Abstract
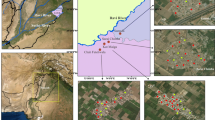
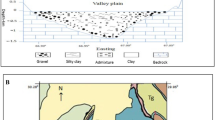
Silurian–Ordovician (S–O) aquifer system is an important drinking water source of central and western Estonia. The fluoride and boron contents of groundwater in aquifer system vary considerably. The fluoride concentration in 60 collected groundwater samples ranged from 0.1 to 6.1 mg/l with a mean of 1.95 mg/l in the study area. Boron content in groundwater varied from 0.05 mg/l to 2.1 mg/l with a mean value of 0.66 mg/l. Considering the requirements of EU Directive 98/83/EC and the Estonian requirements for drinking water quality, the limit value for fluoride (1.5 mg/l) and for boron (1.0 mg/l) is exceeded in 47 and 28 % of wells, respectively. Groundwater with high fluoride and boron concentrations is found mainly in western Estonia and deeper portion of aquifer system, where groundwater chemical type is HCO3–Cl–Na–Mg–Ca, water is alkaline, and its Ca2+ content is low. Groundwater of the study area is undersaturated with respect to fluorite and near to equilibrium phase with respect to calcite. The comparison of TDS versus Na/(Na + Ca) and Cl/(Cl + HCO3) points to the dominance of rock weathering as the main process, which promotes the availability of fluoride and boron in the groundwater. The geological sources of B in S–O aquifer system have not been studied so far, but the dissolution of fluorides from carbonate rocks (F = 100–400 mg/kg) and K-bentonites (F = 2,800–4,500 mg/kg) contributes to the formation of F-rich groundwater.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Apambire, W. B., Boyle, D. R., & Michel, F. A. (1997). Geochemistry, genesis, and health implications of fluoriferous groundwaters in the upper regions of Ghana. Environmental Geology, 33, 13–24.
Billings, R. J., Berkowitz, R. J., & Watson, G. (2004). Teeth. Pediatrics, 113, 1120–1127.
Carillo-Rivera, J. J., Cardona, A., & Edmunds, W. M. (2002). Use of abstraction regime and knowledge of hydrogeological conditions to control high-fluoride concentration in abstracted groundwater: San Luis Potosi basin, Mexico. Journal of Hydrology, 261, 24–47.
Chae, G., Yun, S., Mayer, B., Kim, K., Kim, S., Kwon, J., Kim, K., & Koh, Y. (2007). Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 385, 272–283.
European Union. (1998). Council Directive 98/83/EC on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Official Journal of the European Communities, 330, 32–54.
Cronin, S. J., Neall, V. E., Lecointre, J. A., Hedley, M. J., & Loganathan, P. (2003). Environmental hazards of fluoride in volcanic ash: a case study from Ruapehu volcano, New Zealand. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 121, 271–291.
Desbarats, A. (2009). On elevated fluoride and boron concentrations in groundwaters associated with the Lake Saint-Martin impact structure, Manitoba. Applied Geochemistry, 24, 915–927.
Earle, S., & Krogh, E. (2006). Elevated fluoride and boron levels in groundwater from the Nanaimo group, Vancouver Island, Canada. In Sea to Sky Geotechnique 2006: Proceedings of 59th Canadian Geotechnical Conference and 7th Joint CGS/IAH Groundwater Specialty Conference (pp. 1584–1591). Vancouver, BC, Canada. Vancouver: Canadian Geotechnical Society.
Edmunds, M., & Smedley, P. (2005). Fluoride in natural waters—occurrence, controls and health aspects. In O. Selnius, B. Alloway, J. A. Centeno, R. B. Finkleman, R. Fuge, U. Lindh, & P. Smedley (Eds.), Essentials of medical geology—impacts of the natural environment on public health (pp. 301–329). Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
Gemici, Ü., & Tarcan, G. (2002). Distribution of boron in thermal waters of western Anatolia, Turkey, and examples of their environmental impacts. Environmental Geology, 43, 87–98.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170, 1088–1090.
Gonfiantini, R., & Pennisi, M. (2006). The behaviour of boron isotopes in natural waters and in water–rock interactions. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 88, 114–117.
Guo, Q., Wang, Y., Ma, T., & Ma, R. (2007). Geochemical processes controlling the elevated fluoride concentrations in groundwaters of the Taiyuan Basin, Northern China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93, 1–12.
Haamer, K., & Karro, E. (2006). High fluoride content of K-bentonite beds in Estonian Paleozoic carbonate rocks. Fluoride, 39, 132–137.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS Water Supply Paper 2254. Reston: USGS
Indermitte, E., Saava, A., & Kull, A. (2006). The survey of drinking water supply in Estonia from the point of view of public health. In Ü. Mander, C. A. Brebbia, & E. Tiezzi (Eds.), The sustainable city IV. Urban regeneration and sustainability (pp. 817–826). Boston: WIT Press.
Indermitte, E., Saava, A., Russak, S., & Kull, A. (2007). The contribution of drinking water fluoride to the risk of dental fluorosis in Estonia. In C. Brebbia (Ed.), Environmental health risk IV (pp. 161–170). Boston: WIT Press.
Joogivee kvaliteedi-ja kontrollinõuded ning analüüsimeetodid. (2001). (The quality and monitoring requirements for drinking water and methods of analysis). RTL 2001/100/1369 (in Estonian). Tallinn: Ministry of Justice.
