Abstract
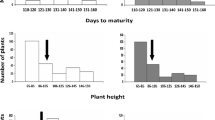
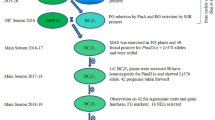
Oryza nivara, the ancestral species of cultivated rice (O. sativa), has been the source of novel alleles for resistance to biotic and abiotic stress lost during domestication. Interspecific advanced backcross (ABC) populations permit the introgression of desirable alleles from the wild species into O. sativa and allow traits to be mapped to chromosomal regions by QTL mapping. An ABC population was developed by crossing M-202, a California medium grain, temperate japonica cultivar with O. nivara (IRGC100195). The population has 177 BC2F2:5 progeny lines and was evaluated for 17 traits including seedling vigor under cool temperature (mesocotyl, coleoptile, shoot and root lengths), agronomic (days to heading, plant height, culm angle, panicle type), yield components (panicles per plant, panicle length, florets and seeds per panicle, 100-seed weight) and quality [kernel length and width, apparent amylose content (AAC), alkali spreading value (ASV)]. Most exciting was that the O. nivara parent improved seedling vigor by increasing both the coleoptile and shoot lengths. Wild donor alleles increased the panicles per plant and seed weight, but M-202 alleles improved fertility. For one locus, the O. nivara alleles accounted for increased kernel length even though this parent had smaller seeds than M-202. The AAC mapped to the WAXY locus and ASV to the ALK locus, with most progeny being similar to M-202 for these quality traits. Select progeny lines could be useful for improving seedling vigor. This interspecific population is the first in the background of a U.S. temperate japonica rice cultivar.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali ML, Sanchez PL, Yu S, Lorieux M, Eizenga GC (2010) Chromosome segment substitution lines: a powerful tool for the introgression of valuable genes from Oryza wild species into cultivated rice (O. sativa). Rice 3:218–234
Ali ML, McClung AM, Jia MH, Kimball JA, McCouch SR, Eizenga GC (2011) A rice diversity panel evaluated for genetic and agro-morphological diversity between subpopulations and its geographic distribution. Crop Sci 51:2021–2035
Aluko G, Martinez C, Tohme J, Castano C, Bergman C, Oard JH (2004) QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O. glaberrima. Theor Appl Genet 109:630–639
Ayres NM, McClung AM, Larkin PD, Bligh HFJ, Jones CA, Park WD (1997) Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 94:773–781
Bergman CJ, Bhattacharya KR, Ohtsubo K (2004) Rice end-use quality analysis. In: Champagne ET (ed) Rice chemistry and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, pp 415–772
Bian J, Li C, He H, Shi H, Yan S (2014) Identification and analysis of QTLs for grain quality traits in rice using an introgression lines population. Euphytica 195:83–93
Brar DS, Singh K (2011) Oryza. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources. Springer, Berlin, pp 321–365
Brondani C, Rangel PHN, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2002) QTL mapping and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203
Cai HW, Morishima H (2002) QTL clusters reflect character associations in wild and cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet 104:1217–1228
Chang TT, Bardenas EA (1965) The morphology and varietal characteristics of the rice plant. Tech Bull 4. Int Rice Res Inst, Los Baños, Philippines
Chapman AL, Peterson ML (1962) The seedling establishment of rice under water in relation to temperature and dissolved oxygen. Crop Sci 2:391–395
Chen M-H, Fjellstrom RG, Christensen EF, Bergman CJ (2010) Development of three allele-specific codominant rice Waxy gene PCR markers suitable for marker-assisted selection of amylose content and paste viscosity. Mol Breed 26:513–523
Couch BC, Kohn LM (2002) A multilocus gene genealogy concordant with host preference indicates segregation of a new species, Magnaporthe oryzae, from M. grisea. Mycologia 94:683–693
Cui KH, Peng SB, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Yu SB, Zhang Q (2002) Molecular dissection of seedling-vigor and associated physiological traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:745–753
Eizenga GC, Prasad B, Jackson AK, Jia MH (2013) Identification of rice sheath blight and blast quantitative trait loci in two different O. sativa/O. nivara advanced backcross populations. Mol Breed 31:889–907
Eizenga GC, Ali ML, Bryant RJ, Yeater KM, McClung AM, McCouch SR (2014) Registration of the Rice Diversity Panel 1 for genome-wide association studies. J Plant Regist 8:109–116
Fjellstrom RG, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44:1790–1798
Fjellstrom RG, McClung AM, Shank AR (2006) SSR markers closely linked to the Pi-z locus are useful for selection of blast resistance in a broad array of rice germplasm. Mol Breed 17:149–157
