Abstract
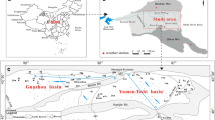
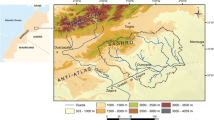
Evolution of groundwater geochemistry in the Sulaimani-Warmawa Sub-basin in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq has been investigated using hydrogeochemical and isotopic methods. This is a semiarid region with seasonal precipitation in winter. Water chemistry generally evolves from Ca-HCO3 groundwater type close to the basin boundaries towards Ca-Mg-HCO3 groundwater type close to the Tanjero River along the axis of the basin. Some samples have increased concentrations of Na, Cl, and SO4 as a consequence of dissolution of halite and gypsum embedded in carbonates. Values of pH are slightly alkaline or alkaline, and redox parameters indicate a moderately reducing environment. Isotopes δ2H and δ18O indicate recharge from winter precipitation with no evaporation. Values of dissolved 13C(DIC) correspond to equilibrium with carbonates and C4 plants as the source of CO2. Values of 87Sr/86Sr in groundwater are in a good agreement with carbonate dissolution as a principal process. The principal geogenic contaminant is Ba with concentrations up to 0.383 mg/L. Dissolved concentrations of other geogenic contaminants such as As, F, Mn, and Cr are low or below the detection limit as expected based on their low contents in carbonate rocks. Inverse geochemical modeling on selected profiles calibrated using δ13C values provided mass transfer coefficients for possible geochemical reactions. Future work should focus on interactions in the hyporheic zone of the Tanjero River.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The used and analyzed datasets in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alarcón-Herrera, M. T., Bundschuh, J., Nath, B., Nicolli, H. B., Gutierrez, M., Martín-Dominguez, I. R., Reyes-Gomez, V. M., Nuñez, D., Martín-Domínguez, A., & Sracek, O. (2013). Co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride in groundwater of semi-arid regions in Latin America: Genesis, mobility and remediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 262, 960–969.
Al-Charideh, A. R. (2011). Environmental isotope study of groundwater discharge from the large karst springs in the west Syria. Environment and Earth Science, 63, 1–10.
Al-Jiburi, H. K. et al. (2015). Hydrogeological map of Iraq, scale 1: 1000 000, 2013. Iraqi Bulletin of Geology and Mining, 11(1):17–26. Available at: https://www.iasj.net/iasj/download/69d0ec38d854102b
Ali, K. K., Al-Kubaisi, Q. Y., & Al-Paruany, K. B. (2015). ‘Isotopic study of water resources in a semi-arid region, western Iraq. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(2), 1671–1686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4172-6
Ali, S. S., (2007). Geology and hydrogeology of Sharazoor - Piramagroon Basin in Sulaimani Area, Northeastern Iraq. Unpublished Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade, Serbia, 330 p.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd ed.). CRC Press.
Bellen, R. C., Dunnington, H. V., Wetzel, R., & Morton, D. (1959). Lexique Stratigraphique International, Iraq. Vol. III, Asie, Fasc. 10a, Paris. 336 p.
Bertolo, R., Bourotte, C., Hirata, R., Marcolan, L., & Sracek, O. (2011). Geochemistry of natural chromium occurrence in a sandstone aquifer in Bauru Basin, São Paulo State, Brazil. Applied Geochemistry, 26, 1353–1363.
Bondu, R., Cloutier, V., Rosa, E., & Roy, M. (2020). An exploratory data analysis approach for assessing the sources and distribution of naturally occuring contaminants (F, Ba, Mn, As) in groundwater from southern Quebec (Canada). Journal of Hydrology, 114, 104500.
Buday, T. (1980). Regional geology of Iraq: Vol. 1, Stratigraphy, I. I. Kassab & S. Z. Jassim (Eds.) D. G. Geo Survey. Min. Invest. Publication. 445 p.
Buday, T., & Jassim, S. Z. (1987). The regional geology of Iraq: Tectonis, magmatism, and metamorphism. I. I. Kassab & M. J. Abbas (Eds.), Baghdad, 445 p.
Clark, I., & Fritz, P. (1997). Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology, Lewis, 328 p.
Craig, H. (1961). Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science, 133, 1702–1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Davies, J. C. (2002). Statistics and data analysis in geology (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Directorate of Groundwater of Sulaimani, DoGWS. (2020). Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resourcses, Kurdistan Regional Government, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. https://gov.krd/moawr
Faimon, J., Ličbinská, M., Zajíček, P., & Sracek, O. (2012). Partial pressures of CO2 in epikarstic zone deduced from hydrogeochemistry of permanent drips, the Moravian Karst. Czech Republic, Acta Carsologica, 41(1), 47–57.
Ford, D., & Williams, D. (2007). Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Frost, C. D., & Toner, R. (2004). Strontium isotopic identification of water-rock interaction and ground water mixing. Ground Water, 42(3), 418–432.
