Abstract
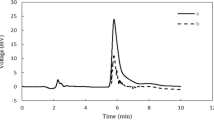
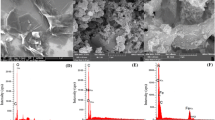
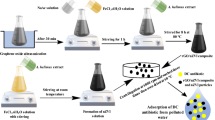
In the present study, the synthesizing of silver@reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite, through a facile precipitation method, is reported. In this method, in the synthesizing step, reduced graphene oxide was applied as a support, silver acetate as a precursor of Ag0, and sodium hydroxide as a medium for reducing procedure. Then synthesized particles were characterized by using transmission electron microscopy analysis, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, field emission scanning microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray, and X-ray diffraction. Adsorbent potentials of the prepared nanocomposite were evaluated for sulfamethoxazole removal from polluted aqueous solutions via two different experimental methods, namely, “one-at-a-time” and “central composite design”. The given results from the one-at-a-time method confirms that 0.007 g of silver@reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite can remove 88% (188.57 mg/g) of sulfamethoxazole from a 0.05 dm3 solution (initial concentration 30 mg/dm3) at pH = 5 after 3600 s’ contact time. However, in the central composite design method, the optimum condition was 95% (79.17 mg/g) uptake of this drug from 0.05 dm3 of polluted solution with initial concentration of 30 mg/dm3 and pH = 7.5, using 0.018 g of the adsorbent in 3600 s. The main mechanism for sulfamethoxazole removal can be suggested as a suitable interaction between S atoms in functional groups in the drug and Ag atoms on the surface of nanoparticles. The pseudo-second-order patterns and Freundlich model described the empirical data isotherm and kinetics for the adsorption processes, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity by experimental and theoretical isotherm methods (Langmuir) obtained 250 and 357 mg/g, respectively. Efficiency of the adsorbent in treatment of SMX from real samples displayed less hardness and electrical conductance samples have the maximum uptake percent while existence of nitrate ions in the solutions did not induce any negative effect on the removal of the SMX. All obtained results indicated loading of Ag nanoparticles on rGO nanosheets is an effective strategy for SMX uptake with high proficiency and shows great promise as pollutant adsorbent for environmental applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou El-Reash, Y. G., Abdelghany, A. M., & Elrazak, A. A. (2016). Removal and separation of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using nano-silver chitosan/polyacrylamide membranes. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 86, 789–798.
Ahmed, I., Bhadra, B. N., Lee, H. J., & Jhung, S. H. (2018). Metal-organic framework-derived carbons: preparation from ZIF-8 and application in the adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole from water. Catalysis Today, 301, 90–97.
Ahsan, M. A., Islam, M. T., Hernandez, C., Kim, H., Lin, Y., Curry, M. L., Gardea-Torresdey, J., & Noveron, J. C. (2018). Adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole and bisphenol a from contaminated water using functionalized carbonaceous material derived from tea leaves. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 4215–4225.
Akhtar, J., Saidina Amin, N., & Aris, A. (2011). Combined adsorption and catalytic ozonation for removal of sulfamethoxazole using Fe2O3/CeO2 loaded activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170, 136–144.
Al-Hamadani, Y. A. J., Jung, C., Im, J., Boateng, L. K., Flora, J. R. V., Jang, M., et al. (2017). Sonocatalytic degradation coupled with single-walled carbon nanotubes for removal of ibuprofen and sulfamethoxazole. Chemical Engineering Science, 162, 300–308.
Ali, I., Al-Othman, Z. A., & Alwarthan, A. (2016). Synthesis of composite iron nano adsorbent and removal of ibuprofen drug residue from water (Vol. 219, pp. 858–864).
Alnajjar, M., Hethnawi, A., Nafie, G., Hassan, A., Vitale, G., Nassar, N. N., (2019). Silica-alumina composite as an effective adsorbent for the removal of metformin from water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering , In Press.
Arslan-Alaton, I., & Dogruel, S. (2004). Pre-treatment of penicillin formulation effluent by advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 112, 105–113.
Banerjee, P., Das, P., Zaman, A., & Das, P. (2016). Application of graphene oxide nanoplatelets for adsorption of ibuprofen from aqueous solutions: evaluation of process kinetics and thermodynamics. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 101, 45–53.
Bao, Q., Zhang, D., & Qi, P. (2011). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 360, 463–470.
Bouki, C., Venieri, D., & Diamadopoulos, E. (2013). Detection and fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environment Safety, 91, 1–9.
Chelliapan, S., Wilby, T., & Sallis, P. J. (2006). Performance of an up-flow anaerobic stage reactor (UASR) in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing macrolide antibiotics. Water Research, 40, 507–516.
Chen, L., Hu, P., Zhang, L., Huang, S., Luo, L., & Huang, C. (2012). Toxicity of graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes against human cells and zebrafish. SCIENCE CHINA Chemistry, 55, 2209–2216.
