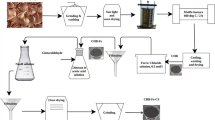
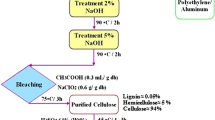
Abstract
The sequestration of heavy metals from multicomponent sorption media has become critical due to the noxious effects of heavy metals on the natural environment and subsequently on human health as well as all life forms. The abatement of heavy metals using bio-adsorbents is one of the efficient and affordable approaches for treating water and wastewater. Therefore, the interactive effect of arsenic [As(III)] ions on the sorption and desorption ability of mercury [Hg(II)] from a binary sorption system was conducted. More so, the impact of reaction time, solution pH, bio-adsorbent particle size, bio-adsorbent dose, initial mono-metal, and binary-metal concentration as well as reaction temperature on the individual and competitive sorption of Hg(II) was explored. The study showed that Hg(II) could be removed effectively from the single-component system and competitively from the aqueous phases by the bio-adsorbent in the coexistence of As(III) species in the bicomponent medium. The adsorptive detoxification of Hg(II) from the monocomponent and bicomponent sorption media showed dependence on all the studied adsorption parameters. The occurrence of As(III) species in the bicomponent sorption medium affected the decontamination of Hg(II) by the bio-adsorbent and the major interactive mechanism was found to be antagonism. The spent bio-adsorbent was effectively recycled using 0.10 M nitric (HNO3) and hydrochloric (HCl) acids solutions and the multi-regeneration cycles showed a high removal efficiency in each cycle. The first regeneration cycle was found to have the highest Hg(II) ions removal efficiencies of 92.31 and 86.88% for the monocomponent and bicomponent systems, respectively. Thus, the bio-adsorbent was found to be mechanically stable and reusable up to the 6.00 regeneration cycle. Therefore, this study concludes that the bio-adsorbent not only has a higher adsorption capacity but also a good recycling performance pointing to good industrial applications and economic prospects.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request.
References
Abou Taleb, M. F., Albalwi, H., & Abou El Fadl, F. I. (2021). Removal of Mercury (II) from Aqueous Solution Using Silver Nanocomposite: Synthesis and Adsorption Mechanism. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 31(4), 1825–1835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01839-5
Adio, S. O., Basheer, C., Hussein, M. O., Siddiqui, M. N., & Tawabini, B. (2019). Comparative Evaluation of Biosynthesized Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron and Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles in Mercury Adsorption. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 145(7), 04019037. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ee.1943-7870.0001515
Ali, H., Khan, E., & Ilahi, I. (2019). Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
An, F. Q., Li, H. F., Guo, X. D., Gao, B. J., Hu, T. P., & Gao, J. F. (2019). Novel ionic surface imprinting technology: Design and application for selectively recognizing heavy metal ions. RSC Advances, 9(5), 2431–2440. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra09948k
Anna, B., Kleopas, M., Constantine, S., Anestis, F., & Maria, B. (2015). Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) onto natural bentonite: study in mono- and multi-metal systems. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(9), 5435–5444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3798-0
Bashir, A., Malik, L. A., Ahad, S., Manzoor, T., Bhat, M. A., Dar, G. N., & Pandith, A. H. (2019). Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 17(2), 729–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-00828-y
Bayuo, J., Rwiza, M. J., & Mtei, K. M. (2023). Non-competitive and competitive detoxification of As(III) ions from single and binary biosorption systems and biosorbent regeneration. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03734-0
Biswas, R., & Sarkar, A. (2019). Characterization of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria to decipher their role in arsenic bioremediation. Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 49(1), 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2018.1476883
Chen, O. P., Lin, Y. J., Cao, W. Z., & Chang, C. T. (2017). Arsenic removal with phosphorene and adsorption in solution. Materials Letters, 190, 280–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.01.030
Dahake, R., Tiwari, P., & Bansiwal, A. (2021). Multicycle adsorption and desorption for recovery of U(VI) from aqueous solution using oxime modified zeolite-A. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(1), 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07482-1
Dawodu, F. A., Akpan, B. M., & Akpomie, K. G. (2020). Sequestered capture and desorption of hexavalent chromium from solution and textile wastewater onto low cost Heinsia crinita seed coat biomass. Applied Water Science, 10(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1114-6
de Morais França, A. M., Sousa, F. W., Loiola, A. R., de Luna, F. M. T., Vidal, C. B., & do Nascimento, R. F. (2021). Study of Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ competitive adsorption on synthetic zeolite: An experimental and theoretical approach. Desalination and Water Treatment, 227, 263–277. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27255