Gat, J. R., & Carmi, I. (1970). Evolution of the isotopic composition of atmospheric waters in the Mediterranean Sea area. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75, 3039–3048. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC075i015p03039
Halm, D., Gaiser, T., & Stahr, K. (2002). Seepage and groundwater recharge in sandy soils of the semi-arid region of Picos, Northeast Brazil. Neues Jahrbuch Fur Geologie Und Palaontologie-Abhandlungen, 225, 85–101.
Hamamin, D. F., et al. (2018). ‘Hazard and risk intensity maps for water-bearing units: A case study’, International. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 15(1), 173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1376-1
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: Paleontological software for education and data analysis. Paleontological Association. https://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm
Harrington, G. A., Cook, P. G., & Herczeg, A. L. (2002). Spatial and temporal variability of groundwater recharge in central Australia: A tracer approach. Ground Water, 40, 518–527.
Jassim, S. Z., & Goff, J. C. (2006). Geology of Iraq. Jassim (Eds.) D. G. Geo Survey. Min. Invest. Publication. 445 p.
Johnson, C. A., & Bretzler, A. (2015). Geogenic Contamination Handbook, Eawag, Switzerland. https://www.eawag.ch/fileadmin/Domain1/Forschung/Menschen/Trinkwasser/Wrq/Handbook/geogenic-contamination-handbook.pdf
Kareem, A., Mustafa, O., & Merkel, B. (2018). Geochemical and environmental investigation of thae water resources of the Tanjero area, Kuristan region, Iraq. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 461.
Karim, K. H. (2004) Basin analysis of Tanjero Formation in Sulaimaniya area, NE-Iraq. PhD Thesis, University of Sulaimani, Iraq.
Karim, K., & Ali, S. S. (2004). Origin of dislocated limestone blocks on the slope side of Baranan (Zirgoez) Homocline: An attempt to outlook the development of western part of Sharazoor Plain. (JZS) Journal of Zankoy Sulaimani, 3(1), 5–21.
Khosravi, R., Zarei, M., & Sracek, O. (2020). Hydraulic and geochemical interactions between surface water and sediment pore water in seasonal hypersaline Maharlu Lake, Iran. Hydrological Processes, 34, 3358–3369.
Markovich, K. H., Manning, A. H., Condon, L. E., & McIntosh, J. C. (2019). Mountain-block recharge: A review of current understanding. Water Resources Research, 55(11), 8278–8304.
Mazor, E. (2004). Chemical and isotopic groundwater hydrology (3rd ed., p. 465p). Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot.
McMahon, P. B., & Chapelle, F. (2008). Redox processes and water quality of selected principal aquifer systems. Ground Water, 46, 259–271.
Mohammadzadeh, H., & Heydarizad, M. (2019). δ18O and δ2H characteristics of moisture sources and their role in surface water recharge in the north-east of Iran. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 55(6), 550–565. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2019.1680552
Mohammadzadeh, H., Eskandari Mayvan, J., & Heydarizad, M. (2020). The effects of moisture sources and local parameters on the 18O and 2H contents of precipitation in the west of Iran and the east of Iraq. Tellus, Series B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 72(1), 25–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/16000889.2020.1721224
Mook, W. G. (2001) ‘Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle: Principles and applications, Volume I: Introduction: Theory, Methods, Review’, International Hydrological Programme IHP-V, 1, pp. 1–165. Available at: http://wwwnaweb.iaea.org/napc/ih/documents/global_cycle/Environmental%20Isotopes%20in%20the%20Hydrological%20Cycle%20Vol%201.pdf
Mustafa, O. (2006). Impact of sewage waste water on the environment of Tanjero River and its basin with Sulaimani City/NE-Iraq, M.Sc. Thesis, University of Sulaimani-College of Science, Dep. of Geology.
Mustafa, O., & Ahmad, H. (2008). Nitrate pollution in groundwater of Sulaimaniyah City, Kurdistan Region, NE Iraq. Iraqi Bulletin of Geology and Mining, 4(2), 73–82.
Mustafa, O., & Merkel, B. (2015). Geochemical evolution and water–rock interactions in Makook Karst aquifers, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Topical issues of rational use of natural resources, April 22–24, 2015a, St. Petersburg, Russia, National Mineral Resources University, p. 12–14.
Mustafa, O., Merkel, B., & Weise, S. (2015). Assessment of hydrogeochemistry and environmental isotopes in karst springs of Makook Anticline, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Hydrology, 2, 48–68.
Mustafa, O., Tichomirowa, M., Kummer, N. A., & Merkel, B. (2016). Assessment of water-rock interaction processes in the karst springs of Makook anticline (Kurdistan Region, Iraq) using Sr-isotopes, rare earth, and trace elements. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9, 368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2344-7
Nier, A. O. (1938). The isotopic constitution of strontium, barium, bismuth, thallium and mercury. Physical Review, 5, 275–279.