Karro, E., Indermitte, E., Saava, A., Haamer, K., & Marandi, A. (2006). Fluoride occurrence in publicly supplied drinking water in Estonia. Environmental Geology, 50, 389–396.
Karro, E., Marandi, A., Vaikmäe, R., & Uppin, M. (2009). Chemical peculiarities of the Silurian–Ordovician and Cambrian–Vendian aquifer systems in Estonia: an overview of hydrochemical studies. Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences, 58, 342–352.
Kiipli, T., Kiipli, E., & Kallaste, T. (1997). Metabentonite composition related to sedimentary facies in the Lower Silurian of Estonia. Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences, Geology, 46, 93–104.
Kim, Y., Kim, J. Y., & Kim, K. (2011). Geochemical characteristics of fluoride in groundwater of Gimcheon, Korea: lithogenic and agricultural origins. Environmental Earth Sciences, 63, 1139–1148.
Mamatha, P., & Rao, S. M. (2010). Geochemistry of fluoride rich groundwater in Kolar and Tumkur districts of Karnataka. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61, 131–142.
Molina, L., Sánchez-Martos, F., Pulido-Bosch, A., & Vallejos, A. (2003). Origin of boron from a complex aquifer in southeast of Spain. Environmental Geology, 44, 301–307.
Msonda, K. W. M., Masamba, W. R. L., & Fabiano, E. (2007). A study of fluoride groundwater occurrence in Nathenje, Lilongwe, Malawi. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 32, 1178–1184.
Naseem, S., Rafique, T., Bashir, E., Bhanger, M. I., Laghari, A., & Usmani, T. H. (2010). Lithological influences on occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in Nagar Parkar area, Thar Desert, Pakistan. Chemosphere, 78, 1313–1321.
Nestor, H., & Einasto, R. (1997). Ordovician and Silurian carbonate sedimentation basin. In A. Raukas & A. Teedumäe (Eds.), Geology and mineral resources of Estonia (pp. 192–204). Tallinn: Estonian Academy Publishers.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259. Reston: USGS
Pennisi, M., Bianchini, G., Muti, A., Kloppmann, W., & Gonfiantini, R. (2006). Behaviour of boron and strontsium isotopes in groundwater-aquifer interactions in Cornia Plain (Tuscany, Italy). Applied Geochemistry, 21, 1169–1183.
Perens, R., & Vallner, L. (1997). Water-bearing formation. In A. Raukas & A. Teedumäe (Eds.), Geology and mineral resources of Estonia (pp. 137–145). Tallinn: Estonian Academy Publishers.
Perens, R., Savva, V., Lelgus, M., & Parm, T. (2001). The hydrogeochemical atlas of Estonia (CD version). Tallinn: Geological Survey of Estonia.
Price, C. J., Marr, M. C., Myeos, C. B., Seely, J. C., Heindel, J. J., & Schwetz, B. A. (1996). The developmental toxicity of boric acid in rabbits. Fundamental and Applied Toxicology, 34, 176–187.
Queste, A., Lacombe, M., Hellmeier, W., Hillermann, F., Bortulussi, B., Kaup, M., Ott, K., & Mathys, W. (2001). High concentrations of fluoride and boron in drinking water wells in the Muenster region—results of a preliminary investigation. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 203, 221–224.
Rafique, T., Naseem, S., Bhanger, M. I., & Usmani, T. H. (2008). Fluoride ion contamination in the groundwater of Mithi sub-district, the Thar Desert, Pakistan. Environmental Geology, 56, 317–326.
Raukas, A., & Teedumäe, A. (1997). Geology and mineral resources of Estonia. Tallinn: Academy Publishers.
Reddy, D. V., Nagabhushanam, P., Sukhija, B. S., Reddy, A. G. S., & Smedley, P. L. (2010). Fluoride dynamics in the granitic aquifer of the Wailapally watershed, Nalonga District, India. Chemical Geology, 269, 278–289.
Saava, A. (1998). Health hazards due to drinking water. Proceedings of the Latvian Academy of Sciences, 52, 162–167.
Saxena, V. K., & Ahmed, S. (2003). Inferring the chemical parameters for the dissolution of fluoride in groundwater. Environmental Geology, 43, 731–736.
Sujatha, D. (2003). Fluoride levels in groundwater of the south-eastern part of Ranga Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Geology, 44, 587–591.
Voutsa, D., Dotsika, E., Kouras, A., Poutoukis, D., & Kouimtzis, T. (2009). Study on distribution and origin of boron in groundwater in the area of Chalkidiki, Northern Greece by employing chemical and isotopic tracers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 1264–1272.
Weinstein, P., & Cook, A. (2005). Volcanic emissions and health. In O. Selnius, B. Alloway, J. A. Centeno, R. B. Finkleman, R. Fuge, U. Lindh, & P. Smedley (Eds.), Essentials of medical geology—impacts of the natural environment on public health (pp. 203–229). Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (3rd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Acknowledgments
This study has been carried out with the financial support of Estonian Science Foundation Grant no. 7403. The groundwater analyses were performed in the Tartu laboratory of Estonian Environmental Research Centre. The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, which have helped to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karro, E., Uppin, M. The occurrence and hydrochemistry of fluoride and boron in carbonate aquifer system, central and western Estonia. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3735–3748 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2824-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2824-5
Keywords
Profiles
- Enn Karro View author profile