Abstract
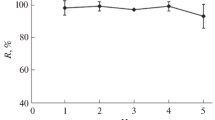
Lead (Pb) is a potentially toxic element with significant environmental interest. Simple and sensitive analytical methods are necessary to allow determination of this element at trace levels using sample preparation procedures related to green chemistry. For this, calcium alginate beads (CA-beads), a low-cost and environmentally friendly biopolymer, have been proposed for extraction and preconcentration of Pb2+ in river water samples and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). CA-beads were prepared and applied to extract and preconcentrate Pb2+ in river water samples, providing an enrichment factor (EF) of 50, enhancement factor (E) of 54, a detection limit of 2 μg L−1, and a relative standard deviation < 5%. The extraction of Pb2+ in CA-beads achieved good selectivity, with recoveries from 94.8 to 100.2% in real samples, demonstrating the good accuracy of the proposed method. The results were also compared to those obtained by ICP-MS. The reuse of CA-beads was evaluated for six cycles, and under these conditions, the extraction and preconcentration efficiency of Pb2+ were not significantly affected. The developed methodology was applied to determine Pb2+ in water samples from rivers that are part of the hydrographic areas of Tibagi and Pitangui Rivers, in which the Pb2+ concentration was less than 2 μg L−1, a concentration lower than that established by Brazilian legislation for class I and II rivers.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, B., Son, H., Chung, J., Choi, J. W., Lee, S. H., & Hong, S. W. (2013). Calcium and hydrogen effects during sorption of copper onto an alginate-based ion exchanger: Batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chemical Engineering Journal, 232, 51–58
Baghban, N., Yilmaz, E., & Soylak, M. (2017). Nanodiamond/MoS2 nanorod composite as a novel sorbent for fast and effective vortex-assisted micro solid phase extraction of lead(II) and copper(II) for their flame atomic absorption spectrometric detection. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 234, 260–267
Bai, H., Zhou, Q., Xie, G., & Xiao, J. (2010). Temperature-controlled ionic liquid-liquid-phase microextraction for the pre-concentration of lead from environmental samples prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta, 80, 1638–1642
Behbahani, M., Hassanlou, P. G., Amini, M. M., Omidi, F., & Esrafili., Farzadkia, M., Bagheri, A. (2015). Application of solvent-assisted dispersive solid phase extraction as a new, fast, simple and reliable preconcentration and trace detection of lead and cadmium ions in fruit and water samples. Food Chemistry, 187, 82–88
Blanchet-Chouinard, G., & Larivière, D. (2018). Determination of Pb in environmental samples after cloud point extraction using crown ether. Talanta, 179, 300–306
Carvalho, G. G. A., Kondaveeti, S., Petri, D. F. S., Fioroto, A. M., Albuquerque, L. G. R., & Oliveira, P. V. (2016). Evaluation of calcium alginate beads for Ce, La and Nd preconcentration from groundwater prior to ICP OES analysis. Talanta, 161, 707–712
Cataldo, S., Gianguzza, A., Merli, M., Muratore, N., Piazze, D., & Liveri, M. L. T. (2014). Experimental and robust modeling approach for lead (II) uptake by alginate gel beads: Influence of the ionic strength and medium composition. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 434, 77–88
Chaduka, M., Guyo, U., Zinyama, N. P., Tshuma, P., & Matsinha, L. C. (2020). Modeling and optimization of lead (II) adsorption by a novel peanut hull-g-methyl methacrylate biopolymer using response surface methodology (RSM). Analytical Letters, 53, 1294–1311
Chiew, C. S. C., Yeoh, H. K., Pasbakhsh, P., Poh, P. E., Tey, B. T., & Chan, E. S. (2016). Stability and reusability of alginate-based adsorbents for repetitive lead (II) removal. Polymer Degradation and Stabilility, 123, 146–154
CONAMA (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente). (2005). Resolução No 357. Ministério do Meio Ambiente, MMA. Brasília. Distrito Federal. http://www.mma.gov.br. (Accessed 02 July 2020).