Omar, A. A., Lawa, F. A., & Sulaiman, S. H. (2015). Tectonostratigraphic and structural imprints from balanced sections across the north-western Zagros fold-thrust belt, Kurdistan region, NE Iraq. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(10), 8107–8129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1682-6
Osati, K., et al. (2014). Spatiotemporal patterns of stable isotopes and hydrochemistry in springs and river flow of the upper Karkheh River Basin, Iran. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 50(2), 169–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2014.857317
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)-a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259, U.S. Geological Survey.
Pin, C., Briot, D., Bassin, C., & Poitrasson, F. (1994). Concomitant separation of strontium and samarium-neodymium for isotopic analysis in silicate samples, based on specific extraction chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta, 298(2), 209–217.
Rashid, C, Tahir, J., & Mustafa, O. (2018). Solid waste management: A case study in Chamchamal (Dwbra Valley Open Dump), Sulaimani, Kurdistan Region. (August):210–19.
Ravenscroft, P., Brammer, H., & Richards, K. (2009). Arsenic pollution, A Global synthesis, Wiley-Blackwell, 588 p.
Razmjooei, M. J., Thibault, N., Kani, A., Ullman, C. V., & Jani, A. M. (2020). Santonian-Maastrichtian carbon-isotope stratigraphy and calcareous nannofossil biostratigraphy of the Zagros Basin: Long-range correlation, similarities and differences of carbon-isotope trends at global scale. Global and Planetary Change, 184, 103075.
Scanlon, B. R., Keese, K. E., Flint, A. L., Flint, L. E., Gaye, B. C., Esmunds, W. M., & Simmers, I. (2006). Global synthesis of groundwater recharge in semiarid and arid regions. Hydrological Processes, 20, 3335–3370.
Sengupta, S., Sracek, O., Jean, J. -S., Yang, H. -J., Wang, C. -H., Kar, S., Babek, O., Lee, C. -Y., & Das, S. (2018). Difference in attenuation among Mn, As, and Fe in riverbed sediments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 341, 277–289.
Sissakian, V. K. (2015). Geological map of Sulaimaniyah, Scale 1:250000’, (October). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.5109.0642
Sracek, O., Berg, M., & Müller, B. (2018). Redox buffering and de-coupling of arsenic and iron in reducing aquifers across the Red River Delta, Vietnam, and conceptual model of de-coupling processes. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(16), 15954–15961.
Sracek, O., Wanke, H., Ndakunda, N. N., Mihaljevič, M., & Buzek, F. (2015). Geochemistry and fluoride levels of geothermal springs in Namibia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148, 96–104.
Stadler, S., Osenbrück, K., Suckow, A. O., Himmelbach, T., & Hötzl, H. (2010). Groundwater flow regime, recharge and regional-scale solute transport in the semi-arid Kalahari of Botswana derived from isotope hydrology and hydrochemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 388(3–4), 291–303.
Stevanovic, Z., & Markovic, M. (2003). Hydrogeology of northern Iraq, climate, hydrology, geomorphology, Geology. Ed. Filed documents, Vol. 1.
Stevanovic, Z., & Markovic, M. (2004). Hydrogeology of Northern Iraq, Vol.2, General Hydrogeology and Aquifer Systems. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome P 264.
Studio Galli Ingegneria (SGI). (2011). Hydrogeological study for the governorate of around the center of the city, Final Report, January, 2011, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. 200p.
Tóth, J. (1999). Groundwater as a geological agent: An overview of the causes, processes, and manifestations. Hydrogeology J., 7, 1–14.
Tóth, J. (2009). Gravitational systems of groundwater flow. Cambridge University Press.
Uugulu, S., & Wanke, H. (2020). Estimation of groundwater recharge in savannah aquifers along a precipitation gradient using chloride mass balance method and environmental isotopes, Namibia. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 116, 102844.
Veizer, J. (1989). Strontium isotopes in seawater through time. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 17, 141–167.
WHO. (2017). Guidelines for Drinking‑water Quality. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550017
Acknowledgements
We thank Martin Mihaljevič for water analyses performed at Charles University in Prague and František Buzek from Czech Geological Survey for comments on isotopes. Thanks to Directorate of Groundwater of Sulaimani for providing archived water well data.
Funding
The first author (MR) received Fisher’s scholarship awarded by Palacky University in Olomouc (Univerzita Palackého v Olomouci).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rebar Mahmmud—collecting data and interpretation; Ondra Sracek—interpretation and modeling; Omed Mustafa—collecting data and evaluation of contaminant sources; Bohuslava Čejková—carbon isotope analysis; Ivana Jačková—carbon isotope analysis; Lenka Vondrovicova—strontium isotope analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmmud, R., Sracek, O., Mustafa, O. et al. Groundwater geochemistry evolution and geogenic contaminants in the Sulaimani-Warmawa Sub-basin, Sulaimani, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Environ Monit Assess 194, 352 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09933-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09933-6