Abstract
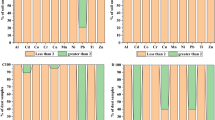
The heavy metal concentrations of soil and dust samples from roadside, residential areas, parks, campus sport grounds, and commercial sites were studied in Guangzhou, South China. Heavy metals in samples were determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrophotometer following acidic digestion with HClO4 + HF + HNO3. High concentrations, especially of Cd, Pb, and Zn, were found with mean concentrations of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the urban dusts being 4.22 ± 1.21, 62.2 ± 27.1, 116 ± 30, 31.9 ± 12.6, 72.6 ± 17.9, and 504 ± 191 mg/kg dry weight, respectively. The respective levels in urban soils (0.23 ± 0.19, 22.4 ± 13.8, 41.6 ± 29.4, 11.1 ± 5.3, 65.4 ± 40.2, and 277 ± 214 mg/kg dry weight, respectively), were significantly lower. The integrated pollution index of six metals varied from 0.25 to 3.4 and from 2.5 to 8.4 in urban soils and dusts, respectively, with 61 % of urban soil samples being classified as moderately to highly polluted and all dust samples being classified as highly polluted. The statistical analysis results for the urban dust showed good agreement between principal component analysis and cluster analysis, but distinctly different elemental associations and clustering patterns were observed among heavy metals in the urban soils. The results of multivariate statistic analysis indicated that Cr and Ni concentrations were mainly of natural origin, while Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn were derived from anthropogenic activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat, K. M., Howari, F. M., & Al-Hamad, A. A. (2005). Heavy metals in urban soils of central Jordan: Should we worry about their environmental risks? Environmental Research, 97, 258–273.
Biasioli, M., Barberis, R., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2006). The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Science of Total Environment, 356, 154–164.
CCME (1999). Contaminated sites cleanup criteria―Recommended Canadian soil quality guidelines. Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. P.D.: PPD97-01.
Chen, T. B., Wong, J. W. C., Zhou, H. Y., & Wong, M. H. (1997). Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environmental Pollution, 96, 61–68.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60, 542–551.
De Miguel, E., Llmas, J. F., Chacón, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Røyset, O., et al. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: Unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31, 2733–2740.
De Miguel, E., Jiménez de Grado, M., Llamas, J. F., Martín-Dorado, A., & Mazadiego, L. F. (1998). The overlooked contribution of compost application to the trace element load in the urban soil of Madrid (Spain). Science of Total Environment, 215, 113–122.
De Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacón, E., & Mazadiego, L. F. (1999). Sources and pathways of trace elements in urban environments: A multi-elemental qualitative approach. Science of Total Environment, 235, 355–357.
Ericson, J. E., & Gonzalez, E. J. (2003). Hierarchical sampling of multiple strata: An innovative technique in exposure characterization. Environmental Research, 92, 221–231.
Gazzetta Ufficiale (1999). Gazzetta Ufficiale delle Repubblica Italiana. Regolamento recante criteri, procedure e modalità per la messa in sicurezza e il ripristino ambientale dei siti inquinati, ai sensi dell’articolo 17 del decreto legislativo 5/2/1997, no. 22, e successive modificazioni e integrazioni 471:67.
Guan, D. S., & Peart, M. R. (2006). Heavy metal concentrations in plants and soils at roadside locations and parks of urban Guangzhou. Journal of Environmental Science, 18, 495–502.
Guney, M., Onay, T. T., & Copty, N. K. (2010). Impact of overland traffic on heavy metal levels in highway dust and soils of Istanbul, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 164, 101–110.
Harrison, R., Johnston, W., Ralph, J., & Wisen, S. (1985). The budget of Pb, Cu and Cd for a major highway. Science of the Total Environment, 46, 137–145.
He, P. J., Xiao, Z., Shao, L. M., Yu, J. Y., & Lee, D. J. (2006). In situ distributions and characteristics of heavy metals in full-scale landfill layers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 1385–1394.
