Abstract
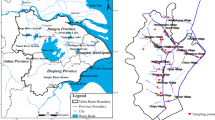
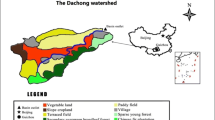
Losses of agricultural pollutants from small catchments are a major issue for water quality in the Three Gorges Region. Solutions are urgently needed. However, before pollutant losses can be controlled, information about spatial and temporal variations in pollutant losses is needed. The study was carried out in the Wangjiagou catchment, a small agricultural catchment in Fuling District, Chongqing, and the data about non-point source losses of nitrogen and phosphorus was collected here. Water samples were collected daily by an automatic water sampler at the outlets of two subcatchments from 2012 to 2014. Also, samples of surface runoff from 28 sampling sites distributed through the subcatchments were collected during 12 rainfall events in 2014. A range of water quality variables were analyzed for all samples and were used to demonstrate the variation in non-point losses of nitrogen and phosphorus over a range of temporal and spatial scales and in different types of rainfall in the catchment. Results showed that there was a significant linear correlation between the mass concentrations of total nitrogen (TN) and nitrate (NO3-N) in surface runoff and that the relationship was maintained with changes in time. Concentrations of TN and NO3-N peaked after fertilizer was applied to crops in spring and autumn; concentrations decreased rapidly after the peak values in spring but declined slowly in autumn. N and P concentrations fluctuated more and showed a greater degree of dispersion during the spring crop cultivation period than those in autumn. Concentrations of TN and NO3-N in surface runoff were significantly and positively correlated with the proportion of the area that was planted with corn and mustard tubers, but were negatively correlated with the proportion of the area taken up with rice and mulberry plantations. The average concentrations of TN and NO3-N in surface runoff reached the highest level from the sampling points at the bottom of the land used for corn only, but lowest in rice fields. Slope gradient had a significant positive correlation with TN’s and total phosphorus (TP)’s concentration losses. Concentrations of TN, NO3-N, and total phosphorus were significantly correlated with rainfall. Peak concentrations of ammoniacal nitrogen occurred during the fertilizer application period in spring and autumn. Different structures of land use types had a significant influence on the concentration losses of nitrogen and phosphorus; thus, using a reasonable way to adjust land use structure and spatial arrangement of whole catchment was an effective solution to control non-point source pollution of the Three Gorges Region.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araya, T., Comelis, W. M., Nyssen, J., et al. (2011). Effects of conservation agriculture on runoff, soil loss and crop yield under rainfed conditions in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Soil Use and Management, 27(3), 404–414.
Barton, A. P., Fullen, M. A., & Mitchell, D. J. (2004). Effects of soil conservation measures on erosion rates and crop productivity on subtropical Ultisols in Yunnan Province, China. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 104(2), 343–357.
Basnyat, P., Teeter, L. D., Flynn, K. M., et al. (1999). Relationships between landscape characteristics and non-point source pollution inputs to coastal estuaries. Environmental Management, 23(4), 539–549.
Bergstorm, L., & Brink, N. (1986). Effects of differentiated applications of fertilizer N on leaching losses and distribution of inorganic N in the soil. Plant and Soil, 93(3), 333–345.
Carey, R. O., Migliaccio, K. W., Li, Y., et al. (2011). Land use disturbance indicators and water quality variability in the Biscayne Bay Watershed, Florida. Ecological Indicators, 11(5), 1093–1104.
Dong, Y., & Wang, Z. Y. (2006). Study on release characteristics of different forms of nitrogen nutrients of slow/controlled release compound fertilizer. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 39(5), 960–967.
Evans, D. M., Schoenholtz, S. H., Wigington, P. J., et al. (2014). Spatial and temporal patterns of dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus in surface waters of a multi-land use basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(2), 873–887.
Franklin, D., Truman, C., Potter, T., et al. (2007). Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses from variable and constant intensity rainfall simulations on loamy sand under conventional and strip tillage systems. Journal of Environment Quality, 36(3), 846–854.
Fu, W. Z., & Shi, Y. X. (2005). Effect on nitrogen output in farmland with different nitrogen fertilization. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 25(12), 1676–1681.
Gao, C., Zhu, J. G., Zhu, J. Y., et al. (2004). Nitrogen export from an agriculture watershed in the Taihu Lake area, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26, 199–207.
Gascho, G. J., Wauchope, R. D., Davis, J. G., et al. (1998). Nitrate-nirogen, soluble, and bioavailable phosphorus runoff from simulated rainfall after fertilizer application. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 62(6), 1711–1718.
Girmay, G., Singh, B. R., Nyssen, J., et al. (2009). Runoff and sediment-associated nutrient losses under different land uses in Tigray Northern Ethiopia. Journal of Hydrology, 376(1–2), 70–80.
Gomez, J. A., Guzman, M. G., Giraldez, J. V., et al. (2009). The influence of cover crops and tillage on water and sediment yield, and on nutrient, and organic matter losses in an olive orchard on as and loam soil. Soil and Tillage Research, 106(1), 137–144.
Han, J. G., Li, Z. B., Li, P., & Tian, J. L. (2010). Nitrogen and phosphorous concentrations in runoff from a purple soil in an agricultural watershed. Agricultural Water Management, 97, 757–762.
Huang, Y. F. (2006). Characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen loss of subwatershed. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 37(7), 801–802.
Jing, G. H., Yu, X. X., & Liu, Q. (2012). Characteristics of soil nitrogen loss under different intense rainfalls in Yimeng mountainous area. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28(6), 120–125.