Daşbaşı, T., Saçmacı, Ş, Ülgen, A., & Kartal, S. (2015). Determination of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in food and water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 174, 591–596
da Silva Fernandes, R., de Moura, M. R., Glenn, G. M., & Aouada, F. A. (2018). Thermal microstructural and spectroscopic analysis of Ca2+ alginate/clay nanocomposite hydrogel beads. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 265, 327–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.06.005
Guo, Y., Zhao, H., Han, Y., Liu, X., Guan, S., Zhang, Q., & Bian, X. (2017). Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of trace copper, nickel, and cobalt ions in water samples using solid phase extraction coupled with partial least squares approaches. Spectrochimica Acta Part a: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 173, 532–536
Hajiaghababaei, L., Badiei, A., Ganjali, M. R., Heydari, S., Khaniani, Y., & Ziarani, G. M. (2011). Highly efficient removal and preconcentration of lead and cadmium cations from water and wastewater samples using ethylenediamine functionalized SBA-15. Desalination, 266, 182–187
Hua, S., Ma, H., Li, X., Yang, H., & Wang, A. (2010). pH-sensitive sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads prepared by combined Ca2+ crosslinking and freeze-thawing cycles for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 46(5), 517–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.03.004
Huang, S., Xiao, Z., Zhai, S., Zhai, B., Zhang, F., & An, Q. (2014). Fabrication of highly-stable Ag/CA@GTA hydrogel beads and their catalytic application. Royal Society of Chemistry Advances, 4, 60460–60466
IBGE (Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística). (2018) Área territorial brasileira, Rio de Janeiro, IBGE
Jalbani, N., & Soylak, M. (2015). Preconcentration/separation of lead at trace level from water samples by mixed micelle cloud point extraction. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 29, 48–51
Kamboh, M. A., Ibrahim, W. A. W., Nodeh, H. R., Zardari, L. A., & Sanagi, M. M. (2019). Fabrication of calixarene-grafted magnetic nanocomposite for the effective removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution. Environmental Technology, 40, 2482–2493
Kardar, Z. S., Beyki, M. H., & Shemirani, F. (2016). Takovite-aluminsilicate@MnFeO4 nanocomposite, a novel magnetic adsorbent for efficient preconcentration of lead ions in food samples. Food Chemistry, 209, 241–247
Krawczyk, M., & Stanisz, E. (2016). Ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction with nano-TiO2 as adsorbent for the determination of Mercury species. Talanta, 161, 384–391
Lagoa, R., & Rodrigues, Jr. (2007). Evaluation of dry protonated calcium alginate beads for biosorption applications and studies of lead uptake. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 143, 115–128
Lai, Y., Annadurai, G., Huang, F., & Lee, J. (2008). Biosorption of Zn(II) on the different Ca-alginate beads from aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 99, 6480–6487
Li, Z., Tang, J., & Pan, J. (2004). The determination of lead in preserved food by spectrophotometry with dibromohydroxyphenylporphyrin. Food Control, 15(7), 565–570
Li, Y. K., Li, W. T., Liu, X., Yang, T., Chen, M. L., & Wang, J. H. (2019). Functionalized magnetic composites based on the aptamer serve as novel bio-adsorbent for the separation and preconcentration of trace lead. Talanta, 203, 210–219
Lorêdo de França, M., Separovic, L., Longo Junior, L. S., Oliveira, D. C., Lourenço, F. R., Calixto, L. A. (2021). Determining uncertainty in a simple UV–Vis spectrometry method employing dimethyl carbonate as green solvent for lead determination in water. Measurement, 173
Maratta, A., Vásquez, S., López, A., Auguso, M., & Pacheco, P. H. (2016). Lead preconcentration by solid phase extraction using oxidized carbon xerogel and spectrophotometric determination with dithizone. Microchemical Journal, 128, 166–171
Mariussen, E., Heierb, L. S., Teien, H. C., Pettersen, M. N., Holth, T. F., Salbu, B., & Rosseland, B. O. (2017). Accumulation of lead (Pb) in brown trout (Salmo trutta) from a lake downstream a former shooting range. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 135, 327–336
Mirghani, M., Al-Mubaiyedh, U. A., Nasser, M. S., & Shawabkeh, R. (2015). Experimental study and modeling of photocatalytic reduction of Pb2+ by WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles. Separation and Purification Technology, 14, 285–293
Mousa, N. E., Simonescu, C. M., Pǎtescu, R., Onose, C., Tardei, C., Culițǎ, D. C., Oprea, O., Patroi, D., & Lavric, V. (2016). Pb+2 removal from aqueous synthetic solution by calcium alginate and chitosan coated calcium alginate. Reactive & Functional Polymers, 109, 137–150
Peters, F. T., Drummer, O. H., & Musshoff, F. (2007). Validation of new methods. Forensic Science International, 165, 216–224
Ren, H., Gao, Z., Wu, D., Jiang, J., Sun, Y., & Luo, C. (2016). Efficient Pb(II) removal using sodium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Carbohydrate Polymers, 137, 402–409
Saçmacı, Ş, & Saçmacı, M. (2020). The rapid determination of lead in food samples by magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction coupled zeta potential analyzer. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1784885
Saracoglu, S., Soylak, M., Peker, D. S. K., Elci, L., Santos, W. N. L., Lemos, V. A., & Ferreira, S. L. C. (2006). A pre-concentration procedure using coprecipitation for determination of lead and iron in several samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 575, 133–137.