Iqbal, J., & Shah, M. H. (2011). Distribution, correlation and risk assessment of selected metals in urban soils from Islamabad, Pakistan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 887–898.
Jiries, A. G., Hussein, H. H., & Halash, Z. (2001). The quality of water and sediments of street runoff in Amman, Jordan. Hydrological Processes, 15, 815–824.
Katsoyiannis, I. A., & Katsoyiannis, A. (2006). Arsenic and other metal contamination of groundwaters in the industrial area of Thessaloniki, Northern Greece. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 123, 393–406.
Lee, C. S., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S. C., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: A study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of Total Environment, 356, 45–61.
Lee, C. S. L., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Li, J., Ding, A. J., & Wang, T. (2007). Heavy metals and Pb isotopic composition of aerosols in urban and suburban areas of Hong Kong and Guangzhou, South China—Evidence of the long-range transport of air contaminants. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 432–447.
Li, X., Poon, C., & Liu, P. S. (2001). Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 1361–1368.
Li, X., Lee, S., Wong, S., Shi, W., & Thornton, I. (2004). The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environmental Pollution, 129, 113–124.
Lu, Y., Gong, Z., Zhang, G., & Burghardt, W. (2003). Concentrations and chemical speciations of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cr of urban soils in Nanjing. China Geoderma, 115, 101–111.
Lu, Y., Zhu, F., Chen, J., Gan, H., & Guo, B. (2007). Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in urban soils of Guangzhou, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 134, 429–439.
Mielke, H. W., Gonzales, C. R., Smith, M. K., & Mielke, P. W. (1999). The urban Environment and Children’s Health: Soils as an integrator of lead, zinc, and cadmium in New Orleans, Louisiana, U.S.A. Environmental Research, 81, 117–129.
Mielke, H. W., Wang, G., Gonzales, C. R., Powell, E. T., Le, B., & Quach, V. N. (2004). PAHs and metals in the soils of inner-city and suburban New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Environmental Toxicology Pharmacology, 18, 243–247.
Morton-Bermea, O., Hernández-Álvarez, E., González-Hernández, G., Romero, F., Lozano, R., & Beramendi-Orosco, L. E. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 101, 218–224.
National Environmental Protection Agency of China (1995). Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618–1995).
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 455–462.
Tan, J. H., Bi, X. H., Duan, J. C., Rahn, K. A., Sheng, G. Y., & Fu, J. M. (2006). Seasonal variation of particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with PM10 in Guangzhou, China. Atmospheric Research, 80, 250–262.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bission, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of paniculate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–858.
Tokalıoğlu, Ş., & Kartal, Ş. (2006). Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the Organized Industrial District in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmospheric Environment, 40, 2797–2805.
Wang, M., Bai, Y., Chen, W., Markert, B., Peng, C., & Ouyang, Z. (2012). A GIS technology based potential eco-risk assessment of metals in urban soils in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 161, 235–242.
Wei, B., & Yang, L. (2010). A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchemical Journal, 94, 99–107.
Wong, C. S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Min, Y. S. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119, 33–44.
Wong, C. S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Peng, X. Z. (2003). Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 767–776.
Wong, C. S. C., Li, X., & Thornton, I. (2006). Urban environmental geochemistry of trace metals. Environmental Pollution, 142, 1–16.
Xia, X., Chen, X., Liu, R., & Liu, H. (2011). Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186, 2043–2050.
Zhang, C. (2006). Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Pollution, 142, 501–511.
Zhuang, P., Zou, H., & Shu, W. (2009). Biotransfer of heavy metals along a soil-plant-insect-chicken food chain: Field study. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 849–853.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30800708, 41001328, 41071211, 41173101), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos.2011020003196, 2011010001083), the High-level Talents Program of Guangdong Universities, the Program of Guangdong Science & Technology Department (No. 2010B020311006), and the Program of Guangzhou Science & Technology Department (No.2010A82070466).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, QY., Mo, CH., Li, HQ. et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and dusts in Guangzhou, South China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 1095–1106 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2617-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2617-x