Abstract
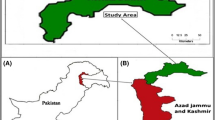
Lower Shiwalik foothill ranges (Kandi regions) are dominated by different land use systems, varying in fertility status due to soil erosion owing to undulating topographical features. For assessment of soil nutrient status of study area, the soil sampling was conducted to investigate the variation in micronutrient status and physicochemical characteristics of soil. Long-range basis soil sampling was carried out in 11 blocks falling in the entire Shiwalik ranges of lower Himalaya under different land use systems (LUSs), viz., agriculture (AG), horticulture (HR), agri-horticulture (AH), grassland (GL), and agroforestry (AF) systems. A total of 440 soil samples were collected from two depths (0–15, 15–30 cm) for analysis. The results had reported that the soils were slightly acidic to slightly alkaline (6.61 to 8.10) in the whole range. Soil organic carbon (SOC) was found to be varying from very low to very high (2.43 to 10.43 g kg−1). DTPA-extractable Fe and Mn were found to be in dominant concentrations in the soils whereas, the deficiency of Zn was found under all existing land uses. Interestingly, Fe (r = 0.62*), Cu (r = 0.44), and Mn (r = 0.35) micronutrients were positively correlated with clay content whereas Zn (r = − 0.02) was negatively correlated. Soil quality based on principal component analysis (SQI-PCA) reported clay, SOC, and Zn are major dominating parameters to be considered of soil in Shiwalik ranges.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abraham, J. (2015). Soil health in different Land use systems in comparison to virgin forest of tropical region of Kerala. Journal of Rubber Science, 28, 8–21.
Amanuel, W., Yimer, F., & Karltun, E. (2018). Soil organic carbon variation in relation to land use changes: the case of Birr watershed, upper Blue Nile River Basin. Ethiopia. Journal of Ecology & Environment, 42(16), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41610-018-0076-1
Anoymous. (2012). Fundamentals of Soil Science by Indian Society of Soil Science.
Arthur, E., Tuller, M., Moldrup, P., & de Jonge, L. W. (2020). Clay content and mineralogy, organic carbon and cation exchange capacity affect water vapour sorption hysteresis of soil. European Journal of Soil Science, 71(2), 204–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12853
Ashraf, M. N., Hu, C., Wu, L., Duan, Y., Zhang, W., Aziz, T., Cai, A., Abrar, M. M., & Xu, M. (2020). Soil and microbial biomass stoichiometry regulate soil organic carbon and nitrogen mineralization in rice-wheat rotation subjected to long-term fertilization. Journal of Soils Sediments, 20, 3103–3113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02642-y
Asima. (2017). Assessment of seasonal variation on soil biochemical properties under different land use system in sub montane Punjab. M.Sc. (Agriculture) Thesis submitted to Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab.
Aumtong, S., Magid, J., Bruun, S., & De Neergaard, A. (2009). Relating soil carbon fractions to land use in sloping uplands in northern Thailand. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Enviroment, 131(3–4), 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.01.013
Barreto, P. A. B., Gama Rodrigues, A. C., Fontes, A. G., Polidoro, J. C., Moco, M. K. S., & Machado, R. C. R. (2010). Distribution of oxidizable organic carbon reactions in soils under cocoa agroforestry system in Southern Bahia, Brazil. Journal of Agroforestry Systems, 8(3), 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-010-9300-4
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2014). The nature and properties of soils. Chapter 15 and 16, pp 673–753.
Brookes, P. C., Landman, A., Pruden, G., & Jekinson, D. S. (1985). Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapidal direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 17, 837–42.
