Summary
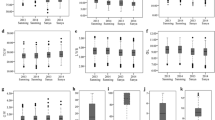
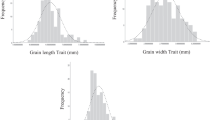
It has been theoretically proposed that multiple linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) play a role in the accumulation of hidden variation within and between populations. In this study, the genetic bases for grain characteristics were examined by comparing two accessions representing the two rice subspecies by QTL analysis. Grain dimensions are known to be quantitative traits and to be diagnostic between these two subspecies. To enhance the power to detect QTL with small effects, after transferring a segment of chromosome 6 from an Indica type into a Japonica type of rice by repeated backcrosses, the introgressed segment was dissected by making recombinant inbred lines (RILs) which were expected to have different sizes of the introgressed segment in the same genetic background. The resulting RILs showed distinct transgression of the grain characteristics examined. Multiple QTLs controlling each of the length and breadth of seeds were detected on the introgressed segment, and showed positive and negative additive effects as well as epistatic interactions. The present study confirmed that transgressive segregation resulted from a breakdown of linkage and that the detection of QTLs was highly dependent upon the genetic effects of the neighboring QTLs, indicating the need for caution in interpreting QTL effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard, R.W., 1956. Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24: 235–278.
Bres-Patry, C., M. Lorieux, G. Clement, M. Bangratz & A. Ghesquiere, 2001. Heredity and genetic mapping of domestication-related traits in a temperate japonica weedy-rice. Theor Appl Genet 102: 118–126.
Cai, H.W. & H. Morishima, 2002. QTL clusters reflect character associations in wild and cultivated rice. Theor Appl Genet 104: 1217–1228.
Chang, T.T., 1976. The origin, evolution, cultivation, dissemination, and diversification of Asian and African rices. Euphytica 25: 435–441.
DeVicente, M.C. & S.D. Tanksley, 1993. QTL analysis of transgressive segregation in an interspecific tomato cross. Genetics 134: 585–596.
Dilda, C.L. & T.F.C. Mackay, 2002. The genetic architecture of Drosophila sensory bristle number. Genetics 162: 1655–1674.
Dung, L.V., T. Inukai & Y. Sano, 1998. Dissection of a major QTL for photoperiod sensitivity in rice: Its association with a gene expressed in an age-dependent manner. Theor Appl Genet 97: 714–720.
Fry, J.D., S.V. Nuzhdin, E.G. Pasyukova & T.F.C. Mackay, 1998. QTL mapping of genotype-environment interaction for fitness in Drosophila malanogaster. Genet Res 71: 133–141.
Glaszmann, J.C., 1987. Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties. Theor Appl Genet 74: 21–30.
Harushima, Y., M. Yano, A. Shomura, M. Sato, T. Shimano, Y. Kuboki, T. Yamamoto, S.Y. Lin, B.A. Antonio, A. Parco, H. Kajiya, N. Huang, K. Yamamoto, Y. Nagamura, N. Kurata, G.S. Khush & T. Sasaki, 1998. A high-density rice genetic linkage map with 2275 markers using a single F2 population. Genetics 148: 479–494.
Huang, N., A. Parco, T. Mew, G. Magpantay, S. McCouch, E. Guiderdoni, J. Xu, P. Subudhi, E.R. Angeles & G.S. Khush, 1997. RFLP mapping of isozymes, RAPD and QTL for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a double haploid rice population. Mol Breeding 3: 105–113.
Kojima, S., Y. Takahashi, Y. Kobayashi, L. Monna, T. Sasaki, T. Araki & M. Yano, 2002. Hd3a, a rice ortholog of the Arabidopsis FT gene, promotes transition to flowering downstream of Hd1 under short-day conditions. Plant Cell Physiol 43: 1096–1105.
Leips, J. & T.F.C. Mackay, 2000. Quantitative trait loci for life span in Drosophila melanogaster; interactions with genetic background and larval density. Genetics 155: 1773–1788.
Lynch, M. & B. Walsh, 1998. Genetics and Analysis of Quantitative Traits. pp. 81–106, pp. 431–489. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland.
Mackay, T.F.C., 2001. The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Annu Rev Genet 35: 303–339.