Du, X., Cui, S., Wang, Q., Han, Q., & Liu, G. (2021). Non-competitive and competitive adsorption of Zn(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) by a granular Fe-Mn binary oxide in aqueous solution. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 40(4), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13611
Egirani, D., Latif, M. T., Wessey, N., Poyi, N. R., & Shehata, N. (2021). Preparation and characterization of powdered and granular activated carbon from Palmae biomass for mercury removal. Applied Water Science, 11(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01343-8
El-Bouhy, Z. M., Reda, R. M., Mahboub, H. H., & Gomaa, F. N. (2021). Bioremediation effect of pomegranate peel on subchronic mercury immunotoxicity on African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(2), 2219–2235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10599-1
Gupta, A. D., Singh, H., Jaiswal, V. K., Goswami, M., & Bhadauria, V. (2021). Improved arsenite adsorption using iron-impregnated marble dust with surface functionalized by quaternary ammonium ions. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 18(10), 2955–2974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03013-3
Hiew, B. Y. Z., Lee, L. Y., Lee, X. J., Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S., & Gan, S. (2021). Utilisation of environmentally friendly okara-based biosorbent for cadmium(II) removal. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(30), 40608–40622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09594-3
Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., Hosseini, M. S., Jalalabadi, Y., Sarwghadi, M., Nedaie, M., Taherian, A., Ghaznavi, A., & Eftekhari, A. (2011). Removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions using a novel impregnated resin containing 1-(2-thiazolylazo)-2-naphthol (TAN). Chemical Engineering Journal, 168(3), 1163–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.02.004
Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., Karimzadeh, M., Sarwghadi, M., Heydarbeigi, A., Hosseini, S. H., Nedaie, M., & Shoghi, H. (2014). Use of a selective extractant-impregnated resin for removal of Pb(II) ion from waters and wastewaters: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 92(3), 581–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2013.10.007
Igberase, E., Osifo, P., & Ofomaja, A. (2017). The Adsorption of Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, and Cd by Modified Ligand in a Single Component Aqueous Solution: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Desorption Studies. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6150209
Kavand, M., Eslami, P., & Razeh, L. (2020). The adsorption of cadmium and lead ions from the synthesis wastewater with the activated carbon: Optimization of the single and binary systems. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 34, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101151
Kim, K. J., Kim, D. H., Yoo, J. C., & Baek, K. (2011). Electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from dredged marine sediment. Separation and Purification Technology, 79(2), 164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.02.010
Krishna, R. H., & Swamy, A. V. V. S. (2012). Physico-Chemical Key Parameters, Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm and Lagergren Rate Constant Studies on the removal of divalent nickel from the aqueous solutions onto powder of calcined brick. International Journal of Engineering Research and Development, 4(1), 29–38.
Labied, R., Benturki, O., Eddine Hamitouche, A. Y., & Donnot, A. (2018). Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by activated carbon obtained from a waste lignocellulosic material (Ziziphus jujuba cores): Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Adsorption Science and Technology, 36(3–4), 1066–1099. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617417750739
Lenka, S. P., Shaikh, W. A., Owens, G., Padhye, L. P., Chakraborty, S., & Bhattacharya, T. (2021). Removal of Copper from Water and Wastewater Using Dolochar. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 232(5), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05135-x
Liu, R., & Lian, B. (2019). Non-competitive and competitive adsorption of Cd2+, Ni2+, and Cu2+ by biogenic vaterite. Science of the Total Environment, 659(1), 122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.199
Liu, Y., Xu, J., Cao, Z., Fu, R., Zhou, C., Wang, Z., & Xu, X. (2020). Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Pb(II) and complex Cu(II) species by biowaste-derived char with amino functionalization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 559(Ii), 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.10.035
Memon, A. Q., Ahmed, S., Bhatti, Z. A., Maitlo, G., Shah, A. K., Mazari, S. A., Muhammad, A., Jatoi, A. S., & Kandhro, G. A. (2021). Experimental investigations of arsenic adsorption from contaminated water using chemically activated hematite (Fe2O3) iron ore. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(10), 12898–12908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11208-x
Mohamed, M. S. M., El-Arabi, N. I., El-Hussein, A., El-Maaty, S. A., & Abdelhadi, A. A. (2020). Reduction of chromium (VI) by chromium-resistant Escherichia coli FACU: a prospective bacterium for bioremediation. Folia Microbiologica, 65(4), 687–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00771-y