Fu A, Zhang P, Tan L, Zhu A, Ma D, Fu Y, Zhan X, Cai H, Sun C (2010) Analysis of QTLs for yield related traits in Yuanjing common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). J Genet Genom 37:147–157
Fuller DQ, Sato YI, Castillo C, Qin L, Weisskopf AR, Kingwell-Banham EJ, Song J, Ahn SM, van Etten J (2010) Consilience of genetics and archaeobotany in the entangled history of rice. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2:115–131
Garris AJ, Tai TH, Coburn J, Kresovich S, McCouch S (2005) Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L. Genetics 169:1631–1638
Huang X, Kurata N, Wei X, Wang ZX, Wang A, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K, Lu H, Li W, Guo Y, Lu Y, Zhou C, Fan D, Weng Q, Zhu C, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X, Xu Q, Dong G, Zhan Q, Li C, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J, Han B (2012) A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 490:497–501
Imai I, Kimball JA, Conway B, Yeater KM, McCouch SR, McClung AM (2013) Validation of yield-enhancing quantitative trait loci from a low-yielding wild ancestor of rice. Mol Breed 32:101–120
Iwata N, Shinada H, Kiuchi H, Sato T, Fujino K (2010) Mapping of QTLs controlling seedling establishment using a direct seeding method in rice. Breed Sci 60:353–360
Jacquemin J, Bhatia D, Singh K, Wing RA (2013) The International Oryza Map Alignment Project: development of a genus-wide comparative genomics platform to help solve the 9 billion-people question. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:1–10
Jia Y, Redus M, Wang Z, Rutger JN (2004) Development of a SNLP marker from the Pi-ta blast resistance gene by tri-primer PCR. Euphytica 138:97–105
Jing Z, Qu Y, Chen Y, Pan D, Fan Z, Chen J, Li C (2010) QTL analysis of yield-related traits using an advanced backcross population derived from common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon L.). Mol Plant Breed 1:1–10. doi:10.5376/mpb.2010.01.0001
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0, an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 23:2788–2789
Johnson CW, Carnahan HL, Tseng ST, Oster JJ, Hill JE (1986) Registration of M-202 rice. Crop Sci 26:198
Jones DB, Peterson ML (1976) Rice seedling vigor at sub-optimal temperatures. Crop Sci 16:102–105
Juliano BO (1985) Criteria and tests for rice grain qualities. In: Juliano BO (ed) Rice chemistry and technology, 2nd edn. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, pp 443–524
Khush GS (1997) Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:25–34
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Larkin P, Park W (2003) Association of waxy gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with starch characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 12:335–339
Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1255–1269
Maas LF, McClung A, McCouch S (2010) Dissection of a QTL reveals an adaptive, interacting gene complex associated with transgressive variation for flowering time in rice. Theor Appl Genet 120:895–908
McCouch SR, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson M, Septiningsih E, Edwards J, Moncada P, Xiao J, Garris A, Tai T, Martinez C, Tohme J, Sugiono M, McClung A, Yuan LP, Ahn SN (2007) Through the genetic bottleneck: O. rufipogon as a source of trait-enhancing alleles for O. sativa. Euphytica 154:317–339
McKenzie KS, Johnson CW, Tseng ST, Oster JJ, Brandon DM (1994) Breeding improved rice cultivars for temperate regions—a case study. Aust J Exp Agric 34:897–905
Nelson JC (1997) QGENE: software for marker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol Breed 3:229–235
Neves, PCF (2002) Introgression of agronomic traits associated with molecular markers from Oryza nivara Sharma & Shastry and O. glaberrima Steud. into O. sativa L. PhD dissertation, University of California, Davis
Ormrod DP, Bunter WA (1961) The evaluation of rice varieties for cold water tolerance. Agron J 53:133–134
Raney F (1963) Rice water temperature. Calif Agric 17:6–7
Redoña ED, Mackill DJ (1996) Genetic variation for seedling vigor traits in rice. Crop Sci 36:285–290
SAS Institute (2008) The SAS system for Windows. Release 9.2. SAS Institute, Cary
Septiningsih EM, Prasetiyono J, Lubis E, Tai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003a) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Septiningsih EM, Trijatmiko KR, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003b) Identification of quantitative trait loci for grain quality in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1433–1441
Shakiba E, Eizenga GC (2014) Unraveling the secrets of rice wild species. In: Yan WG, Bao J (eds) Rice – Germplasm, genetics and improvement. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/58393. Accessed 30 July 2015