Manly, K.F., R.H. Cudmore Jr & J.M. Meer, 2001. Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12: 930–932.
Mather, K. & J.L. Jinks, 1982. Biometrical genetics. 3rd Ed. Chapman and Hall, NY.
Matsubara, K., Khin-Thidar & Y. Sano, 2003. A gene block causing cross-incompatibility hidden in wild and cultivated rice. Genetics 165: 343–352.
McCouch, S.R., L. Teytelman, Y. Xu, K.B. Lobos, K. Clare, M. Walton, B.Y. Fu, R. Maghirang, Z.K. Li, Y.Z. Xing, Q.F. Zhang, I. Kono, M. Yano, R. Fjellstrom, G. DeClerck, D. Schneider, S. Cartinhour, D. Ware & L. Stein, 2002. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9: 199–207.
McKenzie, K.S., C.W. Johnson, S.T. Tseng, J.J. Oster & D.M. Brandon, 1994. Breeding improved rice cultivars for temperate regions – a case study. Aust J Exp Agr 34: 897–905.
Mikami, I., L.-V. Dung, H.-Y. Hirano & Y. Sano, 2000. Effects of the two most common Wx alleles on different genetic backgrounds in rice. Plant Bred 119: 505–508.
Murray, M.G. & W.F. Thompson, 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8: 4321–4325.
Oka, H.I., 1988. Origin of cultivated rice. Elsevier: Tokyo.
Redoña, E.D. & D.J. Mackill, 1998. Quantitative trait locus analysis for rice panicle and grain characteristics. Theor Appl Genet 96: 957–963.
Rieseberg, L.H., M.A. Archer & R.K. Wayne, 1999. Transgressive segregation, adaptation and speciation. Heredity 83: 363–372.
Ronin, Y.I., A.B. Korol & E. Nevo, 1999. Single- and multiple-trait mapping analysis of linked quantitative trait loci: Some asymptotic analytical approximations. Genetics 151: 387–396.
Spickett, S.G. & J.M. Thoday, 1966. Regular responses to selection: 3 Interaction between located polygenes. Genet Res 7: 96–121.
Takahashi, M., T. Kinoshita & K. Takeda, 1973. Character expression of some major genes in rice and their agronomic application – Genetical Studies on Rice Plant, LVI. Jour Facul Agr, Hokkaido Univ Sapporo, 57: 275–292.
Takeda, K., 1986. Developmental mechanisms and inheritance of grain notching in rice. In “Rice genetics”, IRRI, Manila, Philipines: 307–316.
Tan, Y.F., Y.Z. Xing, J.X. Li, S.B. Yu, C.G. Xu & Q. Zhang, 2000. Genetic bases of appearance quality of rice grains in Shanyou 63, an elite rice hybrid. Theor Appl Genet 101: 823–829.
Tanksley, S.D. & S.R. McCouch, 1997. Seed banks and molecular maps: Unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277: 1063–1066.
Thoday, J.M., 1960. Effects of disruptive selection: III Coupling and repulsion. Heredity 14: 35–49.
Umemoto, T., M. Yano, H. Satoh, A. Shomura & Y. Nakamura, 2002. Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties. Theor Appl Genet 104: 1–8.
Van Ooijen, J.W., M.P. Boer, R.C. Jansen & C. Maliepaard, 2002. MapQTL textregistered 4.0, Software for the calculation of QTL position on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Wang, Z.K. & S.D. Tanksley, 1989. Restriction fragments length polymorphism in Oryza sativa L. Genome 32: 1113–1118.
Yano, M., Y. Katayose, M. Ashikari, U. Yamanouchi, L. Monna, T. Fuse, T. Baba, K. Yamamoto, Y. Umehara, Y. Nagamura & T. Sasaki, 2000. Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closed related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. The Plant Cell 12: 2473–2483.
Zeng, Z.-B., 1993. Theoretical basis for separation of multiple linked gene effects in mapping quantitative trait loci. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 90: 10972–10976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagiwara, W.E., Onishi, K., Takamure, I. et al. Transgressive segregation due to linked QTLs for grain characteristics of rice. Euphytica 150, 27–35 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9085-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9085-8