur J Plant Pathol 134: 745–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-012-0050-1
Polesani M, Bortesi L, Ferrarini A et al (2010) General and species-specific transcriptional responses to downy mildew infection in a susceptible (Vitis vinifera) and a resistant (V. Riparia) grapevine species. BMC Genom 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-117
Possamai T, Migliaro D, Gardiman M et al (2020) Rpv mediated defense responses in grapevine offspring resistant to Plasmopara viticola. Plants 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060781
Reid KE, Olsson N, Schlosser J et al (2006) An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-6-27
Revers LF, Welter LJ, Irala PB, et al (2010) Co-localization of QTLs for seedlessness and downy mildew resistance in grapevine. In: Reisch BI, Londo J (eds) Xth Intl Conf on Grapevine Breeding and Genetics. pp 449–456
Ribeiro IJA (2001) Doenças causadas por fungos e bactérias na cultura da videira. In: BOLIANI AC, CORRÊA L de S (eds) Cultura de uvas de mesa: do plantio à comercialização. ALGRAF, Ilha Solteira, pp 237–239
Ruijter JM, Ramakers C, Hoogaars WMH et al (2009) Amplification efficiency: linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp045
Saifert L, Sánchez-Mora FD, Assumpção WT et al (2018) Marker-assisted pyramiding of resistance loci to grape downy mildew. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 53:602–610. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2018000500009
Salmaso M, Malacarne G, Troggio M et al (2008) A grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) genetic map integrating the position of 139 expressed genes. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0741-3
Santos RF, Ciampi-Guillardi M, Fraaije BA et al (2020) The climate-driven genetic diversity has a higher impact on the population structure of Plasmopara viticola than the production system or QoI fungicide sensitivity in subtropical brazil. Front Microbiol 11:575045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.575045
Sargolzaei M, Maddalena G, Bitsadze N et al (2020) Rpv29, Rpv30 and Rpv31: Three novel genomic loci associated with resistance to Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera. Front Plant Sci 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.562432
Schwander F, Eibach R, Fechter I et al (2012) Rpv10: a new locus from the Asian Vitis gene pool for pyramiding downy mildew resistance loci in grapevine. Theor Appl Genet 124:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1695-4
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breed 33:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
Soanes DM, Talbot NJ (2008) Moving targets: rapid evolution of oomycete effectors. Trends Microbiol 16:507–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2008.08.002
Takken FL, Albrecht M, Tameling WIL (2006) Resistance proteins: molecular switches of plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2006.05.009
Tessmann DJ, Vida JB (2005) Principais doenças fúngicas da videira. Rev Atualidades Agrícolas 14–15
Toffolatti SL, Maddalena G, Maghradze D, Bianco PA (2016) Evidence of resistance to the downy mildew agent Plasmopara Viticola in the Georgian Vitis Vinifera Germplasm. Vitis. https://doi.org/10.5073/vitis.2016.55.121-128
Unger S, Büche C, Boso S, Kassemeyer HH (2007) The course of colonization of two different Vitis genotypes by Plasmopara viticola indicates compatible and incompatible host-pathogen interactions. Phytopathology 97:780–786. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-97-7-0780
van Heerden CJ, Burger P, Vermeulen A et al (2014) Detection of downy and powdery mildew resistance QTL in a ‘Regent’ × ‘RedGlobe’ population. Euphytica 200:281–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1167-4
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Troggio M et al (2007) A high quality draft consensus sequence of the genome of a heterozygous grapevine variety. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001326
Venuti S, Copetti D, Foria S et al (2013) Historical introgression of the downy mildew resistance gene Rpv12 from the Asian species Vitis amurensis into grapevine varieties. PLoS ONE 8:e61228. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061228
Vezzulli S, Salacarne GM, Masuero D et al (2019) The Rpv3-3 haplotype and stilbenoid induction mediate downy mildew resistance in a grapevine interspecific population. Front Plant Sci 10:234. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00234
Wang P, Liu C, Wang D et al (2013) Isolation of resistance gene analogs from grapevine resistant to downy mildew. Sci Hortic (amsterdam) 150:326–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.11.035
Welter LJ, Göktürk-Baydar N, Akkurt M et al (2007) Genetic mapping and localization of quantitative trait loci affecting fungal disease resistance and leaf morphology in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L). Mol Breed 20:359–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9097-7
Xiang J, Li X, Wu J et al (2016) Studying the mechanism of Plasmopara viticola RxLR effectors on suppressing plant immunity. Front Microbiol 7:709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00709
Yin L, An Y, Qu J et al (2017) Genome sequence of Plasmopara viticola and insight into the pathogenic mechanism. Sci Rep 7:46553. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46553
Zeng Y, Yang T (2002) RNA isolation from highly viscous samples rich in polyphenols and polysaccharides. Plant Mol Biol Report 20:417a–417e. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772130
Zyprian E, Ochßner I, Schwander F et al (2016) Quantitative trait loci affecting pathogen resistance and ripening of grapevines. Mol Genet Genom 291:1573–1594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1200-5
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support from the Embrapa Funding System (SEG code 02.08.07.004.00.05.04, 02.13.03.006.00.02.006 and 02.12.12.003.00.00).
Funding
We are grateful for the financial support from the Embrapa Funding System (SEG code 02.08.07.004.00.05.04, 02.13.03.006.00.02.006 and 02.12.12.003.00.00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.F.R, J.M., A.W. and D.D.P. conceived original screenings, research plans, designed experiments and analyzed resulting data; L.F.R supervised experiments and writing; J.M., A.W and V.B. performed most experiments; L.F.R, R.T. and D.D.P provided technical assistance and performed the statistical analysis. J.M. and A.W wrote the article with contributions from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare to have no competing interests, both financial and non-financial.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wairich, A., Malabarba, J., Buffon, V. et al. Molecular characterization of the Rpv3 locus towards the development of KASP markers for downy mildew resistance in grapevine (Vitis spp.). Euphytica 218, 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02952-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02952-3