Chen, H., Gao, B., & Li, H. (2015). Removal of sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 282, 201–207.
Chen, B., Sun, W., Wang, C., & Guo, X. (2017). Size-dependent impact of inorganic nanoparticles on sulfamethoxazole adsorption by carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 316, 160–170.
Dolar, D., Košutic, K., Periša, M., & Babićb, S. (2013). Photolysis of enrofloxacin and removal of its photodegradation products from water by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. Separation and Purification Technology, 115, 1–8.
Dutta, S., Ray, C., Sarkar, S., Pradhan, M., Negishi, Y., & Pal, T. (2013). Silver nanoparticle decorated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheet: a platform for SERS based low-level detection of uranyl ion. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5, 8724–8732.
Ghaedi, M., Mazaheri, H., Khodadoust, S., Hajati, S., & Purkait, M. K. (2015). Application of central composite design for simultaneous removal of methylene blue and Pb2+ ions by walnut wood activated carbon. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 135, 479–490.
Guo, Y., Sun, X., Liu, Y., Wang, W., Qiu, H., & Gao, J. (2012). One pot preparation of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) or Au (Ag) nanoparticle-RGO hybrids using chitosan as a reducing and stabilizing agent and their use in methanol electrooxidation. Carbon, 50, 2513–2523.
Huang, B., Liu, Y., Li, B., Liu, S., Zeng, G., Zeng, Z., Wang, X., Ning, Q., Zheng, B., & Yang, C. (2017). Effect of Cu(II) ions on the enhancement of tetracycline adsorption by Fe3O4@SiO2 chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite. Carbohydrate Polymers, 157, 576–585.
Jara, C. C., Fino, D., Specchia, V., & Spinelli, P. (2007). Electrochemical removal of antibiotics from wastewater. Applied Catalysis, 70, 479–487.
Jeyapragasam, T. (2016). Synthesis of silver-graphene oxide nanocomposite for removal of anionic dye by adsorption. Materials Today, 3, 2146–2154.
Keshan Balavandy, S., Shameli, K., & Zainal Abidin, Z. (2015). Rapid and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via sodium alginate media. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 10, 486–497.
Keshvardoostchokami, M., Piri, F., & Zamani, A. (2017). One-pot synthesis of chitosan/iron oxide nanocomposite as an eco-friendly bioadsorbent for water remediation of methylene blue. Micro and Nano Letters, 12, 338–343.
Kurade, M. B., Xiong, J. Q., Govindwar, S. P., Roh, H. S., Saratale, G. D., Jeon, B. H., & Lim, H. (2019). Uptake and biodegradation of emerging contaminant sulfamethoxazole from aqueous phase using Ipomoea aquatica. Chemosphere, 225, 696–704.
Liu, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, G., Ma, T., Du, T., Yang, Y., et al. (2019). Adsorptive removal of sulfamethazine and sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution by hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide modified activated carbon. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 564, 131–141.
Luo, D. C., Zhang, G. X., Liu, J. F., & Sun, X. M. (2011). Evaluation criteria for reduced graphene oxide. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115, 11327–11335.
Mourid, E. H., Lakraimi, M., Benaziz, L., Elkhattabi, E. H., & Legrouri, A. (2019). Wastewater treatment test by removal of the sulfamethoxazole antibiotic by a calcined layered double hydroxide. Applied Clay Science, 168, 87–95.
Murphy, S., Huang, L., & Kamat, P. V. (2013). Reduced graphene oxide - silver nanoparticle composite as an active SERS material. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117, 4740–4747.
Nam, S., Jung, C., Li, H., Yu, M., Flora, J. R. V., Boateng, L. K., et al. (2015). Adsorption characteristics of diclofenac and sulfamethoxazole to graphene oxide in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 136, 20–26.
Roosta, M., Ghaedi, M., & Mohammadi, M. (2014). Removal of Alizarin Red S by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon combined with ultrasound device: optimization by experimental design methodology. Powder Technology, 267, 134–144.
Salem, M. A., Elsharkawy, R. G., & Hablas, M. F. (2016). Adsorption of brilliant green dye by polyaniline/silver nanocomposite: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. European Polymer Journal, 75, 577–590.
Segura, P. A., Francois, M., Gagnon, C., & Sauve, S. (2009). Review of the occurrence of anti-infectives in contaminated wastewaters and natural and drinking waters. Environmental Health Perspectives, 117, 675–684.
Sekimoto, T., Nishihama, S., Yoshizuka, K., & Maeda, R. (2018). Adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole with shell-core chitosan immobilized metal ion. Separation Science and Technology, 53(7), 1116–1123.
Snyder, S. A., Westerhoff, P., Yoon, Y., & Sedlak, D. L. (2003). Pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and endocrine disruptors in water: implications for the water industry. Environmental Science and Technology, 20, 449–469.