Bunemann, E. K., Bongiorno, G., Bai, Z., Creamer, R. E., De Deyn, G., de Goede, R., Fleskens, L., Geissen, V., Kuyper, T. W., Mäder, P., Pulleman, M., Sukkel, W., Van Groenigen, J. W., & Brussaard, L. (2018). Soil quality - A critical review. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 120, 105–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.01.030
Cakmak, I., & Kutman, U. B. (2018). Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: A review. European Journal of Soil Science, 69, 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12437
Chakravarty, S., Rai, P., Pala, N. A., & Shukla, G. (2020). Litter production and decomposition in tropical forest. In: Bhadouria R, Tripathi S, Srivastava P, Singh P (Ed.), Handbook of research on the conservation and restoration of tropical dry forests, IGI Global pp 193–212. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-0014-9.ch01
Chandel, S., & Hadda, M. (2018). Soil loss tolerance assessment under different land uses in submontane Punjab. Journal of Soil & Water Conservation, 17(4), 303–310. https://doi.org/10.5958/2455-7145.2018.00046.2
Chandran, P., Ray, S. K., Durge, S. L., Raja, P., Nimkar, A. M., Bhattacharyya, T., & Pal, D. K. (2009). Scope of horticultural land-use system in enhancing carbon sequestration in ferruginous soils of the semi-arid tropics. Journal of Current Sciences, 97, 1039–1046.
Cowie, A. L., Orr, B. J., Castillo Sanchez, V. M., Chasek, P., Crossman, N. D., Erlewein, A., Louwagie, G., Maron, M., Metternicht, G. I., Minelli, S., Tengberg, A. E., Walter, S., & Welton, S. (2018). Land in balance: the scientific conceptual framework for land degradation neutrality. Environment Science and Policy, 79, 25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2017.10.011
Dallimer, M., Stringer, L. C., Orchard, S. E., Osano, P., Njoroge, G., Wen, C., & Gicheru, P. (2018). Who uses sustainable land management practices and what are the costs and benefits? Insights from Kenya. Land Degradation and Development, 29, 2822–2835. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3001
Das, D. K. (2015). Micronutrients: their behaviour in soils and plants, Kalyani publishers.
Deekor, T. N., Iwara, A. I., Ogundele, F. O., Amiolemen, S. O., & Ita, A. E. (2012). Changes in soil properties under different land use cover in parts of Odukpani, Cross River State, Nigeria. Journal of Environment & Ecology, 3, 86–99. https://doi.org/10.5296/2Fjee.v3i1.2265
Devdas, D. L. K., & Chandrakar, K. (2013). Status of available micronutrients on the basis of correlation between physico-chemical properties of pH, OC and available Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu in black soil of Navagarh block under Janjgir district in Chhattisgarh. An Asian Journal of Soil Science, 8(2), 416–418. https://doi.org/10.5296/jee.v3i1.2265
Dhaliwal, S. S. (2003). Effect of different land use system on soil quality in Kandi region of Punjab, Ph.D Thesis submitted to Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab.
Dhaliwal, S. S., Naresh, R. K., Mandal, A., Singh, R., & Dhaliwal, M. K. (2019). Dynamics and transformations of micronutrients in agricultural soils as influenced by organic matter build-up: A review. Environmental & Sustainability Indicators, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2019.100007
Dhaliwal, S. S., Sharma, B. D., & Singh, B. (2009a). Micronutrients status of different land use system in relation to soil quality and sustainability under different watersheds in submontaneous tract of Punjab. Annals of Arid Zone, 48(2), 103–112.
Dhaliwal, S. S., Sharma, B. D., & Khera, K. L. (2009b). Soil quality and yield trends of different crops in low productive submontaneous tract and highly productive area in Punjab India. Indian Journal of Dryland Agricultural Research & Development, 24, 39–45.
Di Giuseppe, D., Melchiorre, M., Tessari, U., & Faccini, B. (2016). Relationship between particle density and soil bulk chemical composition. Journal of Soils Sediments, 16, 909–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1275-3
Di, H. J., Cameron, K. C., & Shen, J. (2013). The role of bacteria and archaea in nitrification, nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions in nitrogen-rich grassland soils. Molecular Environmental Soil Science, 79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4177-5_4
Domingues, R. R., Sánchez Monedero, M. A., Spokas, K. A., Melo, L. C. A., Trugilho, P. F., Valenciano, M. N., & Silva, C. A. (2020). Enhancing cation exchange capacity of weathered soils using biochar: Feedstock, pyrolysis conditions and addition rate. Agronomy, 10, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060824
Dotaniya, M. L., & Meena, V. D. (2015). Rhizosphere effect on nutrient availability in soil and its uptake by plants: A review. Proceed National Academy of Science: India Section B. Biological Science, 85(1), 1–12.
