Abstract
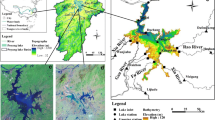
Urban lakes are typically characterized by fragile ecological capacities and complex management of their hydrospheric ecosystems. The aims of this study are to establish a reliable hydrodynamic-water quality model for an urban lake, to investigate the responses of water quality to different extreme hydrological conditions associated with rainstorms, and to explore the results from different modeled scenarios surrounding the pollution threats associated with a sewage leak. A three-dimensional hydrodynamic water quality model was developed in this study. The model was calibrated and validated using observed data. The model results agreed well with the observed data, and the averaged relative root mean-squared error (RRMSE) for all of the compared variables was 33.3 %. The validated model was applied to analyze water quality responses for different extreme historical rainfall scenarios from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2012. The model results indicate that for Lake Tianyinhu, rainstorms adversely affect water quality due to larger nutrient loads, generated by larger rainfall events, and the limited water storage capacity of the lake. Moreover, the responses of water quality to sewage leak events were studied through four scenarios with different leak intensities and durations. The model results indicate that sewage leaks have measureable negative effects on water quality and that it is vital to inspect and promptly eliminate any possible leaks within pipes surrounding the lake. This study may provide a useful tool for hydrological ecosystem protection and management techniques for similar urban lakes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LTYHM:
-
Lake Tianyinhu Model
References
Friese, K., Schmidt, G., de Lena, J. C., Nalini, H. A., & Zachmann, D. W. (2010). Anthropogenic influence on the degradation of an urban lake–the Pampulha reservoir in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Limnologica-Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 40, 114–125.
Yang, G., Ma, R., Zhang, L., Jiang, J., Yao, S., Zhang, M., & Zeng, H. D. (2010). Lake status, major problems and protection strategy in China. Journal of Lake Sciences, 22, 799–810.
Gao, L., Zhou, J. M., Yang, H., & Chen, J. (2005). Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake. Environmental Geology, 48, 835–844.
Jing, H. W., Hua, L., Sun, C. H., & Guo, J. (2008). Analysis on urban lakes’ eutrophication status in Beijing. Journal of Lake Sciences, 20, 357–363.
Yang, T., Liu, Q., Chan, L., & Liu, Z. (2007). Magnetic signature of heavy metals pollution of sediments: case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1639–1650.
Miller, J. D., Kim, H., Kjeldsen, T. R., Packman, J., Grebby, S., & Dearden, R. (2014). Assessing the impact of urbanization on storm runoff in a peri-urban catchment using historical change in impervious cover. Journal of Hydrology, 515, 59–70.
Silva, T., Vinçon-Leite, B., Lemaire, B., Le Vu, B., Quiblier, C., Prévot, Freissinet, C.,Calzas, M., Degres, Y., &Tassin, B. (2011, April). Water quality in urban lakes: from continuous monitoring to forecasting. Application to cyanobacteria dynamics in Lake Enghien (France). In European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2011.
Missaghi, S., Hondzo, M., & Melching, C. (2013). Three-dimensional lake water quality modeling: sensitivity and uncertainty analyses. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 1684–1698.
Hamrick, J. M. (1992). A three-dimensional environmental fluid dynamics computer code: Theoretical and computational aspects. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary.
Tech, T. (2006). The environmental fluid dynamics code, theory and computation: volume 1: hydrodynamics. Fairfax: Tetra Tech. Inc.
Hamrick, J. M., & Mills, W. B. (2000). Analysis of water temperatures in Conowingo Pond as influenced by the Peach Bottom atomic power plant thermal discharge. Environmental Science & Policy, 3, 197–209.
Cerco, C. F., & Cole, T. (1993). Three-dimensional eutrophication model of Chesapeake Bay. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 119, 1006–1025.
Park, K., Jung, H. S., Kim, H. S., & Ahn, S. M. (2005). Three-dimensional hydrodynamic-eutrophication model (HEM-3D): application to Kwang-Yang Bay, Korea. Marine Environmental Research, 60, 171–193.