Satarpi, T., Shiowatana, J., & Siripinyanound, A. (2016). Paper-based analytical device for sampling on-site preconcentration and detection of ppb lead in water. Talanta, 154, 504–510.
SEMA (Secretaria de Estado do Meio Ambiente e Recursos Hidrícos). (2010). Bacias Hidrográficas do Paraná – Série Histórica. Curitiba, 75–78
Sereshti, H., Heravi, Y. E., & Samadi, S. (2012). Optimized ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction for simultaneous trace multielement determination of heavy metals in real water samples by ICP-OES. Talanta, 97, 235–241
Shamsipur, M., Ramezani, M., & Sadeghi, M. (2009). Preconcentration and determination of ultra-trace amounts of palladium in water samples by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchimica Acta, 166, 235–242
Silva, E. L., & Roldan, P. S. (2009). Simultaneous flow injection preconcentration of lead and cadmium using cloud point extraction and determination by atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161, 142–147
Smichowski, P., & Londonio, A. (2020). A retrospective and prospective of the use of bio- and nanomaterials for preconcentration, speciation, and determination of trace elements: A review spanning 25 years of research. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 10, 1007–1021
Simonescu, P. M., Mason, T. J., Călinescu, I., Lavric, V., Vînătoru, M., Melinescu, A., Culiţă, D. C. (2020). Ultrasound assisted preparation of calcium alginate beads to improve absorption of Pb+2 from water. Ultrasonic Sonochemistry, 68, 105191
Tahtat, D., Bouaicha, M. N., Benamer, S., Nacer-Khodja, A., & Mahlous, M. (2017). Development of alginate gel beads with a potential use in the treatment against acute lead poisoning. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 105, 1010–1016
Taverniers, I., De Loose, M., & Van Bockstaele, E. (2004). Trends in quality in the analytical laboratory. II. Analytical method validation and quality assurance. TrAC-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 23, 535–552
Tokalioğlu, Ş, Papak, A., & Kartal, Ş. (2017). Separation/preconcentration of trace Pb(II) and Cr(II) with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole impregnated Amberlite XAD-1180 resin and their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, 19–23
Uslu, H., Büyükpinar, Ç., Unutkan, T., Serbest, H., San, N., Turak, F., & Bakirdere, S. (2018). A novel analytical method for sensitive determination of lead: Hydrogen assisted T-shape slotted quartz tube-atom trap-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 137, 155–159
Verma, R., Asthama, A., Singh, A. K., Prasad, S., & Susan, M. A. B. H. (2017). Novel glycine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles entrapped calcium alginate beads for effective removal of lead. Microchemical Journal, 130, 168–178
Wang, J., Yang, Q., Zhang, L., Liu, M., Hu, N., Zhang, W., Zhu, W., Wang, R., Suo, Y., & Wang, J. (2018). A hybrid monolithic column based on layered double hydroxide-alginate hydrogel for selective solid phase extraction of lead ions in food and water samples. Food Chemistry, 257, 155–162
Wang, Z., Wu, S., Zhang, Y., Miao, L., Zhang, Y., & Wu, A. (2020). Preparation of modified sodium alginate aerogel and its application in removing lead and cadmium ions in wastewater. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 157, 687–694.
Wouthuyzen, S., Herandarudewi, S. M. C., & Komatsu, T. (2016). Stock assessment of brown seaweeds (Phaeophyceae) along the Bitung-Bentena Coast, North Sulawesi Province, Indonesia for alginate product using satellite remote sensing. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 33, 553–561
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for financial support. K.B.F have scholarship from CNPq and E.S.C. has a research scholarship from CNPq.
Funding
This study received financial support from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Beik, J., Fontana, K.B., Medeiros, D.C.C.S. et al. Feasibility of calcium alginate beads to preconcentrate lead in river water samples prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Environ Monit Assess 193, 666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09453-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09453-9