Franchini, J. C., Crispino, C. C., Souza, R. A., Torres, E., & Hungria, M. (2007). Microbiological parameters as indicators of soil quality under various soil management and crop rotation systems in Southern Brazil. Soil & Tillage Research, 92, 18–29.
Gibbs, P. A., Chambers, B. J., Chaudhari, A. M., McGrath, S. P., Carlton Smith, C. H., Bacon, J. R., Campbell, C. D., & Ait ken, M. N. (2006). Initial results from a long-term, multi-site field study of the effects on soil fertility and microbial activity of sludge cakes containing heavy metals. Soil Use Manage, 22, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-2743.2006.00003.x
Guo, L. B., & Gifford, R. M. (2002). Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a meta analysis. Journal of Global Change Biology, 8, 345–360.
Haider, M. U., Hussain, M., Farooq, M., & Nawaz, A. (2020). Zinc nutrition for improving the productivity and grain biofortification of mungbean. Journal of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00215-z
Hodgson, J. F. (1963). Chemistry of micronutrient elements in soils. Advances in Argonomy, 15, 119–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60398-3
Huizing, H. G. J. (1971). A reconnaissance study of the mineralogy of sand fractions from East Pakistan sediments and soils. Geoderma, 6, 109–133.
Jassal, H. S., Kumar, R., & Sharma, B. D. (2008). Description of benchmark soils. In Annual Progress Report of Research Scheme-Elemental Association in Relation to Mineralogical Assemblage of the Benchmark Soils of Punjab; Punjab Agricultural University: Ludhiana, India.
Jena, J., Sethy, P., Jena, T., Misra, S. R., Sahoo, S. K., Dash, G. K., & Palai, J. B. (2018). Rice Biofortification: A brief Review. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 7(1), 2644–2647.
Jha, A. B., & Warkentin, T. D. (2020). Biofortification of pulse crops: Status and future perspectives. Plants, 9(1), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9010073
Kakar, R., Sultanpuri, A., Sheoran, H. S., & Tripathi, D. (2018). Soil micronutrients status assessment in north western Himalayas of India. Chemical Science Review & Letters, 7(25), 83–87.
Kaur, L., & Kaur, G. (2019). Scope of food-processing in Kandi region of Punjab state Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 8(1S), 6–9.
Kaur, R., & Toor, A. S. (2012). Effect of different agricultural land uses on carbon sequestration in soils of sub-montaneous districts of Punjab. M.Sc (Agri.) Thesis submitted to Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab.
Kaur, R., Singh, B., & Dhaliwal, S. S. (2020a). Dynamics of soil cationic micronutrients in a chrono sequence of poplar based agroforestry system in India. Journal of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00272-4
Kaur, T., Sehgal, S. K., Singh, S., Sharma, S., Dhaliwal, S. S., & Sharma, V. (2021). Assessment of seasonal variability in soil nutrients and its impact on soil quality under different land use systems of lower Shiwalik foothills of Himalaya, India. Sustainability, 13, 1398. su13031398.
Kaur, A., Kaur, S., Singh, D., Singh, S., & Singh, M. (2020b). Fortification of wheat (Triticumaestivum L.) with zinc and manganese. Journal of Krishi Vigyan, 8(2), 142– 149. https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-4433.2020.00031.8
Kaur, R., & Bhat, Z. A. (2017). Effect of different agricultural land use systems on physico-chemical properties of soil in sub-mountainous districts of Punjab, North-West India. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 6(3), 226–233.
Khanday, M. D., Ram, D., Ali, T., Mehraj, S., Sartaj, A., Wani, R. J., Rukhsana, J., Bhat, M. A., & Bhat, S. J. A. (2017). Strategy for optimization of higher productivity and quality in field crops through micronutrients. Economic Affair, 62(1), 139–147.