Lawniczak, A. E., Zbierska, J., Nowak, B., et al. (2016). Impact of agriculture and land use on nitrate contamination in groundwater and running waters in central-west Poland. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(3), 1–17.
Liang, X. Q., Chen, Y. X., Li, H., et al. (2006). Effect of rainfall intensity and rain-fertilization interval on N export by runoff in oilseed rape land. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(6), 14–17.
McDowell, R. W. (2012). Minimising phosphorus losses from the soil matrix. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 23(6), 860–865.
Moog, D. B., & Whiting, P. J. (2002). Climatic and agricultural factors in nutrient exports from two watersheds in Ohio. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(1), 72–83.
Nadal-Romero, E., Regues, D., & Latron, J. (2008). Relationships among rainfall, runoff, and suspended sediment in a small catchment with badlands. Catena, 74(2), 127–136.
Oenema, O., Oudendag, D., & Velthof, G. L. (2007). Nutrient losses from manure management in the European Union. Livestock Science, 112(3), 261–272.
Pu, Y. L., Xie, D. T., Lin, C. W., et al. (2013). Characteristics of soil comprehensive anti-erodibility under sloped cropland with hedgerows. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29(18), 125–134.
Saraswathy, R., Suganya, S., & Singaram, P. (2007). Environmental impact of nitrogen fertilization in tea ecosystem. Journal of Environmental Biology, 28(4), 779–788.
Steegen, A., Covers, G., Takken, I., et al. (2001). Factors controlling sediment and phosphorus export from two Belgian agricultural catchments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(4), 1249–1258.
Sun, Z. B., Chen, Z. J., Liao, X. Y., Wang, H. M. (2011). Characteristics of agricultural non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus losses in a typical small watershed in Three Georges Reservoir area. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30(8), 1270–1275.
Tim, U. S., & Jolly, R. (1994). Evaluating agriculture non-point source pollution using integrated geographic information systems and hydrologic/water quality model. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23(1), 25–35.
Udawatta, R. P., Motavalli, P. P., Garrett, H. E., et al. (2006). Nitrogen losses in runoff from three adjacent agricultural watersheds with clay pan soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 117(1), 39–48.
Vagstad, N., Jansons, V., Loigu, E., et al. (2000). Nutrient losses from agricultural areas in the Gulf of Riga drainage basin. Ecological Engineering, 14(4), 435–441.
Vezina, F., Speakman, J. R., & Williams, T. D. (2006). Individually variable energy management strategies in relation to energetic costs of egg production. Ecology, 87(10), 2447–2458.
Wang, F., Wang, Z. Y., & Zhao, H. (2012). Effects of slow release compound fertilizer on yield, quality and nutrient content of tumorous stem mustard. China Vegetables, 20, 68–72.
Wang, T., Zhu, B., Luo, Z. X., & Zhang, J. (2008). Runoff characteristic of slope cropland in the hilly area of purple soil. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(6), 30–34.
Wei, O. Y., Skidmore, A. K., Toxopeus, A. G., et al. (2010). Long-term vegetation landscape pattern with non-point source nutrient pollution in upper stream of Yellow River basin. Journal of Hydrology, 389(3), 373–380.
Wu, L., Long, T. Y., Liu, X., et al. (2013). Modeling impacts of sediment delivery ratio and land management on adsorbed non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus load in a mountainous basin of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(3), 1405–1422.
Xin, W., Zhu, B., Tang, J. L., et al. (2008). Simulation study of characteristics of runoff and sediment yield in the hill area with purple soils. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(2), 31–35.
Yan, J. Z., Zhuo, R. G., & Zhang, Y. L. (2010). Land use characters of farmers of different livelihood strategies: cases in Three Gorges Reservoir area. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65(11), 1401–1410.
Zeng, S. C., Su, Z. Y., & Chen, B. Q. (2008). Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses from orchard soils in south Chirm as affected by fertilization depths and rates. Pedosphere, 18(1), 45–53.
Zeng, L. X., Huang, Z. S., Xiao, W. F., Tian, Y. W. (2012). Nitrogen and phosphorus loss in different land use types and its response to environmental factors in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Environmental Science, 33(10), 3390–3396.
Zhang, Y., Ni, J. P., Zhou, C., et al. (2014). Effects of configuration mode of crop-mulberry system in purple arid hillside field on SMBC and SMBN in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 22(7), 766–773.
Zhang, Y., Fan, F.L., Zhou, C., et al. (2015). Effects of crop/mulberry intercropping on surface nitrogen and phosphorus losses in Three Gorges Reservoir area. Acta Pedologica Sinica. http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1119.p.20151013.0940.006.html.
Zhu, J. Y., Gao, C., Zhu, J. G., & Hosen, Y. (2006). Nitrogen exports via overland runoff under different land uses and their seasonal pattern. Journal of Nanjing University, 42(6), 621–627.
Zhu, Q., Schmidt, J. P., Buda, A. R., Bryant, R. B., & Folmar, G. J. (2011). Nitrogen loss from a mixed land use watershed as influenced by hydrology and seasons. Journal of Hydrology, 405(3–4), 307–315.
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (2012ZX07104-003) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2015D020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Gao, M., Xie, D. et al. Spatial and temporal variations in non-point source losses of nitrogen and phosphorus in a small agricultural catchment in the Three Gorges Region. Environ Monit Assess 188, 257 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5260-0