Skamnioti P, Gurr SJ (2009) Against the grain: safeguarding rice from rice blast disease. Trends Biotech 27:141–150
Smith AM, Denyer K, Martin C (1997) The synthesis of the starch granule. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:67–87
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Shobhar Rani N, Prasad GSV, Viraktamath BC, Ashok Reddy G, Sarla N (2012) QTL analysis for grain quality traits in 2 BC2F2 populations derived from crosses between Oryza sativa cv Swarna and 2 accessions of O. nivara. J Hered 103:442–452
Tai T, Tanksley SD (1990) A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol Biol Rep 8:297–303
Tan L, Zang P, Liu F, Wang G, Ye S, Zhu Z, Fu Y, Cai H, Sun C (2008) Quantitative trait loci underlying domestication-and yield-related traits in an Oryza sativa x Oryza rufipogon advanced backcross population. Genome 51:692–704
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Tung C-W, Zhao K, Wright M, Ali ML, Jung J, Kimball J, Tyagi W, Thomson MJ, McNally K, Leung H, Kim HJ, Ahn SN, Reynolds A, Scheffler B, Eizenga G, McClung AM, Bustamante C, McCouch SR (2010) Development of a research platform for dissecting phenotype genotype associations in rice (Oryza spp.). Rice 3:205–217
Umemoto T, Aoki N (2005) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in rice starch synthase IIa that alter starch gelatinization and starch association of the enzyme. Funct Plant Biol 32:763–768
Umemoto T, Aoki N, Lin H, Nakamura Y, Inouchi N, Sato Y, Yano M, Hirabayashi H, Maruyama S (2004) Natural variation in rice starch synthase IIa affects enzyme and starch properties. Funct Plant Biol 31:671–684
Van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: versatile software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99:232–236
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap 4. Software for genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kayazma, Wageningen
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang Y, Li J (2008) Rice, rising. Nat Genet 40:1273–1275
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Xie X, Jin F, Song MH, Suh JP, Hwang HG, Kim YG, McCouch SR, Ahn SN (2008) Fine mapping of yield-enhancing QTL cluster associated with transgressive variation in an Oryza sativa x Oryza rufipogon cross. Theor Appl Genet 116:613–622
Yu B, Lin Z, Li H, Li X, Li J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhu Z, Zhai W, Wang X, Xie D, Sun C (2007) TAC1, a major quantitative trait locus controlling tiller angle in rice. Plant J 52:891–898
Yuan PR, Kim HJ, Chen QH, Ju HG, Lee SJ, Ji SD, Ahn S-N (2009) QTL dissection of agronomic and domestication traits using introgression lines carrying wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) segments in cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) background. J Crop Sci Biotech 2:245–252
Zhang ZH, Qu X-S, Wan S, Chen L-H, Zhu Y-G (2005a) Comparison of QTL controlling seedling vigour under different temperature conditions using recombinant inbred lines in rice (Oryza sativa). Ann Bot 95:423–429
Zhang ZH, Yu SB, Yu T, Huang Z, Zhu YG (2005b) Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for seedling-vigor using recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Field Crops Res 91:161–170
Zhao K, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Reynolds A, Mezey J, McClung AM, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR (2011) Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nature Commun 2:467. doi:10.1038/ncomms1467
Acknowledgments
The financial support of the Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuaria (EMBRAPA) to P.C.F. Neves is gratefully acknowledged, as well as the support of the University of California and USDA-ARS at Davis, California, for the research conducted at Davis. The studies conducted at Davis, California, were part of the Ph.D. dissertation research for P.C.F. Neves. Dr. Thomas H. Tai is acknowledged for sharing the seed with G.C. Eizenga. At the USDA-ARS DB NRRC in Stuttgart, Arkansas, the excellent technical assistance of Quynh P.-H. Grunden is acknowledged in all phases of the work. Both Melissa H. Jia and Aaron K. Jackson in the Genomics Core Facility are recognized for running markers, allele calling and assisting with creating the final linkage map. The support of the Arkansas Rice Research and Promotion Board through the University of Arkansas for H.A. Agrama is gratefully acknowledged. Lastly, the excellent review with suggestions for improving the manuscript by Dr. Shannon R. Pinson is gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eizenga, G.C., Neves, P.C.F., Bryant, R.J. et al. Evaluation of a M-202 × Oryza nivara advanced backcross mapping population for seedling vigor, yield components and quality. Euphytica 208, 157–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1613-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1613-y