Kizilgoz, I., & Sakin, E. (2010). The effects of increased phosphorus application on shoot dry matter, shoot Pand Zn concentrations in wheat (Triticum durum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) grown in a calcareous soil. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9(36), 5893–5896.
Krishan, G., Singh, R. P., Rao, M. S., Gupta, S., & Tiwari, P. K. (2015). Fluoride, Iron and nitrate affected areas of Punjab. Suresh Gyan Vihar International Journal of Water and Research, 1, 1–8.
Kukal, S. S., & Bawa, S. S. (2013). Temporal variations in runoff and soil loss in relation to soil conservation practices in catchments in Shiwaliks of lower Himalayas. International Soil Water Conservation Research, 1, 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-6339(15)30036-8
Kumar, A., Brar, N. S., Pal, S., & Singh, P. (2017). Available soil macro and micro- nutrients under rice wheat cropping system in district Tarn Taran of Punjab, India. Ecology, Environment & Conservation, 23(1), 202–207.
Kumar, M., & Babel, A. L. (2011). Available micronutrient status and their relationship with soil properties of Jhunjhunu tehsil, district Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India. Journal of Agricultural Science, 3(2), 97–106. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v3n2p97
Kumar, M., Singh, S. K., Raina, P., & Sharma, B. K. (2011). Status of available major and micronutrients in arid soils of churu district of western Rajasthan. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 59(2), 188–192.
Kumar, V., Srivastava, A., Singh, V., & Kumar, S. (2018). Availability of macro and micronutrients and their correlation with some physico-chemical properties in soils of Udham Singh Nagar district of Uttarakhand. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 6(3), 1445–1449.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of DTPA Soil test method for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 42, 421–428.
Mahajan, T. S. (2001). Status and distribution of micronutrients in relation to the properties of lateritic soils under mango orchards in South Konkan. M.Sc. (Agri.) Thesis submitted to Balasahebsawant Konkan Krishi Vidyapeeth, Dapoli, Dist. Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
Mandal, A., & Dhaliwal, S. S. (2018). Distribution of micronutrients in soils under different land-uses in south-western plains of Punjab. In: 83rd Annual Convention of ISSS. 27-30 Nov. Anand Agricultural University, Anand, Gujarat, India. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.20095.15527
Mandal, D., Dhyani, B. L., Kumar, A., Singh, C., Bihari, B., Muruganandam, M., & Madhu, M. (2013). Impact of different land use systems on soil quality in northwestern Himalayan region India. Journal of Soil Water Conservation, 41, 200–205.
Mandavgade, R. R., Waikar, S. L., Dhamak, A. L., & Patil, V. D. (2017). Evaluation of micronutrient status of soils and their relation with some chemical properties of soils of northern tehsils (Jintur, Selu&Pathri) of Parbhani district. Journal of Agriculture & Veterinary Science, 8(2), 38–41. https://doi.org/10.9790/2380-08213841
Mohammed, S. (2009). The effect of soil organic matter on runoff, soil loss, crop yield at Anjeni, West Gojjam .M.Sc Thesis, Alemaya University Ethiopia.
Monreal, C. M., DeRosa, M., Mallubhotla, S. C., Bindraban, P. S., & Dimkpa, C. O. (2016). Nanotechnologies for increasing the crop use efficiency of fertilizer-micronutrients. Biology & Fertility of Soils, 52(3), 423–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1073-5
Nanganoa, L., Justin, O., Missi, V., Tueche, J. R., Levai, L., & Nkengafac, N. (2019). Impact of different land-use systems on soil physicochemical properties and macrofauna abundance in the humid tropics of Cameroon. Applied & Environmental Soil Science, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5701278
Negasa, D. J. (2020). Effects of land use types on selected soil properties in central highlands of Ethiopia, Applied & Environmental Soil Science, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7026929
Neha, Bhople, & B.S., & Sharma, S. (2020). Seasonal variation of rhizospheric soil properties under different land use systems at lower Shivalik foothills of Punjab, India. Agroforestry Systems, 94, 1959–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-020-00512-7
Onwudike, S. U., Abbani, L., Ihem, E., & Onyegbule, U. (2017). Influence of land use types on soil properties and micronutrient concentrations on soils of similar lithology in Owerri, Southeastern Nigeria. MAYFEB Journal of Agricultural Science, 4, 1–9.