Song, Q., Wang, H., Yang, B., Wang, F., & Sun, X. (2016). A novel adsorbent of Ag-FMWCNTs for the removal of SMX from aqueous solution. RSC Advances, 6, 75855–75861.
Sun, X., Qin, J., Xia, P., Guo, B., Yang, C., Song, C., et al. (2015). Graphene oxide–silver nanoparticle membrane for biofouling control and water purification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 281, 53–59.
Tang, Y., Guo, H., Xiao, L., Yu, S., Gao, N., & Wang, Y. (2013). Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/magnetite composites and investigation of their adsorption performance of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Colloids and Surfaces A, 424, 74–80.
Teixido, M., Pignatello, J. J., Beltran, J. L., Granados, M., & Peccia, J. (2011). Speciation of the ionizable antibiotic sulfamethazine on black carbon (biochar). Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 10020–10027.
Tonucci, M. C., Alves Gurgel, L. V., & de Aquino, S. F. (2015). Activated carbons from agricultural byproducts (pine tree and coconut shell), coal, and carbon nanotubes as adsorbents for removal of sulfamethoxazole from spiked aqueous solutions: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Industrial Crops and Products, 74, 111–121.
Tran, H. V., Tran, L. D., & Nguyen, T. N. (2010). Preparation of chitosan/magnetite composite beads and their application for removal of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from aqueous solution. Materials Science and Engineering C, 30, 304–310.
Vijayakumar, G., Tamilarasan, R., & Dharmendirakumar, M. (2012). Adsorption, kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on the removal of basic dye Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution by the use of natural adsorbent perlite. Journal of Materials Environmental Science, 3, 157–170.
Wu, Q., Cao, H., Luan, Q., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Warner, J. H., et al. (2008). Biomolecule-assisted synthesis of water-soluble silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Inorganic Chemistry, 47, 5882–5888.
Wu, J., Zhao, H., Chen, R., Pham-Huy, C., Hui, X., & He, H. (2016). Adsorptive removal of trace sulfonamide antibiotics by water-dispersible magnetic reduced graphene oxide-ferrite hybrids from wastewater. Journal of Chromatography B, 1029-1030, 106–112.
Xu, W., Zhang, L., Li, J., Lu, Y., Li, H., Wang, Y. M. W., et al. (2011). Facile synthesis of silver@graphene oxide nanocomposites and their enhanced antibacterial properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21, 4593–4597.
Yao, Y., Zhang, Y., Gao, B., Chen, R., & Wu, F. (2018). Removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and sulfapyridine (SPY) from aqueous solutions by biochars derived from anaerobically digested bagasse. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 25659–25667.
Yu, F., Li, Y., Han, S., & Ma, J. (2016). Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution using carbon materials. Chemosphere, 153, 365–385.
Yuwei, C., & Jianlong, W. (2011). Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan nanoparticles and its application for Cu(II) removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168, 286–292.
Zamani, A. A., Shokri, R., Yaftian, M. R., & Parizanganeh, A. H. (2013). Adsorption of lead, zinc and cadmium ions from contaminated water onto Peganum harmala seeds as biosorbent. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 10, 93–102.
Zeng, X., McCarthy, D. T., Deletic, A., & Zhang, X. (2015). Silver/reduced graphene oxide hydrogel as novel bactericidal filter for point-of-use water disinfection. Advanced Functional Materials, 25, 4344–4351.
Zhang, T., Wang, M., Yang, W., Yang, Z., Wang, Y., & Gu, Z. (2014). Synergistic removal of copper(II) and tetracycline from water using an environmental-friendly chitosan-based flocculant. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53, 14913–14920.
Zheng, H. L., Yang, S. S., Zhao, J., & Zhang, Z. C. (2014). Synthesis of rGO–Ag nanoparticles for high-performance SERS and the adsorption geometry of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole on Ag surface. Applied Physics A, 114, 801–808.
Zhou, Y., Yang, J., He, T., Shi, H., Cheng, X., & Lu, Y. (2013). Highly stable and dispersive silver nanoparticle-graphene composites by a simple and low-energy consuming approach and their antimicrobial activity. Small, 9, 3445–3454.
Zhuang, Y., Yu, F., & Ma, J. (2015). Enhanced adsorption and removal of ciprofloxacin on regenerable long TiO2 nanotube/graphene oxide hydrogel adsorbents. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015, 1–8.
Acknowledgments
The Alborz Darou Pharmaceutical Company is acknowledged for their kind cooperation and offer of the utilized pharmaceuticals in this project. The authors also especially appreciate the contributions of students and members of the Environmental Science Research Laboratory, University of Zanjan, Zanjan, Iran, in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshvardoostchokami, M., Rasooli, S., Zamani, A. et al. Removal of sulfamethoxazole antibiotic from aqueous solutions by silver@reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Environ Monit Assess 191, 374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7494-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7494-0