Naga, B. A., Raja, S. T., Srinivasa, R. D., Suresh, K. G., & Krishna, M. G. V. (2021). Experimental and statistical analysis of As(III) adsorption from contaminated water using activated red mud doped calcium-alginate beads. Environmental Technology (United Kingdom), 42(12), 1810–1825. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1681520
Pasgar, A., Nasiri, A., & Javid, N. (2022). Single and competitive adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ by tea pulp from aqueous solutions. Environmental Health Engineering and Management, 9(1), 65–74. https://doi.org/10.34172/EHEM.2022.08
Peng, S. H., Wang, R., Yang, L. Z., He, L., He, X., & Liu, X. (2018). Biosorption of copper, zinc, cadmium and chromium ions from aqueous solution by natural foxtail millet shell. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165, 61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.084
Priyadarshanee, M., & Das, S. (2021). Biosorption and removal of toxic heavy metals by metal tolerating bacteria for bioremediation of metal contamination: A comprehensive review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104686
Sajjadi, S. A., Mohammadzadeh, A., Tran, H. N., Anastopoulos, I., Dotto, G. L., Lopičić, Z. R., Sivamani, S., Rahmani-Sani, A., Ivanets, A., & Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. (2018). Efficient mercury removal from wastewater by pistachio wood wastes-derived activated carbon prepared by chemical activation using a novel activating agent. Journal of Environmental Management, 223(May), 1001–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.06.077
Sellaoui, L., Soetaredjo, F. E., Ismadji, S., Benguerba, Y., Dotto, G. L., Bonilla-Petriciolet, A., Rodrigues, A. E., Lamine, A. B., & Erto, A. (2018). Equilibrium study of single and binary adsorption of lead and mercury on bentonite-alginate composite: Experiments and application of two theoretical approaches. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 253, 160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.056
Shivangi, Bhardwaj, S., & Sarkar, T. (2022). Simultaneous removal of cadmium and lead ions from aqueous solutions by nickel oxide-decorated reduced graphene oxides. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(6), 5595–5610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03510-z
Tekin, B., & Unsal, A. (2022). Adsorption Isotherms for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions (Copper and Nickel) from Aqueous Solutions in Single and Binary Adsorption Processes. Gazi University Journal of Science, 36(2), 495–509. https://doi.org/10.35378/gujs.1066137
Tho, P. T., Van, H. T., Nguyen, L. H., Hoang, T. K., Ha Tran, T. N., Nguyen, T. T., Hanh Nguyen, T. B., Nguyen, V. Q., Le Sy, H., Thai, V. N., Tran, Q. B., Sadeghzadeh, S. M., Asadpour, R., & Thang, P. Q. (2021). Enhanced simultaneous adsorption of As(III), Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solution using cassava root husk-derived biochar loaded with ZnO nanoparticles. RSC Advances, 11(31), 18881–18897. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra01599k
Touihri, M., Guesmi, F., Hannachi, C., Hamrouni, B., Sellaoui, L., Badawi, M., Poch, J., & Fiol, N. (2021). Single and simultaneous adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu (II) on a novel Fe3O4/pine cones gel beads nanocomposite: Experiments, characterization and isotherms modeling. Chemical Engineering Journal, 416(January), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129101
Vakili, M., Deng, S., Cagnetta, G., Wang, W., Meng, P., Liu, D., & Yu, G. (2019). Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 224(May), 373–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.05.040
Wang, M., Bera, G., Mitra, K., Wade, T. L., Knap, A. H., & Phillips, T. D. (2021). Tight sorption of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by edible activated carbon and acid-processed montmorillonite clay. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(6), 6758–6770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10973-z
Zhao, J., Liu, T., Shi, H., Zhang, J., Li, H., Ge, W., & Chi, Y. (2019). Preparation and characterization of MnO2-impregnated granular activated carbon for Reactive Black 5 removal. Desalination and Water Treatment, 171, 428–435. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24782
Acknowledgements
The Partnership for Applied Sciences, Engineering, and Technology (PASET), under whose funding this study was fruitful, is highly appreciated by the authors.
Funding
This work was supported by the Partnership for Applied Sciences, Engineering, and Technology (PASET)-Regional Scholarship and Innovation Fund (RSIF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jonas Bayuo was in charge of conceptualization, funding acquisition; methodology; investigation; data curation; formal analysis; and writing — original draft. Mwemezi J. Rwiza and Kelvin Mark Mtei were also in charge of supervision; validation; writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bayuo, J., Rwiza, M.J. & Mtei, K.M. Adsorption and desorption ability of divalent mercury from an interactive bicomponent sorption system using hybrid granular activated carbon. Environ Monit Assess 195, 935 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11540-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11540-y