Onwudike, S. U., Ihem, E. E., Irokwe, I. F., & Onwuso, G. (2015). Variability in the physico-chemical properties of soils of similar lithology inthree land use types in AhiazuMbaise, Imo State Nigeria. Journal of Agriculture and Crops, 1(3), 38–43.
Phuphong, P., Cakmak, I., Dell, B., & Thaii, C. P. (2018). Effects of foliar application of zinc on grain yield and zinc concentration of rice in farmers’ fields. CMU Journal of Natural Sciences, 17(3), 81–190.
Post, W. M., & Kwon, K. C. (2000). Soil carbon sequestration & landuse change: Processes and potential. Global Change Biology, 6, 317–327. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00308.x
Rai, A. P., Tundup, P., Mondal, A. K., Kumar, V., Samanta, A., Kumar, M., Arora, R. K., & Dwivedi, M. C. (2018). Cationic micronutrient status of some soils under different cropping system of Kishtwar District (J&K), India. International Journal of Current Microbiology & Applied Sciences, 7(1), 3596–3602. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.422
Ray, R., Mukhopadhyay, K., & Biswas, P. (2006). Soil aggregation and its relationship with physico- chemical properties under various land use systems. Indian Journal of Soil Conservation, 34, 28–32.
Saha, D. (2010). Effect of land use on soil aggregation and soil organic carbon footprint in Shiwaliks of Punjab. M.Sc. (Agri.) Thesis submitted to Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab.
Saha, S., Saha, B., Seth, T., Ray, M., Pal, B., Mukhopadhyay, P. S., & Hazra, G. (2019). Micronutrients availability in soil–plant system in response to long-term integrated nutrient management under rice– wheat cropping system. Journal of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 19, 712–724.
Sehgal, J. (2005). A Text Book of Pedology: Concepts and Applications. Revised and (expanded). Kalyani.
Sharma, A. (2011). Status and distribution of micronutrients under different land uses in soils of Kangra District. M.Sc Thesis. Department of Soil Science, CSK Himachal Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya, Palampur, India.
Sharma, B. D., & Jassal, H. S. (2013). Study of a toposequence for variability in micronutrients from the moist subhumid Siwalik agro-ecological subregion of Punjab. Archives of Agronomy & Soil Science, 59(4), 573–591. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2012.663488
Sharma, B. D., Kumar, R., Singh, B., & Sethi, M. (2008). Micronutrient distribution in salt – affected soils of the Punjab in relation to soil properties. Archives of Agronomy & Soil Science, 55(4), 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340802552387
Sharma, V. K., Kaistha, B. P., Dubey, Y. P., & Sharma, R. P. (2002). Soil fertility ratings in Fatehpur block of Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh for growing medicinal and aromatic plants. Himachal Journal of Agricultural Research, 28(1), 20–25.
Shukla, A. K., Malik, R. S., Tiwari, P. K., Prakash, C., Behera, S. K., Yadav, H., & Narwal, R. P. (2015). Status of micronutrient deficiencies in soils of Haryana. Indian Journal of Fertilisers, 11(5), 16–27.
Sidhu, G. S., & Sharma, B. D. (2010). Diethylenetriamine penta acetic acid Extractable micronutrients status under rice- wheat cropping system and their relationship with soil properties in different agro-climatic zones of Indo Gangetic plains of India. Communication in Soil Science & Plant Analysis, 41(1), 29–51.