Liu, T., Yang, L. Y., Hu, Z. X., & Sun, Y. N. (2012). Spatial-temporal features of atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus to the Lake Taihu. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 24, 20–24.
Deng, J. J., Wang, T. J., Li, S., Xie, M., & Fan, J. L. (2009). Study on atmospheric nitrogen oxidant and deposition flux in suburban of Nanjing. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 29, 25–30.
Di Toro, D. M., & Fitzpatrick, J. J. (1993). Chesapeake Bay sediment flux model. Mahwah: Hydroqual Inc.
He, G., Fang, H., Bai, S., Liu, X., Chen, M., & Bai, J. (2011). Application of a three-dimensional eutrophication model for the Beijing Guanting Reservoir, China. Ecological Modelling, 222, 1491–1501.
Arhonditsis, G. B., & Brett, M. T. (2005). Eutrophication model for lake Washington (USA): part II—model calibration and system dynamics analysis. Ecological Modelling, 187, 179–200.
Li, Y., Acharya, K., Chen, D., & Stone, M. (2010). Modeling water ages and thermal structure of Lake Mead under changing water levels. Lake and Reservoir Management, 26, 258–272.
James, R. T., BiermanJr, V. J., Erickson, M. J., & Hinz, S. C. (2005). The Lake Okeechobee water quality model (LOWQM) enhancements, calibration, validation and analysis. Lake and Reservoir Management, 21, 231–260.
Jia, H., Zhang, Y., & Guo, Y. (2010). The development of a multi-species algal ecodynamic model for urban surface water systems and its application. Ecological Modelling, 221, 1831–1838.
Tang, C. Y. (2015). Mathematical model for water environment setup and application based on the internal nutrient release and parametric optimization in Lake Taihu. (Doctoral dissertation). Hohai University, NJ.
Wu, G., & Xu, Z. (2011). Prediction of algal blooming using EFDC model: case study in the Daoxiang Lake. Ecological Modelling, 222, 1245–1252.
Zhang, W., & Rao, Y. R. (2012). Application of a eutrophication model for assessing water quality in Lake Winnipeg. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 38, 158–173.
Jin, K. R., & Ji, Z. G. (2004). Case study: modeling of sediment transport and wind-wave impact in Lake Okeechobee. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 130, 1055–1067.
Jin, K. R., & Ji, Z. G. (2005). Application and validation of three-dimensional model in a shallow lake. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 131, 213–225.
Jin, K. R., & Ji, Z. G. (2001). Calibration and verification of a spectral wind–wave model for Lake Okeechobee. Ocean Engineering, 28, 571–584.
Li, Y. P., Tang, C. Y., Wang, C., Tian, W., Pan, B., Hua, L., Lau, J., Yu, Z. B., & Acharya, K. (2013). Assessing and modeling impacts of different inter-basin water transfer routes on Lake Taihu and the Yangtze River, China. Ecological Engineering, 60, 399–413.
Lehman, J. T. (2014). Understanding the role of induced mixing for management of nuisance algal blooms in an urbanized reservoir. Lake and Reservoir Management, 30, 63–71.
Missaghi, S., & Hondzo, M. (2010). Evaluation and application of a three-dimensional water quality model in a shallow lake with complex morphometry. Ecological Modelling, 221, 1512–1525.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by Science and Technology Project of JiangSu Province (BZ2014005 and BE2014739),National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2014BAC09B02), the National Science Foundation of China (41371121), Key Laboratory of Poyang Lake Wetland and Watershed Research, Ministry of Education (Jiangxi normal University, PK2015008), and Key Laboratory of Karst Ecosystem and Rocky Desertification Control, Ministry of Land and Resources. We would like to thank the Archives of the Nanjing Institute of Technology and the Laboratory of Environmental Engineering School, Nanjing Institute of Technology, for providing topographic and monitoring data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, R., Xu, L., Wang, D. et al. Water Quality Modeling for a Typical Urban Lake Based on the EFDC Model. Environ Model Assess 21, 643–655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-016-9519-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-016-9519-1