Singh, H., & Singh, J. (2017). Soil fertility status as influenced by cropping system in submountain zone of lower Shiwalik hills in Punjab. Journal of Krishi Vigyan, 6(1), 197–199. https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-4433.2017.00079.4
Singh, H., Pathak, P., Kumar, M., & Reghubanshi, S. A. (2011). Carbon sequestration potential of Indo-Gangetic agro ecosystem soils. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 52(2), 223–228.
Singh, M. J., & Khera, K. L. (2008). Soil erodibility indices under different land uses in lower Shiwaliks. Tropical Ecology, 49, 113–119.
Singh, S. K., Dey, P., Sharma, P. K., Singh, Y. V., Latare, A. M., Singh, C. M., Kumar, D., Kumar, O., Yadav, S. N., & Varma, S. S. (2016). Primary and Cationic Micronutrient Status of Soils in Few Districts of Eastern Uttar Pradesh. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 64(4), 319–332.
Six, J., Paustian, K. E. T., & Combrink, C. (2000). Soil structure and organic matter distribution of aggregate size classes and aggregated associated carbon. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 64, 681–689. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2000.642681x
Reid, K. (2021). Soil sampling and analysis for managing crop nutrients. Ministry of Agriculture, food and rural affairs.
Somasundaram, J., Singh, R. K., Parandiyal, A. K., & Prasad, S. N. (2009). Micronutrient status of soils under different land use system in Chambal ravines. Journal of the Indian Society Soil Science, 57, 307–312. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2015.619297
Sondhi, A. K. (1992). Soil resources inventory of NARA, DADA Manshi watershed of Hoshiarpur district. (MSc Thesis). Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana.
Sukirtee, Sharma, & M. K., Devraj, Chaudhary, K., & Bhardwaj, K. K. (2021). Impact of long term FYM application on micronutrient status of soil after 52 years of experimentation. Journal of Plant Development Sciences, 13(4), 183–188.
Thakur, R., Kauraw, D. L., & Singh, M. (2011). Profile distribution of micronutrient cations in a vertisol as influenced by long term application of manure and fertilizers. Journal of Indian Society of Soil Science, 59, 239–244.
Thomas, C. L., Acquah, G. E., Whitmore, A. P., McGrath, S. P., & Haefele, S. M. (2019). The effect of different organic fertilizers on yield and soil and crop nutrient concentrations. Agronomy, 9, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120776
Toru, T., & Kibert, K. (2019). Carbon stock under major land use/ land cover types of Hades sub watershed, eastern Ethiopia. Carbon Balance & Management, 14, 7–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13021-019-0122-z
UN. (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 agenda for sustainable development. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
UNCCD. (2016). Achieving land degradation neutrality at the country level: Building blocks for LDN target setting. UNCCD, Bonn.
UNSC. (2016). Report of the Inter-agency and Expert Group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. Annex IV. Final List of Proposed Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. E/CN.3/2016/2/Rev.1.
Vashisht, B. B., Maharjan, B., Sharma, S., & Kaur, S. (2020). Soil Quality and Its Potential Indicators under Different Land Use Systems in the Shivaliks of Indian Punjab. Sustainability, 12(8), 3490. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083490
Wang, Z. P., Han, X. G., & Li, L. H. (2008). Effects of cropland and conversion to grasslands on soil organic carbon in the temperate Inner Mongolia. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.12.004
Wani, S. A., Najar, G. R., Wani, M. A., Sajad, M., & Rasool, R. (2016). Micronutrient indexing of pear orchards of Pulwama district in Kashmir, India. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia, 13(4), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2397
Wei, X., Liu, S., Müller, K., Song, Z., Guan, G., Luo, J., & Wang, H. (2019). Urbanization-induced acid rain causes leaching loss of calcium from limestone-derived soil in South China. Journal of Soils Sediments, 19, 3797–3804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02324-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H., Sehgal, S.K., Dhaliwal, S.S. et al. Monitoring and assessment of soil quality based on micronutrients and physicochemical characteristics in semi-arid submountainous Shiwalik ranges of lower Himalayas, India. Environ Monit Assess 193, 639 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09442-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09442-y